Method for extracting sinonovacula constricta DNA in vivo
A technique for constricting razor clams and living bodies, which is applied in the field of extracting biological DNA, can solve the problems of detecting growth traits, the effect of germplasm utilization, and the like, and achieve the effect of improving breeding efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
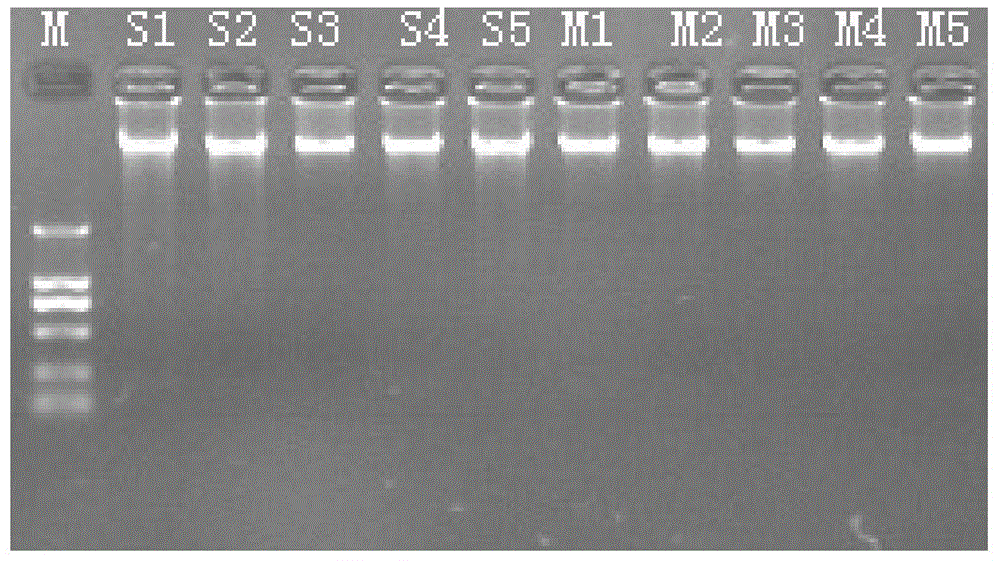
[0026] In order to verify that the DNA extracted from the mantle and the outlet tube of the same individual is the same, this Example 1 uses a pair of common primers to perform PCR detection on the DNA extracted from the mantle and outlet tube of 5 constriction razor clams.
[0027] 1. Obtaining the mantle and outlet pipe of Sinonovacula constricta
[0028] The Ministry of Education Key Laboratory of Aquatic Germplasm Resources Discovery and Utilization was jointly established in Shanghai Ocean University, selected Ningbo Changjie constriction as the experimental material, and temporarily raised 20 constriction in a seawater culture tank with a water temperature of 25℃ and a specific gravity of 1.015. 3 Five days later, 5 constrictions were randomly selected. The outlet pipe of Sinonovacula constricta is labeled s1-5; the mantle of Sinonovacula constricta is labeled m1-5.
[0029] 2. DNA extraction
[0030] Add 250μl of DNA extraction solution to the tissue collected in the water out...
Embodiment 2
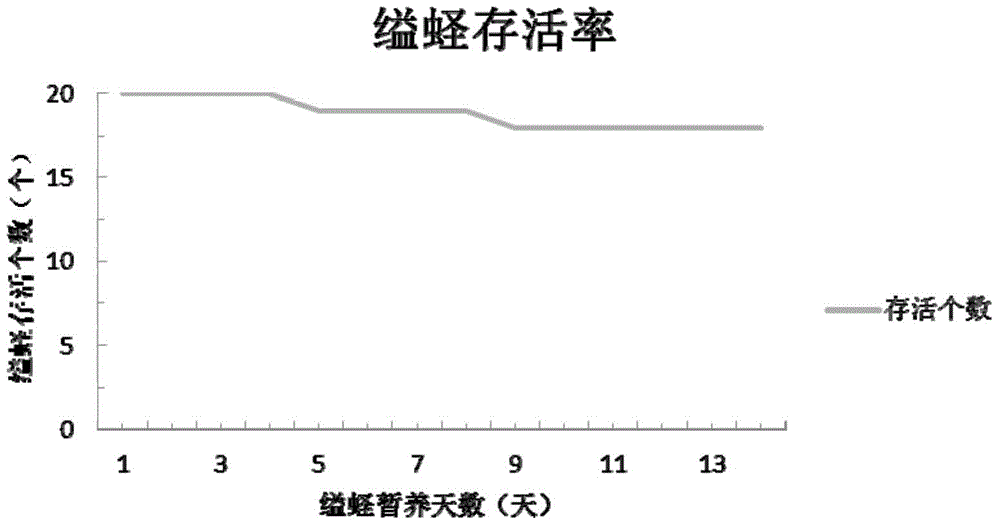
[0041] In order to confirm that the removal of the outlet pipe of the constriction does not affect the survival of the constriction, we performed the operation of cutting out the water pipes of 20 constrictions, and temporarily raising the treated individuals.
[0042] 1. Put the constrictor snails from the tissue to be taken into a seawater culture tank with a water temperature of 25°C for 3 days, and stick a numbered mark on the shell of the constrictor snails. When DNA needs to be extracted, place the constriction of the tissue to be taken on ice, anesthetize the constriction for 3-5 minutes, use scissors to cut out the water pipe of the constriction 0.5cm, and put the treated constriction back into the culture barrel.
[0043] 2. Inflate the culture barrel and feed Chrysophyllum and Chaetoceros daily for 2 weeks. During this period, the survival rate of Sinonovacula constricta is recorded, see image 3 .
[0044] 3. The experimental results show that cutting the outlet pipe of S...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com