A method of preparing medical polypropylene monofilament with improved biocompatibility
A technology of biocompatibility and polypropylene, which is applied in the field of preparing medical polypropylene monofilament with improved biocompatibility, can solve the problems of complex process, shedding of pearl powder on the surface of the fiber, and increased cost, and achieve an excellent cell proliferation rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
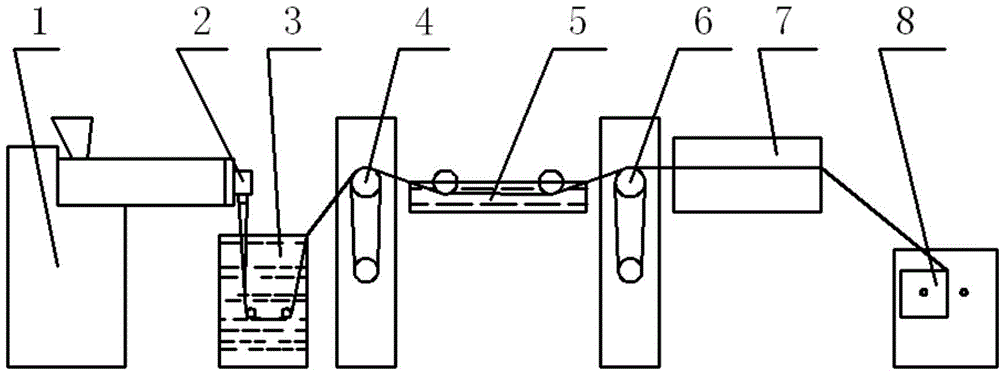
[0026] Melt Flow Index (MFI) 230℃ / 2.16kg 8g / 10min medical grade polypropylene pellets are used as raw materials. Each time, 2kg of polypropylene pellets and 30g of pearl powder (100nm in particle size) were put into the kneader for kneading. The kneaded mixed pellets (pearl powder content about 1.48%) are directly added into the spinning machine 1 for spinning. figure 1 It is the flow chart of blended monofilament spinning, which consists of melt spinning machine 1, machine head 2, cooling water tank 3, first drafting roll 4, hot drawing water tank 5, second drafting roll 6, air heat setting box 7. Winding device 8. It consists of eight major parts. In the spinning process, the raw materials pass through the melt spinning machine 1, and then enter the cooling water tank 3 through the spinneret. After stretching and winding, the required pearl powder modified polymer is obtained. Acrylic monofilament.
[0027] Kneading conditions
[0028] Kneading temperature: 50°C
[0029...
Embodiment 2
[0044] 2 kg of medical-grade polypropylene pellets with a melt index of 12g / 10min were mixed with pearl powder (400nm) of 80 to obtain blended pellets through a kneading mechanism. The kneading conditions
[0045]Kneading temperature: 80°C
[0046] Kneading speed: 30r / min
[0047] Kneading time: 2h
[0048] Spinning conditions
[0049] Screw zone 1-5 temperature: 210 / 230 / 240 / 250 / 255 / 260°C
[0050] Spinning assembly temperature: 260°C
[0051] Spinneret hole diameter: 3mm
[0052] Temperature of cooling water tank 3: 30°C
[0053] Hot stretching water tank 5 temperature 90°C
[0054] Stretch ratio: 7 times
[0055] Air heat setting box 7 Temperature: 140°C
[0056] Winding device 8 speed: 130m / min
[0057] Spun into a modified polypropylene monofilament with a pearl powder content of 4%.
[0058] Various performance tests show that the modified medical polypropylene monofilament has a fineness of 200dtex, a monofilament breaking strength of 4.5cN / dtex, and a breaking ...
Embodiment 3
[0062] Three batches of 2 kg of medical grade polypropylene pellets with a melt index of 16g / 10min were mixed with 20g, 60g, and 100g of pearl powder (1000nm) respectively to obtain blended pellets through a kneading mechanism. The kneading conditions
[0063] Kneading temperature: 100°C
[0064] Kneading speed: 10r / min
[0065] Kneading time: 3h
[0066] Spinning conditions
[0067] Screw zone 1-5 temperature: 210 / 230 / 240 / 240 / 245 / 250℃
[0068] Spinning assembly temperature: 250°C
[0069] Spinneret hole diameter: 3mm
[0070] Temperature of cooling water tank 3: 20°C
[0071] Hot stretching water tank 5 temperature 95°C
[0072] Stretch ratio: 7 times
[0073] Air heat setting box 7 Temperature: 140°C
[0074] Winding device 8 speed: 120m / min
[0075] Spun into three specifications of pearl powder modified polypropylene monofilament (about 1%, 3%, 5%).
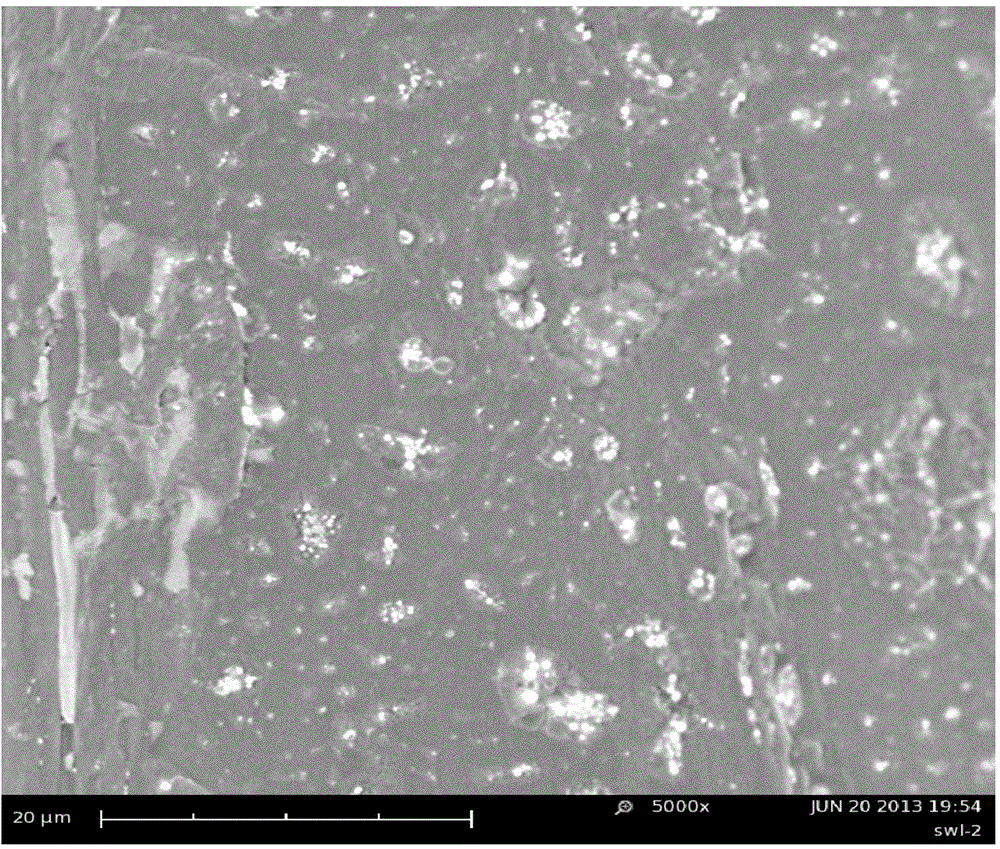
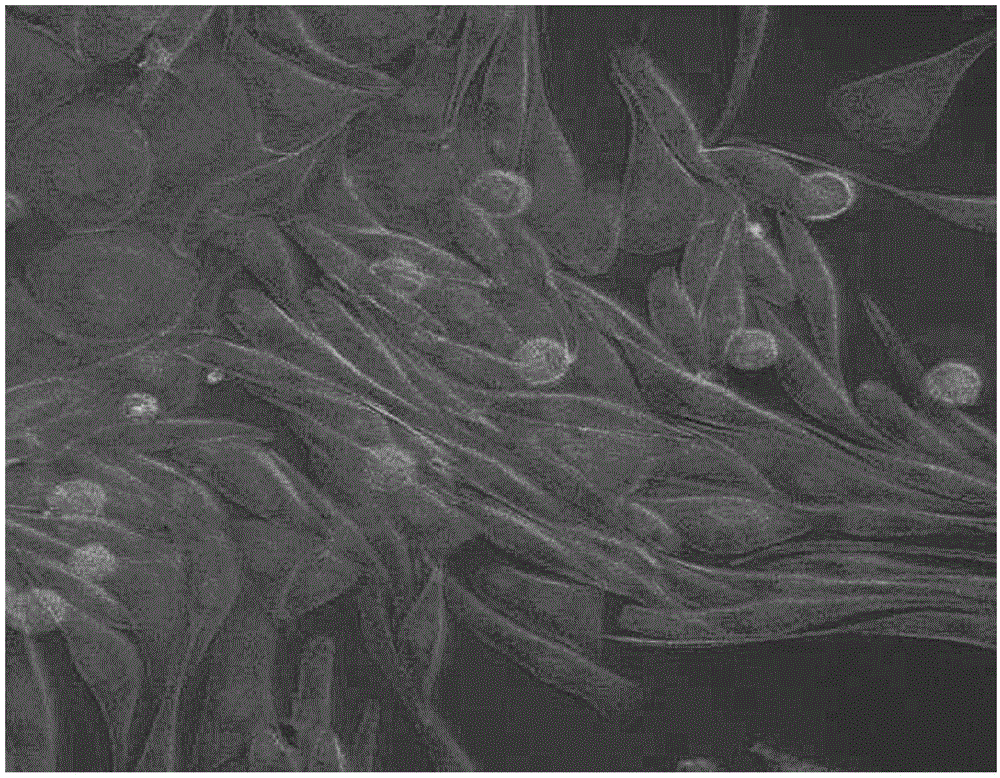
[0076] The performance tests are shown in Table 1. Table 1 shows that the three kinds of modified medical polypro...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melt flow index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com