Bacterially formed microcin s, a new antimicrobial peptide, effective against pathogenic microorganisms, e.g. enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli (EHEC)
An antimicrobial, microcin technology, applied in the field of coating dressing materials, producing and using the polypeptide, treating or preventing microbial infection, primers and probes, functional gastrointestinal diseases or treating tumors, can Address issues such as limited treatment options
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0242] Example 1: Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
[0243] Bacterial strains used in this paper are listed in Table 3.
[0244] Table 3: Bacterial strains used
[0245]
[0246]
[0247]
[0248] a DSM17252
Embodiment 2
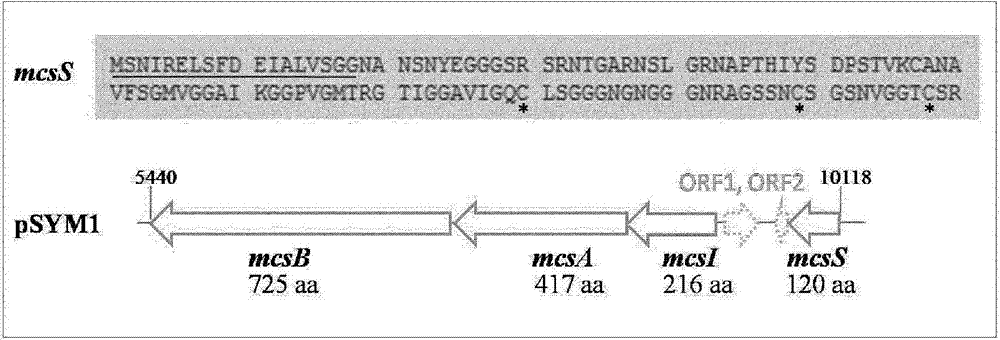
[0249] Example 2: Identification of a microcin-encoding gene cluster in G3 / 10 of E. coli
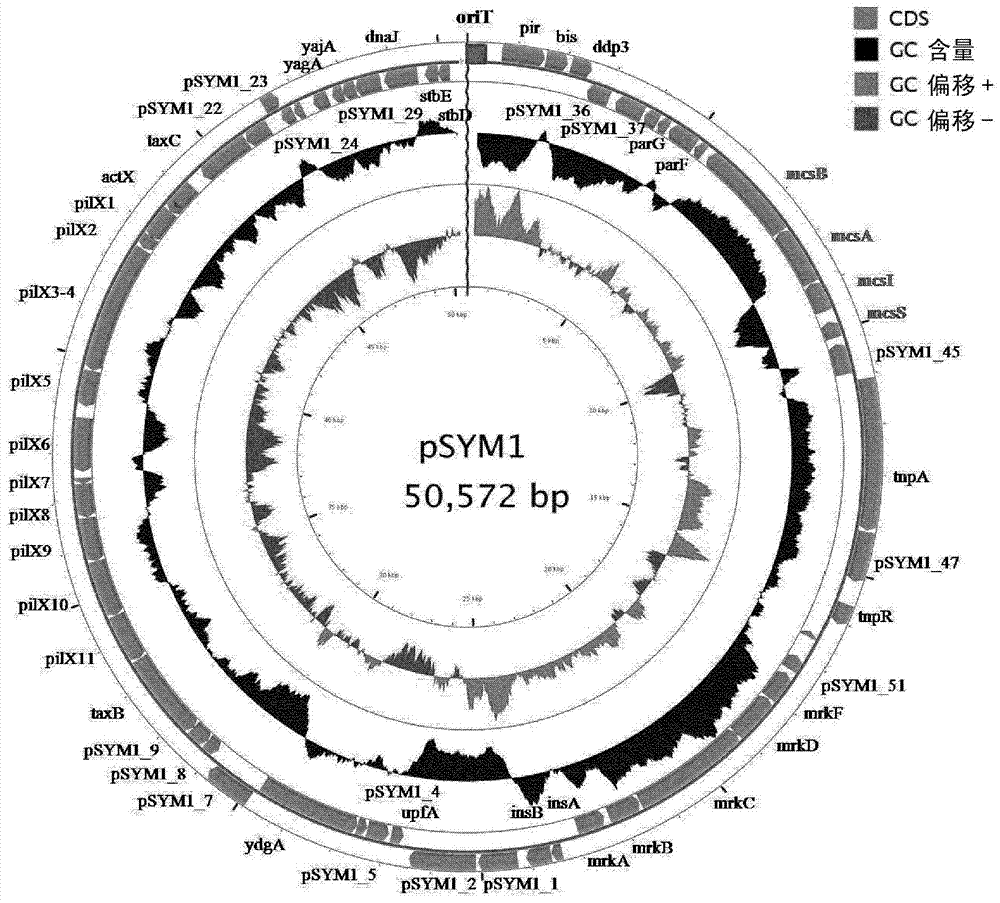
[0250] The genomes of six E. coli species: E. coli G1 / 2, G3 / 10, G4 / 9, G5, G6 / 7 and G8 were sequenced. Annotation shows that there are no known microcins in E. coli G3 / 10. Escherichia coli G3 / 10 contains a large conjugative plasmid pSYM1 ( figure 1 ). The plasmid is 99% identical to the plasmid pMAS2027 of the uropathogenic E. coli isolate. Furthermore, it contained a 10 kb insert, but BLAST analysis only revealed uncharacterized and unnamed genes. In order to identify the source of the bactericidal effect, an attempt was made to cure the strain E. coli G3 / 10 by its large plasmid pSYM1. Despite many common treatments such as mitomycin C (mitomycin C) or heat treatment, the strains could not be treated. Thus, plasmid pSYM1 was transferred to E. coli G4 / 9 by conjugation. To allow selection of conjugants, a first ampicillin resistance cassette was integrated into pSYM1, resulting in p...
Embodiment 3
[0251] Example 3: Functional Characterization of Microcin S and Interpretation of Its Autoimmunity
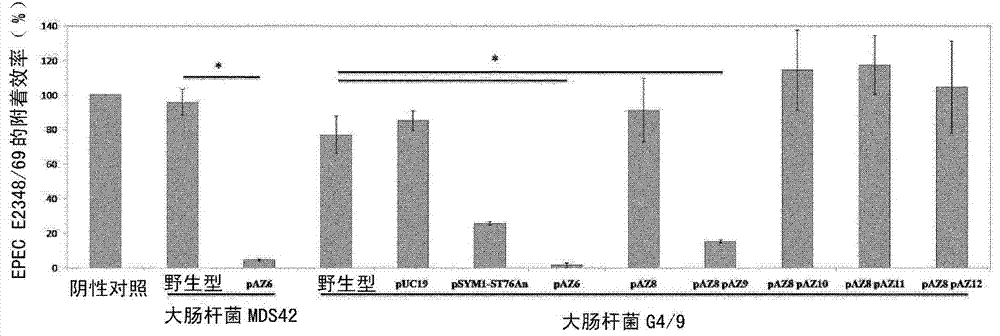
[0252] Bacterial attachment is a critical first step in many infectious diseases. Therefore, a test system that quantifies the inhibition of attachment of human intestinal epithelial cells is suitable for demonstrating beneficial effects on the host. In the first experiment, a confluent monolayer of CACO-2 was pre-incubated at a 100:1 MOI of E. coli to host cells using the bacterial test strain EcN, E. coli G3 / 10, E. coli G4 / 9, or E. coli G4 / 9pAZ6 or LOVO cells. After two hours of incubation, cells were washed and infected with EPEC E2348 / 69 using a 100:1 MOI of EPEC to host cells. E. coli G3 / 10 and E. coli G4 / 9pAZ6 were able to inhibit EPEC attachment similarly to EcN. showed that EcN attachment inhibition depends on strain microcin activity. Attachment efficiency in % is expressed as attachment of EPECs compared to attachment without any pre-incubation (negative control),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com