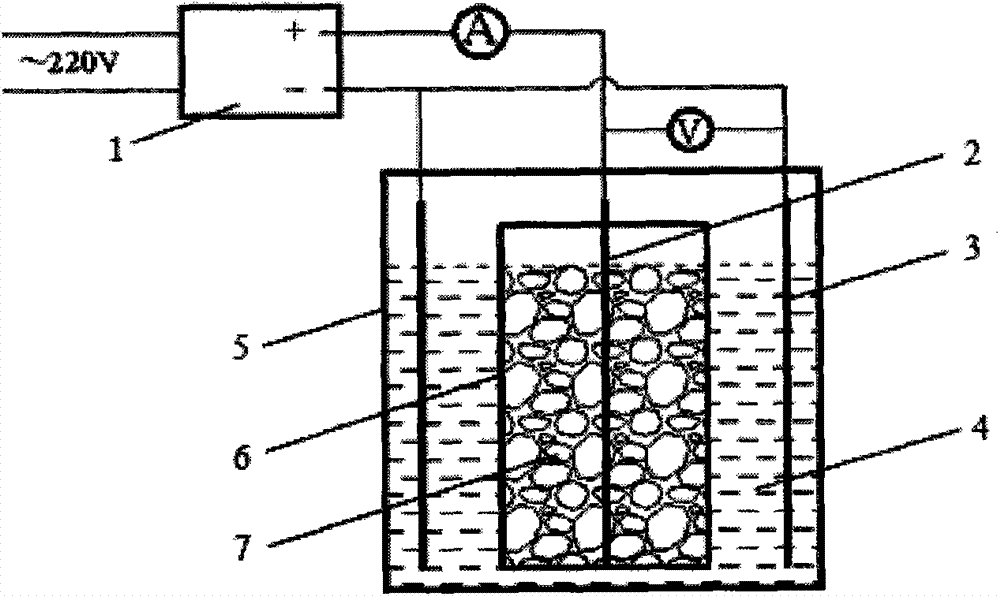
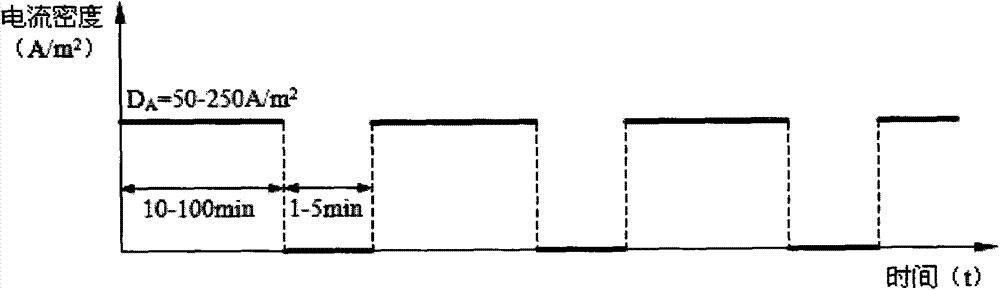
Method for electrochemically recycling low-cobalt WC-Co hard alloy waste material
A cemented carbide, recycling and processing technology, applied in optics, process efficiency improvement, photography process and other directions, can solve the problems of no systematic conclusion, low metal yield, uncontrollable process, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] The processed tungsten hard gold alloy scrap is a cemented carbide with a metal cobalt content of 6%, and the scrap is crushed to 10mm and the electrolyte composition is 0.5mol / LH 2 SO 4 , 10g / L NaF; the electrode spacing d is 20mm, the electrolyte temperature T is 60℃, the ratio of the electrolyte circulation flow rate to the cross-sectional area of the electrolytic cell (called the circulating flow rate, the same below) is 20cm / min; continuous Electrolyze for 100min and stop for 3min. The experimental results show that according to the concentration of metallic cobalt in the solution, the calculated current efficiency of cobalt electrolysis is 99.1%. Anode current density D A 200A / m 2 , Continuous operation for 24h, the electrolysis efficiency has no obvious change. The measured cell voltage is 1.26 volts, and the calculated power consumption is 1156Kwh / T cobalt.
Embodiment 2
[0025] The processed tungsten hard gold alloy scrap is a cemented carbide with a metal cobalt content of 11%, and the scrap is crushed to 12mm; the electrolyte composition is 0.5mol / LH 2 SO 4 , 10g / L NaF; electrode spacing d is 20mm, electrolyte temperature T is 60℃, electrolyte circulation flow rate is 20cm / min; continuous electrolysis for 100min, stop for 3min. The experimental results show that the current efficiency of cobalt electrolysis is 99.5%. Anode current density D A 240A / m 2 , Continuous operation for 24h, the electrolysis efficiency has no obvious change. The measured cell voltage is 1.51 volts, and the calculated electrical energy consumption is 1380Kwh / T cobalt.
Embodiment 3
[0027] The processed tungsten hard gold alloy scrap is a cemented carbide with a metal cobalt content of 11%, and the scrap is crushed to 12mm; the electrolyte composition is 0.5mol / LH 2 SO 4 , No additives are used; the electrode spacing d is 20mm, the electrolyte temperature T is 60°C, the electrolyte circulation flow rate is 20cm / min and the continuous electrolysis is 100min, and the stop is 3min. The experimental results show that the current efficiency of cobalt electrolysis is 99.6%. Anode current density D A 150A / m 2 , Continuous operation for 24h, the electrolysis efficiency has no obvious change. The measured cell voltage is 0.82 volts, and the calculated electrical energy consumption is 750Kwh / T cobalt. Further increase the current density to 175A / m 2 After 90 minutes of electrolysis, the cell voltage rose sharply to 1.42 volts. It can be seen that no additives are used, and anode passivation is prone to occur under high current density.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Flow density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Current efficiency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com