Sample heating rack for microscope or analysis device using electron beam, and sample heating method using same
A technology of an analysis device and a heating method, which is applied to circuits, discharge tubes, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of changes in the contrast of observed images, inability to completely suppress contamination, and reduction in element analysis accuracy, and achieve thermal drift suppression and high precision. Image observation, the effect of preventing the growth of contamination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Use copper double-sided tape (copper-containing double-sided tape) to fix the ceramic PTC thermistor with a Curie temperature of 92°C, a working voltage of 100V, and a stable current of 32mA on the existing aluminum sample holder for scanning electron microscopes. Obtain the sample heating frame of the present invention, use copper adhesive tape to fix the nickel-chromium wire heater and thermocouple through insulation coating on the above-mentioned aluminum sample frame, and obtain the comparative sample heating frame that can carry out PID control, The following tests were carried out using the sample heating rack of the present invention and the heating rack for comparison.
[0034] On the heated portion of these sample heating racks, a silicon wafer, a commercially available, mirror-polished silicon wafer that was air-dried after washing with isopropanol for 10 minutes, was fixed with copper double-sided tape as a sample. The silicon wafer was set on a sample stage ...
Embodiment 2
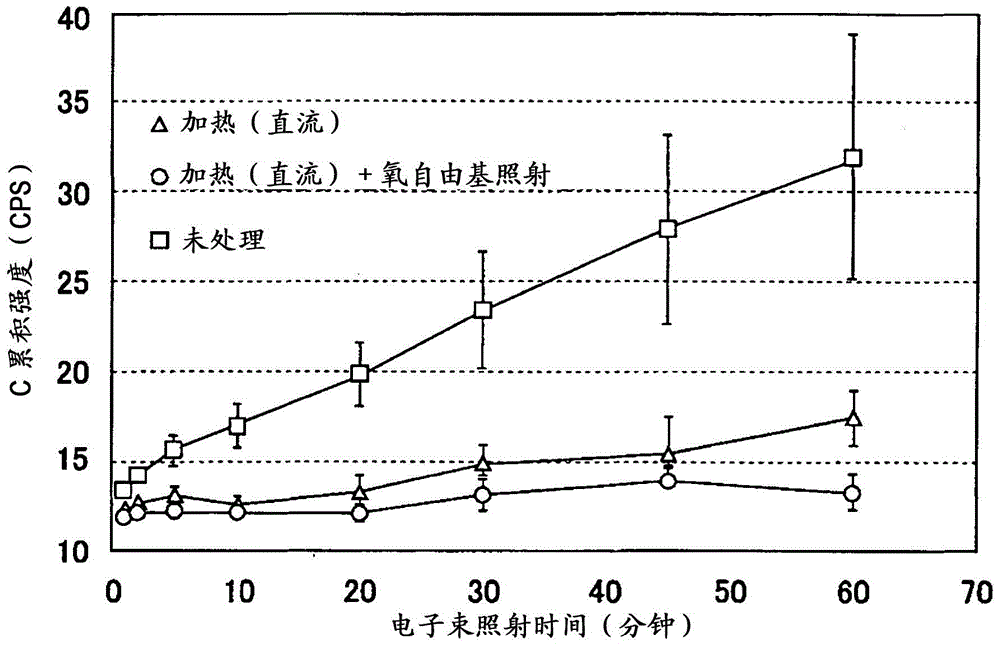
[0044] On the sample heating rack of the present invention, fix pure iron (commercially available plate-shaped standard sample: purity 99.9%) to replace the silicon wafer used in Example 1 as a sample, after heating, heating+oxygen free radicals In the irradiated and unheated untreated state, the amount of contamination on the sample surface (C accumulation intensity) was measured by changing the electron beam irradiation time. At this time, heating was performed under the same conditions as in Example 1, and oxygen radical irradiation was performed using a commercially available high-frequency plasma generator. In addition, the surface of pure iron is active, so it is easier to attach contamination than silicon wafers. When electron beams are irradiated for a long time, the analysis is hindered by contamination. Therefore, the contamination was measured up to the irradiation time of 60 minutes. Quantity changes over time. The measurement was performed under the same conditio...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Using the same method as in Example 1, a ceramic PTC thermistor with a Curie temperature of 92°C, a working voltage of 100V, and a stable current of 32mA was fixed to the existing scanning electron microscope with copper double-sided tape (copper-containing double-sided tape). The following tests were performed on the sample heating rack of the present invention obtained on an aluminum sample rack.
[0049] On the heating part of the sample heating rack, copper double-sided adhesive tape was used to fix an extremely low carbon steel plate as a sample. A dried commercially available ultra-low carbon steel sheet was set on a sample stage of a scanning electron microscope SUPRA55VP manufactured by Carl Zeiss, and the temperature was set at 92° C. to perform image observation. At this time, DC voltage and AC voltage were supplied to the sample heating rack through the current introduction terminal attached to the front surface of the SUPRA55VP sample stage, and image observ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com