Method for preparing titanium oxide crystal
A technology of trititanium pentoxide and titanium dioxide, which is applied in the field of preparation of trititanium pentoxide crystals, can solve problems such as differences in oxygen content, influence on coating efficiency, and influence on the purity and quality of the coating layer, and achieve shortening of pre-melting time, purity and Effects of improving quality and shortening coating time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
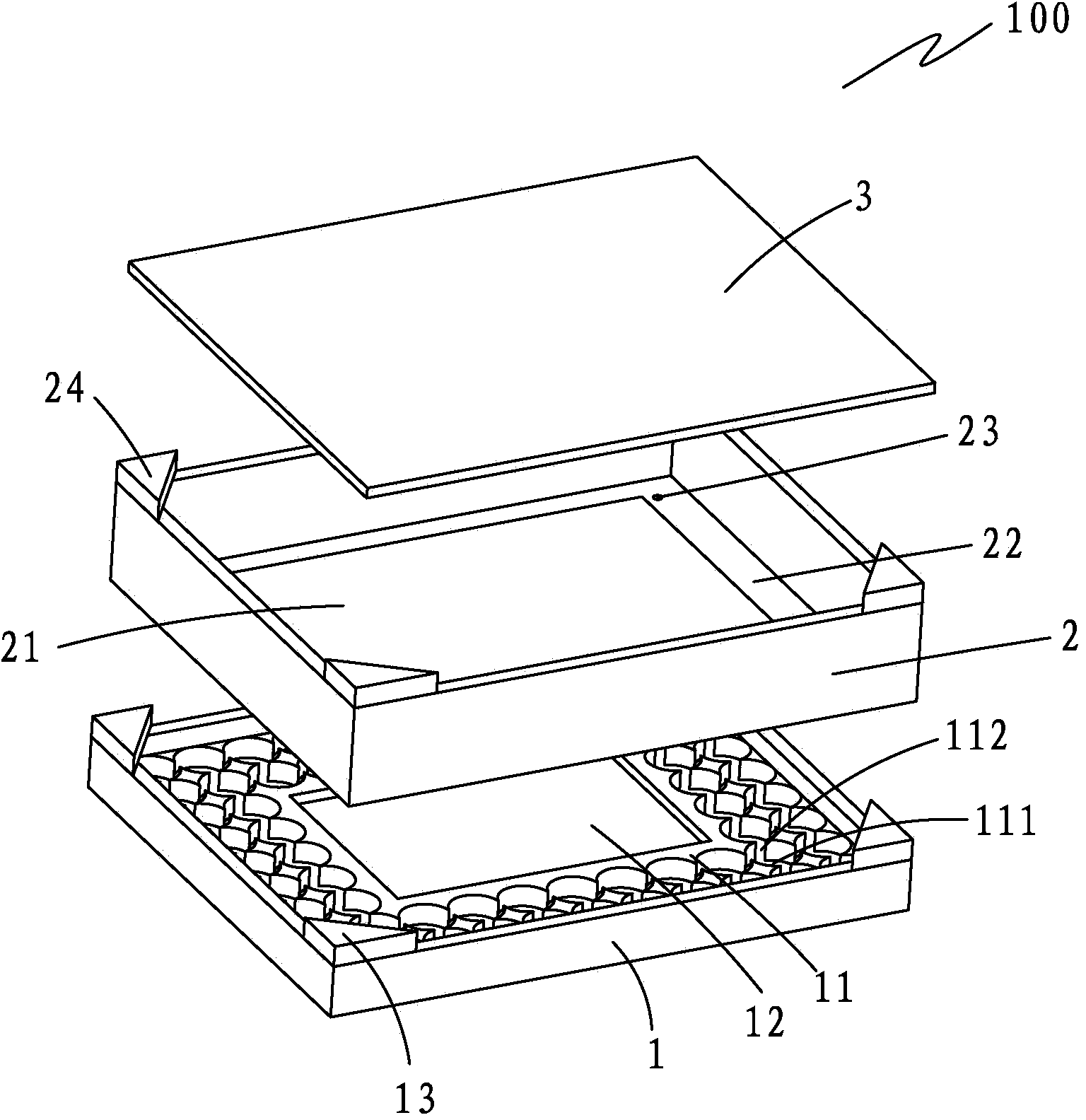
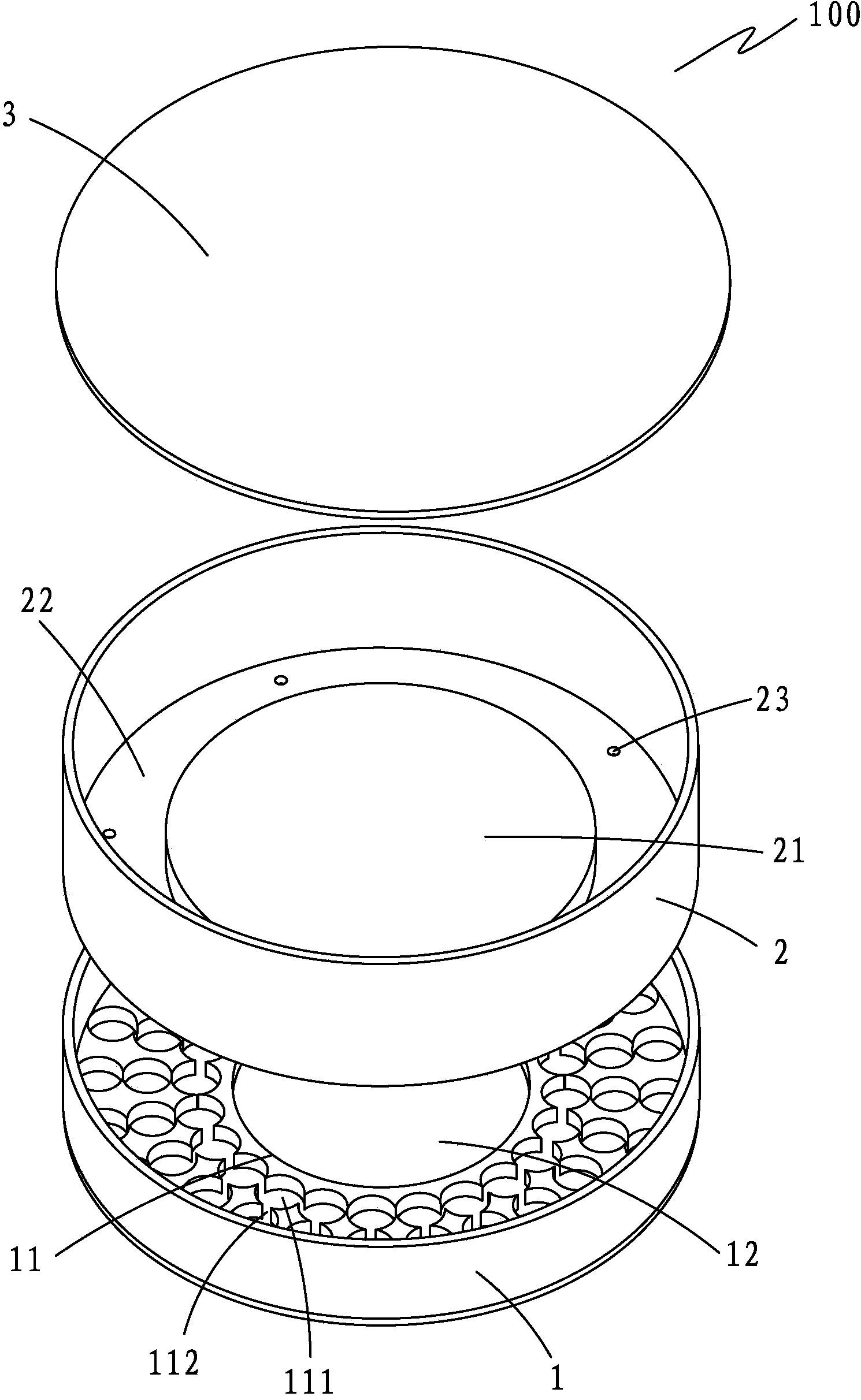
[0029] see again figure 1 , the preparation method specifically includes the following steps:
[0030] Step 1: Mix titanium powder and titanium dioxide according to the mass ratio of titanium: titanium dioxide = 1:8.25; then put the mixed raw materials in the crucible 2 of the sintering mold 100, and use 400 N of pressure to flatten and compact; The particle size of the titanium powder is 10-12 μm, and the purity is above 99.9%; the particle size of the titanium dioxide is 3-5 μm, and the purity is above 99.99%.
[0031] Step 2: Place the sintering mold 100 in a vacuum sintering furnace, and evacuate until the vacuum degree in the furnace is 10 -1 below pa;
[0032] Step 3: Heating and sintering in stages, the parameter requirements of each stage are as follows:
[0033] A. Normal temperature -1200°C, heating rate is 6°C / min, vacuum degree is kept at 3.0×10 -2 pa;
[0034] At this stage, the heating rate is fast, the raw material titanium and titanium dioxide do not react...
Embodiment 2
[0045] This part differs from Example 1 in that:
[0046] Step 1: Use 800 N of pressure to tile and compact;
[0047] Step 3:
[0048] A. The heating rate is 7°C / min, and the vacuum degree is kept at 1.0×10 -2 pa;
[0049] B. The heating rate is 4°C / min, and the vacuum degree is kept at 2.0×10 -2 pa;
[0050] C. The heating rate is 2°C / min, and the vacuum degree is kept at 4.0×10 -2 pa;
[0051] D. The heating rate is 1.5°C / min, and the vacuum degree is 6.0×10 -2 pa;
[0052] E. Insulate at 1805°C for 5 hours;
[0053] Step 4: The vacuum sintering furnace is cooled to 1600° C. at a rate of 3° C. / min.
Embodiment 3
[0055] This part differs from Example 1 in that:
[0056] Step 1: Use 600 N of pressure to tile and compact;
[0057] Step 3:
[0058] A. The heating rate is 8°C / min, and the vacuum degree is kept at 2.0×10 -2 pa;
[0059] B. The heating rate is 5°C / min, and the vacuum degree is kept at 3.0×10 -2 pa;
[0060] C. The heating rate is 2.5°C / min, and the vacuum degree is kept at 5.0×10 -2 pa;
[0061] D. The heating rate is 2°C / min, and the vacuum degree is 7.0×10 -2 pa;
[0062] E. Insulate at 1805°C for 8 hours;
[0063] Step 4: The vacuum sintering furnace is cooled to 1600° C. at a rate of 2° C. / min.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com