Method for extracting low-caffeine high-content tea polyphenol from fresh tea
A technology of fresh tea leaves and low caffeine, applied in the direction of reducing the alkali content of tea, can solve the problems of high equipment investment and high operating costs, and achieve the effects of short production cycle, high separation efficiency and simple operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
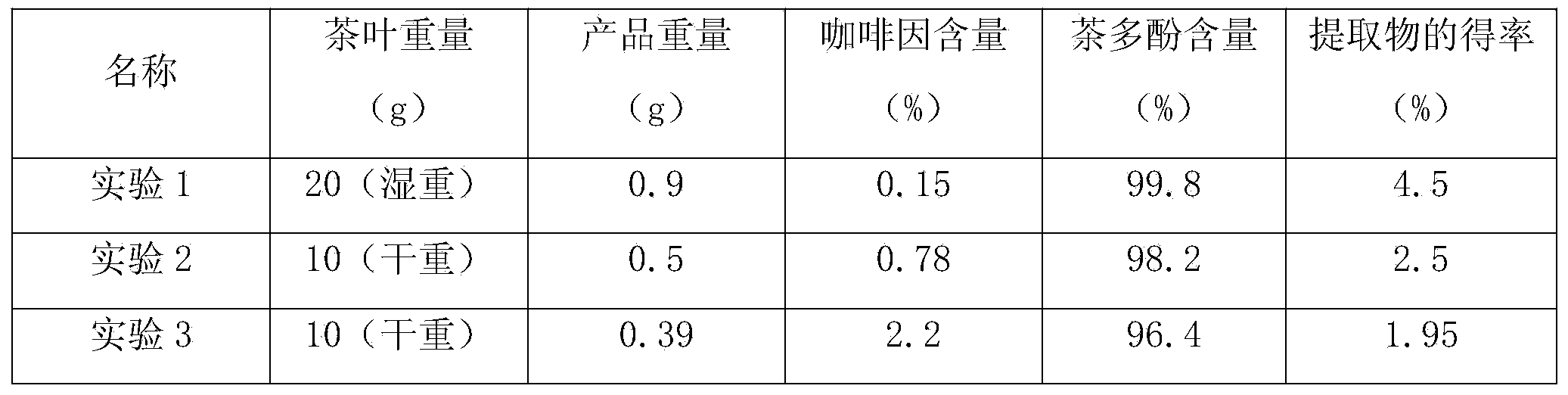
[0023] Embodiment 1: a kind of method extracting low-caffeine high-content tea polyphenols from fresh tealeaves, it comprises the following steps:
[0024] S1. Leaching: 2000kg of fresh tea leaves are placed in an extractor, 16000kg of ethyl acetate is added, soaked at a constant temperature for 3h, and the mixed solution in the extractor is passed through a 18-mesh sieve to obtain a filtrate; wherein, the soaking temperature at a constant temperature is 50°C;
[0025] S2. Primary evaporation and concentration: heat the filtrate to 70°C, evaporate and concentrate for 110 minutes, and obtain a solid-liquid mixture, that is, a primary evaporation concentrate;
[0026] S3. Water sinking: add the primary evaporation concentrate into purified water, and discard the solid after water sinking, and the solid content of the obtained liquid reaches 4-6%; wherein, the weight ratio of the primary evaporation concentrate to purified water is 1:4;
[0027] S4. CF filtration: use CF filter ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2: a kind of method extracting low-caffeine high-content tea polyphenols from fresh tealeaves, it comprises the following steps:
[0034] S1. Leaching: 2000kg of fresh tea leaves are placed in an extractor, 20000kg of ethyl acetate is added, soaked at a constant temperature for 4h, and the mixed solution in the extractor is passed through a 24 mesh sieve to obtain a filtrate; wherein, the constant temperature soaking temperature is 60°C;
[0035] S2. Primary evaporation and concentration: heat the filtrate to 70-75°C, evaporate and concentrate for 130 minutes, and obtain a solid-liquid mixture, that is, a primary evaporation concentrate;
[0036] S3. Water sinking: add the primary evaporation concentrate to purified water, and discard the solid after water sinking. The solid content of the obtained liquid reaches 6%; wherein, the weight ratio of the primary evaporation concentrate to purified water is 1:8;
[0037] S4. CF filtration: Use CF filter to filter ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Embodiment 3: a kind of method extracting low-caffeine high-content tea polyphenols from fresh tea leaves, it comprises the following steps:
[0044] S1. Leaching: 2000kg of fresh tea leaves are placed in an extractor, 18000kg of ethyl acetate is added, soaked at a constant temperature for 3.5 hours, and the mixed solution in the extractor is passed through a 20-mesh sieve to obtain a filtrate; wherein, the constant temperature soaking temperature 55°C;
[0045] S2. Primary evaporation and concentration: heat the filtrate to 70-75°C, evaporate and concentrate for 120 minutes, and obtain a solid-liquid mixture, that is, a primary evaporation concentrate;
[0046] S3. Water sinking: adding the primary evaporation concentrate to purified water, and discarding the solid after water sinking, the obtained liquid has a solid content of 5%; wherein, the weight ratio of the primary evaporation concentrate to purified water is 1:6;
[0047] S4. CF filtration: Use CF filter to fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com