Method and device for detecting rain amount through laser
A technology of laser detection and rainfall, which is applied in measuring devices, rainfall/precipitation gauges, meteorology, etc., can solve problems such as mechanical principle limitations, rain gauge blockage, imaging changes, etc., to ensure parallelism and distribution uniformity, The effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
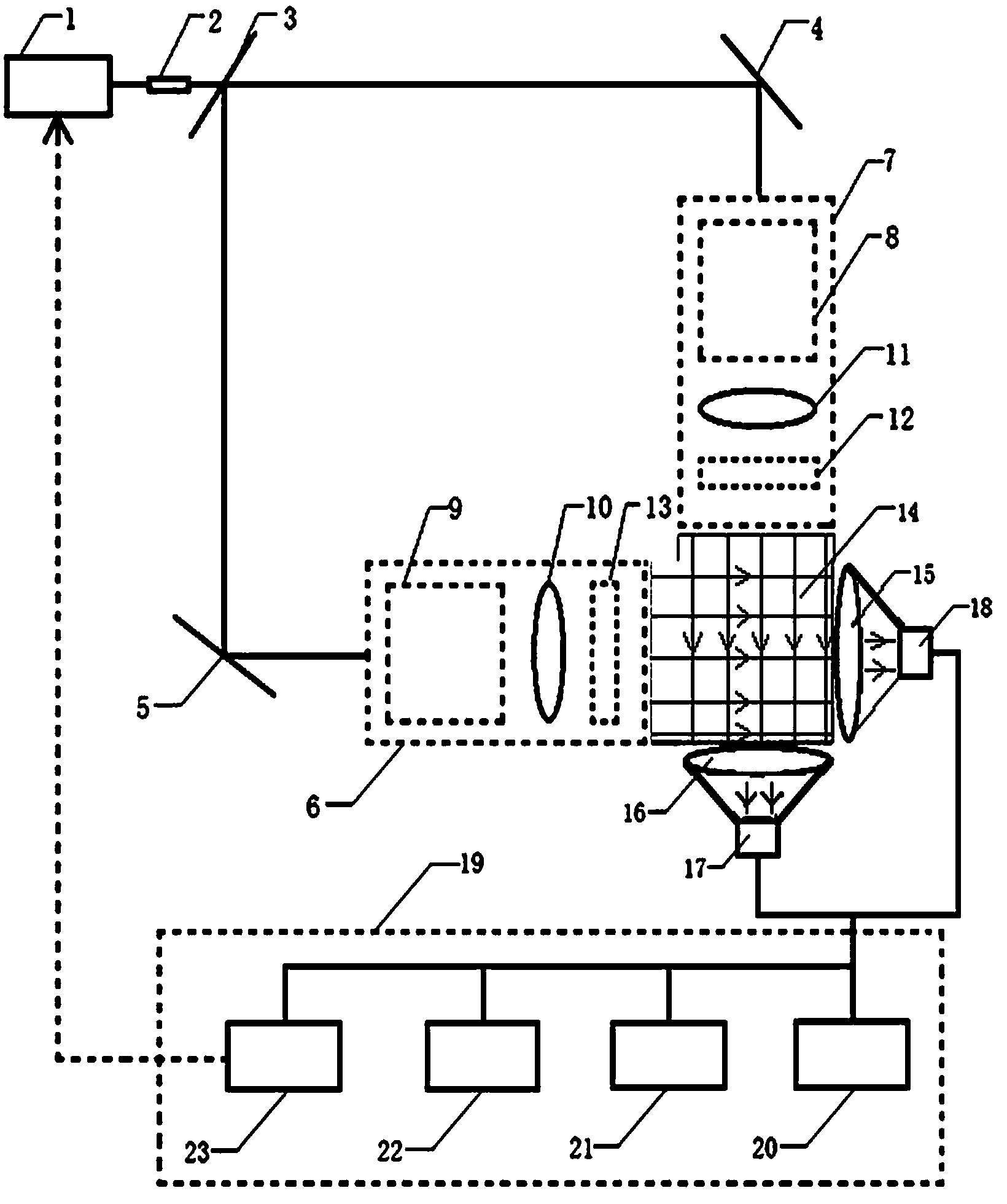
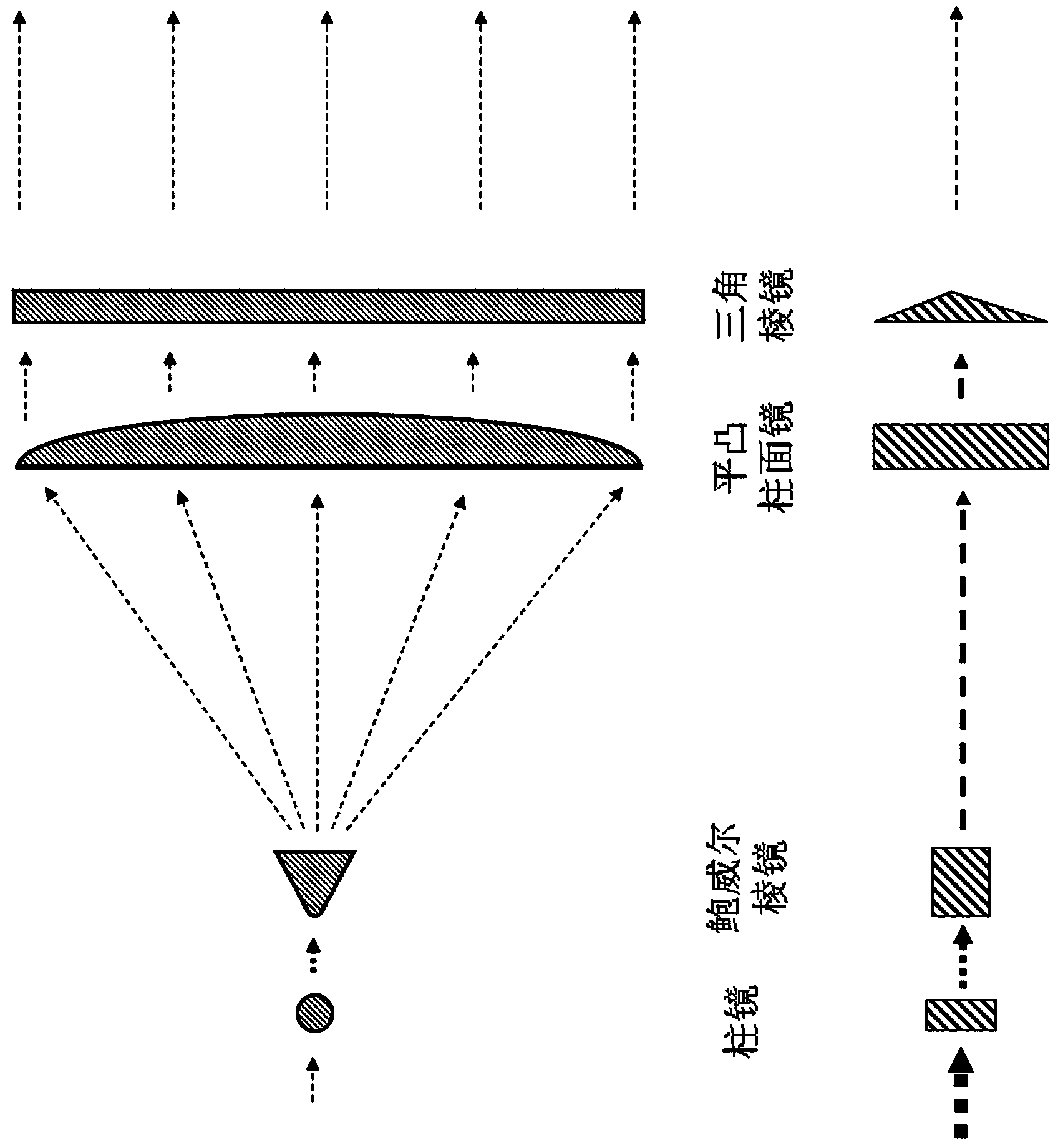
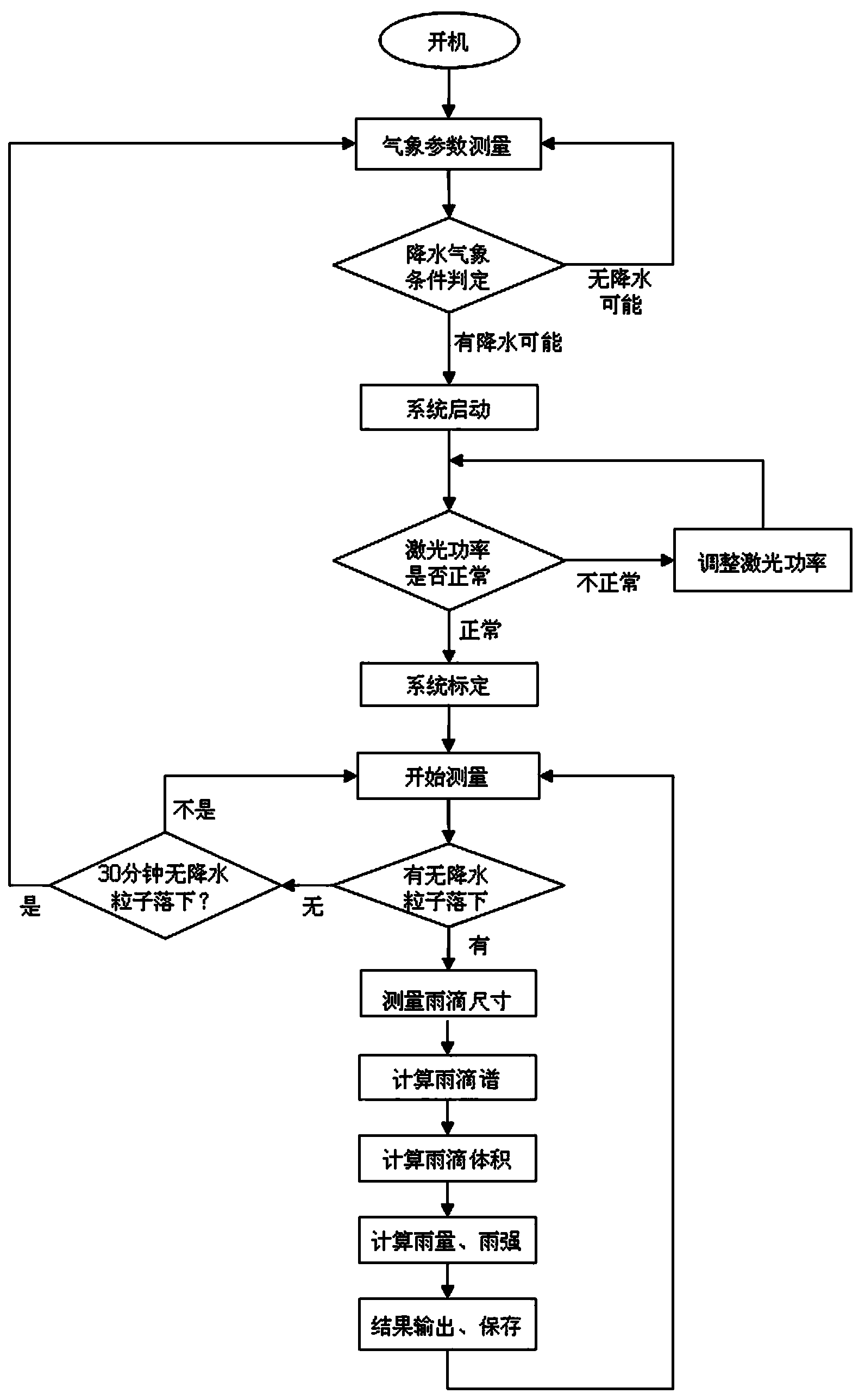
[0056] Example 1: The basic composition of the optical rain gauge system involved is as attached figure 1 As shown, it includes semiconductor laser (wavelength 405nm, power 6mW) 1, collimator 2 (diameter 6.0mm, focal length 4.7mm aspheric glass lens), beam splitter 3 (light intensity is divided into 1:1 beam splitter), mirror 4 (coated mirror with high reflectance ratio), mirror 5 (coated mirror with high reflectance ratio), parallel sheet light beam generation system 6, parallel sheet light beam generation system 7, sheet Light generator (cylindrical lens + Powell prism) 8, sheet light generator (cylindrical lens + Powell prism) 9, cylindrical plano-convex lens 10 (width 10cm, focal length 15cm), cylindrical plano-convex lens 11 (width 10cm, focal length is 15cm), triangular prism 12, triangular prism 13 (length is 12cm, width is 1cm, base angle is ), sampling space 14 (size 10cm×10cm), cylindrical convex lens 15 (width 10cm, focal length 12cm), cylindrical convex lens 16...
Embodiment 2
[0060] This embodiment uses the same optical structure as in Embodiment 1. The line array sensor adopts a CMOS high-speed line array sensor with 2048 pixels, the pixel size is 10 μm×10 μm, the acquisition line frequency is 50 kHz, and the light source adopts laser light sources of different wavelengths to compare the measurement results. Comparison. When the semiconductor lasers used are purple light (wavelength 405nm) and red light (wavelength 650nm), the same static object at the same position is measured and compared, and the two scanned grayscale profiles are obtained. The results are as follows Figure 5 shown. It can be seen from the upper figure in the figure that the result measured under purple light is closer to the actual size of the falling object, and the result is more accurate. and Figure 5 The figure below shows that when red light with a longer wavelength is used as the detection light source, the effect of light diffraction is obvious, and the measured...
Embodiment 3
[0062] In this embodiment, the difference produced by the presence or absence of a triangular prism in the parallel plate light generation system is compared, and the experiment uses an optical system similar to that in Embodiment 1.
[0063] At first considering the scope that needs triangular prism to produce effect (high concentrating parallel sheet light beam range), the triangular prism width that selects in the embodiment 1 is 1cm, and base angle is 4 ° because of the following reasons: when the width of triangular prism is constant, the triangular prism produced There is a certain functional relationship between the beam range of the high-concentration parallel plate light and its base angle. attached Image 6 Shown is the curve relationship between the beam range of the high-concentration parallel sheet light and the angle of the base angle of the triangular prism when the width is 1cm. The required sampling space in Example 1 is 10cm in size, and considering the infl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com