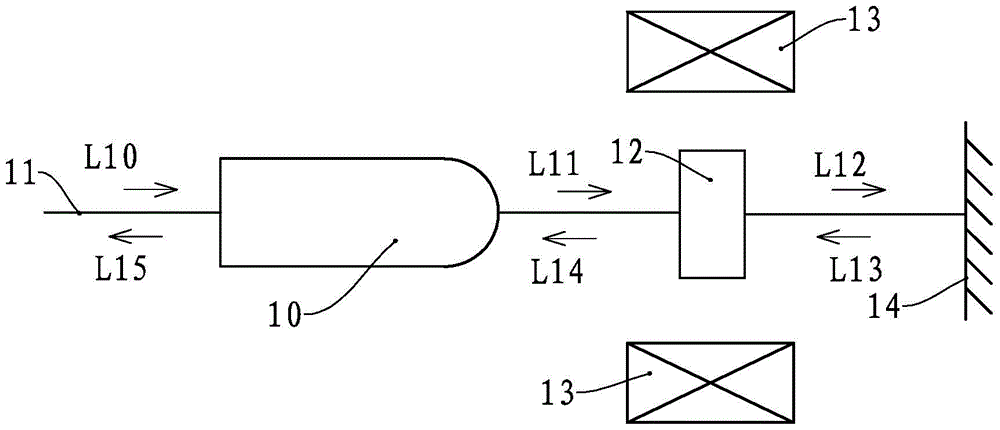
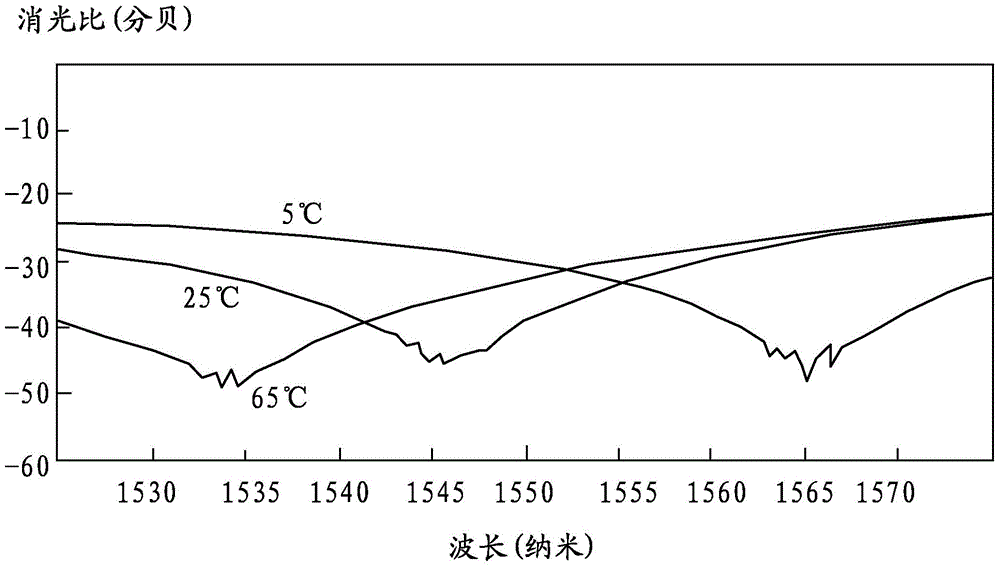
Faraday rotating mirror and fiber optic interferometer
A Faraday rotation and fiber optic interferometer technology, applied in the field of fiber optic interferometers, can solve the problems of unguaranteed and limited use range of fiber optic interferometers, and achieve the effects of insensitivity to temperature changes, low wavelength requirements, and wide wavelength ranges
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
[0036] see image 3 , the Faraday rotating mirror of the present embodiment has a single-fiber collimator 20, and the output end of the single-fiber collimator 20 is provided with a polarization light-splitting light-combining device, and the polarization light-splitting light-combining device of the present embodiment consists of a Wollaston prism 22 And roof prism 24 constitutes. The Wollaston prism 22 is located at the output end of the single fiber collimator 20, and a beam splitter 23 is provided inside it. After the light beam of any polarization state enters the Wollaston prism 22, the polarization states are perpendicular to each other on the beam splitter 23. The two beams of light exit from the exit surface of the Wollaston prism 22.
[0037] The roof prism 24 is located on the exit surface of the Wollaston prism 22 , and its roof surface 25 faces the exit end of the Wollaston prism 22 . After the two light beams emitted from the Wollaston prism 22 are incident on ...
no. 2 example
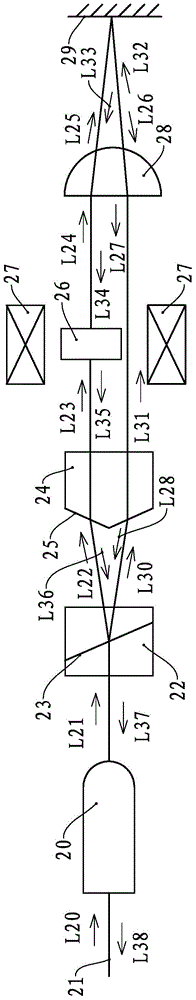
[0049] see Figure 5 and Figure 6 , the Faraday rotating reflector of the present embodiment has double-fiber collimator 30, the polarization light-splitting light-combining device that is positioned at double-fiber collimator 30 exit ends, and the polarization light-splitting light-combining device of the present embodiment is made of Wollaston prism 33 and roof The prism 35 is constituted, the Wollaston prism 33 has a dichroic surface 34 , and the roof surface 36 of the roof prism 35 faces the Wollaston prism 33 .
[0050] The outgoing end of the roof prism 35 is provided with a Faraday rotator 37 , and the outer side of the Faraday rotator 37 is provided with a magnetic field generating device 38 , and the Faraday rotator 37 is located on an outgoing optical path of the roof prism 35 . The outgoing end of the Faraday rotator 37 is provided with a focusing lens 39 , and the outgoing end of the focusing lens 39 is provided with a reflective mirror 40 .
[0051] The optical...
no. 3 example
[0057] see Figure 7 , the present embodiment has a single fiber collimator 41, a birefringent crystal 43 positioned at the exit end of the single fiber collimator 41, the exit end of the birefringence crystal 43 is provided with a Faraday rotator 44, and the exit end of the Faraday rotator 44 is provided with a focusing Lens 46 , reflective mirror 47 is provided at the output end of the focusing lens 46 , and the reflective surface of the reflecting mirror 47 faces the focusing lens 46 and is located at the focal point of the focusing lens 46 . In this embodiment, the birefringent crystal 43 is a polarization splitting and combining device for splitting or combining light beams. The birefringent crystal 43 can be a discrete birefringent crystal, or a composite birefringent crystal. In addition, the Faraday rotator 44 is located on one of the outgoing light paths of the birefringent crystal 43 , and a magnetic field generating device 45 is provided outside it.
[0058] The o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com