Full-solid-state single-spectral-line narrow linewidth yellow light laser
An all-solid-state, narrow-linewidth technology, applied in the direction of lasers, laser components, phonon exciters, etc., can solve the problems of unstable laser spectral output, aggravated mutual coupling, and poor power stability, so as to improve the light-to-light conversion efficiency , Small size, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
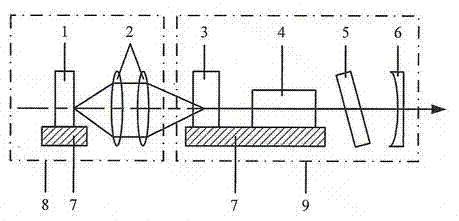
[0020] see figure 1 As shown, an all-solid-state single-spectrum narrow-linewidth yellow laser includes a pump source system 8, and the pump source system 8 mainly includes a laser diode LD1 arranged in sequence on an optical path and a focusing coupling lens In system 2, the working mode of the pump source system 8 is continuous working mode, the maximum continuous pumping power is 5W, and the output wavelength is 808nm.
[0021] It also includes a straight resonant cavity device 9, the straight resonant cavity device 9 includes a laser gain medium 3 and a yellow light output mirror 6 sequentially arranged in the straight cavity, and the laser gain medium 3 and the yellow light output mirror 6 A frequency doubling crystal 4 is placed between them, and a birefringent filter 5 is placed between the frequency doubling crystal 4 and the yellow light output mirror 6 .
[0022] Further, the laser diode LD1 , the laser gain medium 3 and the frequency doubling crystal 4 have coo...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Roughly the same as Example 1, the differences are as follows:
[0030] (1) The birefringent filter 5 selects quartz crystal, puts it into the resonant cavity at Brewster's angle (56°), and adjusts its tuning angle to 46.6°.
[0031] (2) Frequency doubling crystal 4 is a lithium triborate (LBO) crystal with a size of 2×2×10mm 3 , both ends of the crystal are coated with 558nm and 1116nm anti-reflection coatings (T>99%); the matching method adopts type I phase matching, and the cutting angle is θ=90°, φ=8°.
Embodiment 3
[0033] Roughly the same as Example 1, the differences are as follows:
[0034] (1) The birefringent filter 5 selects quartz crystal, puts it into the resonant cavity at Brewster's angle (56°), and adjusts its tuning angle to 45.9°.
[0035] (2) Frequency doubling crystal 4 is a lithium triborate (LBO) crystal with a size of 2×2×10mm 3 , both ends of the crystal are coated with 556nm and 1112nm anti-reflection coatings (T>99%); the matching method adopts type I phase matching, and the cutting angle is θ=90°, φ=8.3°.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com