Selective hydrogenation catalyst for improving coking resistance
A technology for selective hydrogenation and catalysts, applied in metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalysts, physical/chemical process catalysts, chemical instruments and methods, etc. lifespan and other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1~3
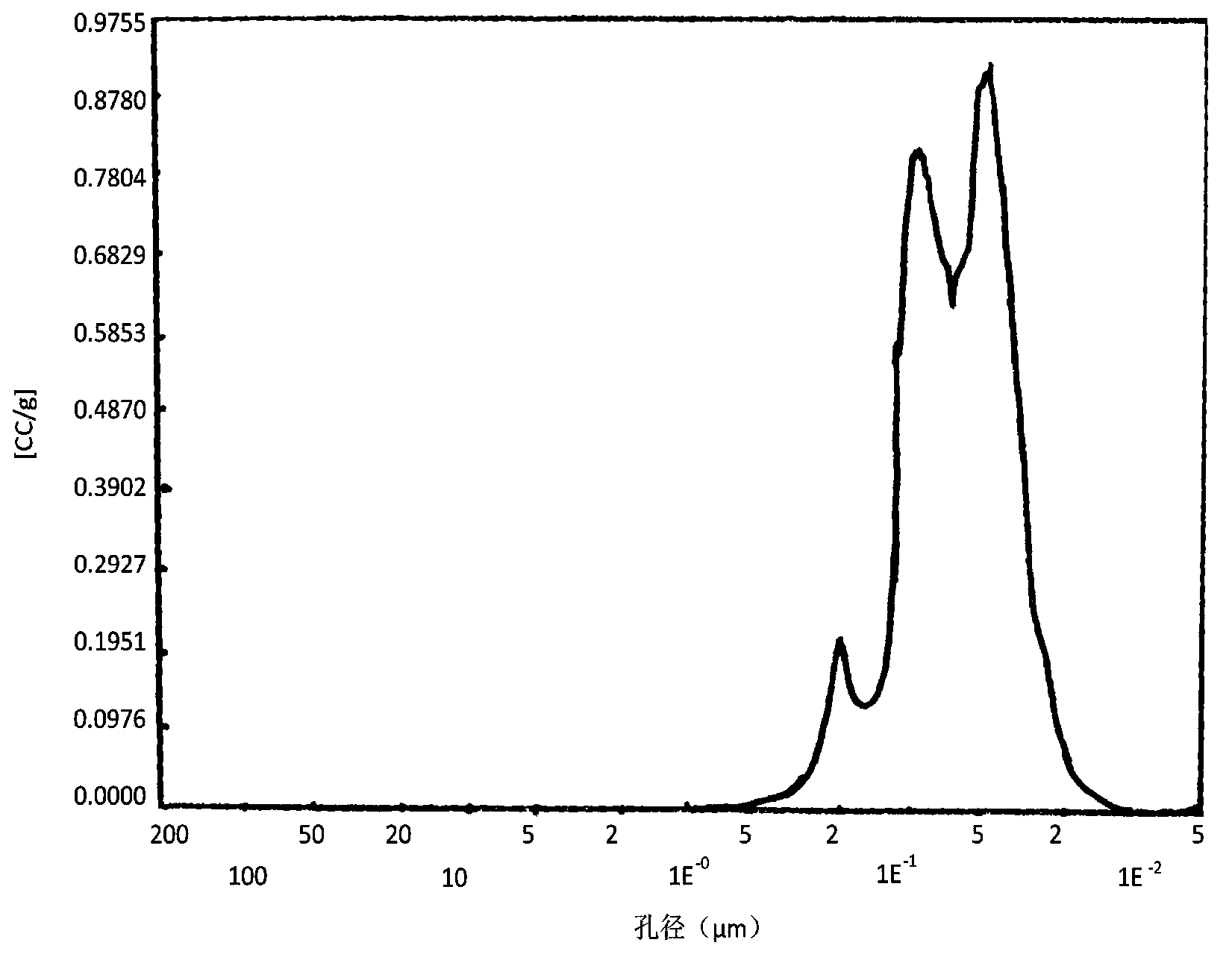
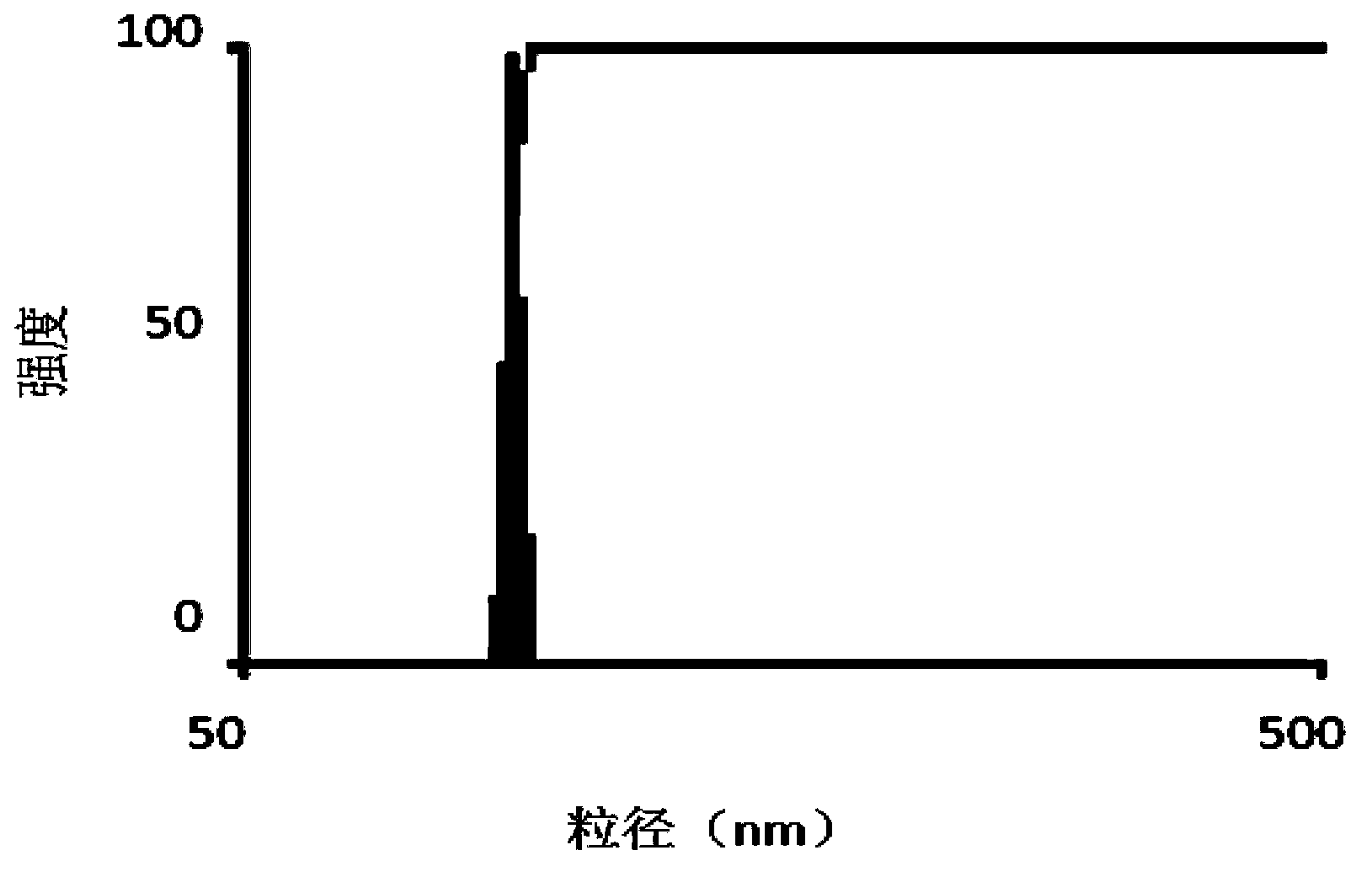
[0060] Adjust the pH value of the Ni precursor aqueous solution, prepare a Ni microemulsion at 20°C, put 100g each of the burnt carriers 1 to 3 into the prepared microemulsion for impregnation, and dry the filtered solid after impregnation , roasted, and then prepare a Pd aqueous solution, adjust its pH to 2.0, and add the roasted Ni-containing carrier into the Pd aqueous solution for impregnation, dry and roast after impregnation to obtain the desired catalyst. The specific parameters are shown in Table 1.
[0061] Measure the Pd content and nickel content in embodiment 1~3 with atomic absorption spectrometry, in embodiment 1, the content of Pd is 0.03%, and nickel content is 0.079%, and the thickness of Pd layer is 150 μ m; Among the embodiment 2, Pd content is 0.038%, the nickel content is 0.35%, and the Pd layer thickness is 200 μm; in Example 3, the Pd content is 0.045%, the nickel content is 3.5%, and the Pd layer thickness is 300 μm. The catalyst prepared in Examples 1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com