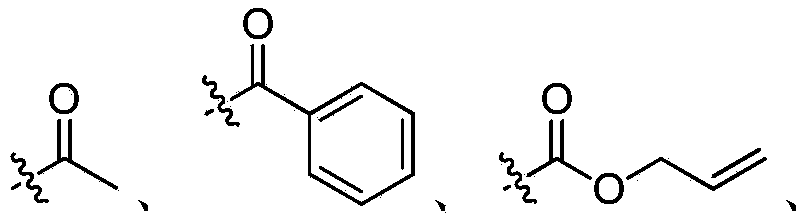
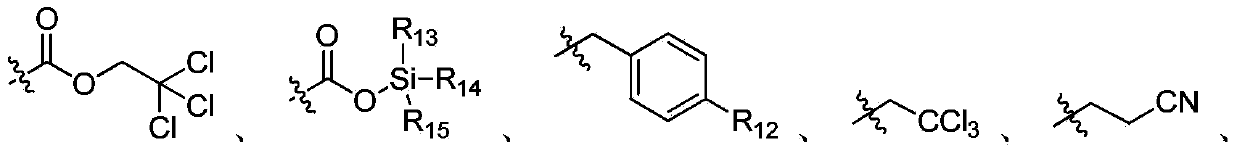
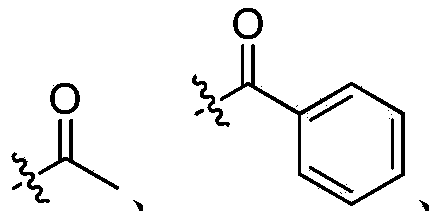
Ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors and methods of use
A technology for deprotecting agents and compounds, which is applied in the field of ribonucleotide reductase inhibitors and applications, and can solve problems such as the lack of progress in the research and development of RR inhibitors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0206] Example 1: Identification of RRM2 as a target for anticancer therapy:
[0207] The RRM2-luciferase fusion construct ("pR2Luc") was administered to explants by high pressure tail vein injection (HPTV) alone or in combination with RRM2 siRNA ("siR2B+5") [plasmid 0.25 mg / kg, siRNA 1.25 mg / kg]. Female BALB / c mice harboring human HepG2 hepatoma cells were injected. In vivo bioluminescent imaging reveals robust downregulation of ( figure 1 ). Mice receiving RRM2 in combination with RRM2 siRNA exhibited a significant reduction in tumor growth compared to mice receiving RRM2 alone or RRM2 in combination with a control siRNA ("si control"). These results suggest that RRM2 plays a critical role in cancer growth and validate it as a therapeutic target.
[0208] RRM2 mRNA expression levels were measured by RT-PCR in 35 human fresh-frozen breast cancer biopsy samples and corresponding normal tissue samples. Determination of optimal PCR primer and probe concentrations for RRM2 an...
Embodiment 2
[0210] Example 2: Identification of novel RR inhibitors:
[0211] A virtual screening process was performed on a diverse compound library from NCI's Developmental Therapeutics Program (DTP) to identify potential RR inhibitors. The DTP library contains 2,000 different compounds. A novel ligand-binding pocket (PDB2UW2) on human RRM2 identified from X-ray crystal structure was selected to identify a site close to the RRM1 / RRM2 interface but away from the dityrosyl-diiron center to avoid side effects of iron chelation Potential inhibitor compounds. This ligand-binding pocket consists of 32 amino acid residues that are conserved among the human and mouse RRM2 protein families, and lies next to the RRM1 / RRM2 interface. The structure of the ligand binding pocket is shown in Figure 4 middle. The pocket consists of helices α7, α8 and α10 at the C-terminal domain. The narrow inner end of the V-shaped pocket is lined with hydrophobic residues near the rear of the center of the dity...
Embodiment 3
[0215] Example 3: Characterization of novel NCI-3 analogs:
[0216]NCI-3 and the NCI-3 analogs synthesized in Example 2 were tested for their ability to inhibit RR activity using the in vitro holoenzyme assay described above. COH4 exhibited a significant RR inhibitory effect. COH20 was even more potent, inhibiting the recombinant RRM1 / RRM2 complex by 90.2% in vitro ( Image 6 ). The IC50 results for various compounds are shown in Table 1.
[0217] Table 1:
[0218] compound
IC50±S.D.(μM)
HU
148.0±7.34
3-AP
1.2±0.13
NCI-3
19.1±0.43
COH4
15.3±1.8
COH20
9.3±2.3
[0219] In stark contrast to 3-AP, the inhibitory effect of COH20 on RR was barely affected by iron addition (Table 2).
[0220] Table 2:
[0221]
[0222] Site-directed mutagenesis, Biacore analysis, and NMR saturation shift difference (STD) analysis were performed to verify the binding pocket and ligand / protein interaction between COH20 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com