Common steel boriding and quenching combined treatment process
A composite treatment, general-purpose steel technology, applied in the field of heat treatment, can solve the problems of increased heat treatment processing costs, low versatility, etc., to prevent spalling, prolong service life, and reduce brittleness.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
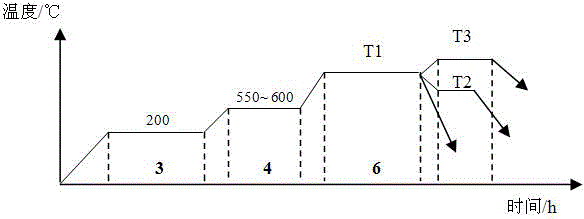
[0036] The boriding and quenching composite treatment process of hot work die steel H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1) includes the following steps:
[0037] (1) Clean and preheat the commonly used hot work die steel H13 workpiece, heat it at 100°C for 1 hour and dry it, place it in a container filled with solid powdery boronizing agent, and send it into an RJ or FXL heat treatment furnace;
[0038] (2) Raise the temperature of the furnace to 200°C and keep it warm for 3 hours;
[0039] (3) Raise the furnace temperature to 550-600°C at a temperature of 60-70°C / h, and keep it warm for 4 hours;
[0040] (4) Raise the furnace temperature to 1000°C at a temperature of 60-70°C / h and keep it warm for 6 hours;
[0041] (5) Quenching: Lift out the workpiece and quench it out of the furnace;
[0042] (6) Tempering: Tempering at 560°C for 2 to 3 times.
[0043] The boronizing temperature of hot work die steel H13, Cr12MoV, Cr12, and 2Cr13 is very close to the quenching temperature, so it is directly b...
Embodiment 2
[0047]The boronizing and quenching composite treatment process of medium carbon quenched and tempered steel 40Cr includes the following steps:
[0048] (1) Clean and preheat the commonly used medium carbon quenched and tempered steel 40Cr workpiece, heat it at 200°C for 2 hours and dry it, place it in a container filled with solid powder boronizing agent, and send it into an RJ or FXL heat treatment furnace ;
[0049] (2) Raise the temperature of the furnace to 200°C and keep it warm for 3 hours;
[0050] (3) Raise the furnace temperature to 550-600°C at a temperature of 70-80°C / h, and keep it warm for 4 hours;
[0051] (4) Raise the furnace temperature to 930-1000°C at a temperature of 70-80°C / h, and keep it warm for 6 hours;
[0052] (5) Lower the furnace temperature to 850°C and keep it warm for 2 to 3 hours;
[0053] (6) Quenching: Lift out the workpiece and quench it out of the furnace;
[0054] (7) Tempering: 1 or 2 times at a low temperature of 200°C.
[0055] The ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The boriding and quenching composite treatment process of niobium-containing high-speed steel 65Nb comprises the following steps:
[0060] (1) Clean and preheat the niobium-containing high-speed steel 65Nb (65Cr4W3Mo2VNb) workpiece, dry it at 150°C for 1.5h, place it in a container filled with solid powder boronizing agent, and send it to RJ or FXL heat treatment in the furnace;
[0061] (2) Raise the temperature of the furnace to 200°C and keep it warm for 3 hours;
[0062] (3) Raise the furnace temperature to 550-600°C at a temperature of 50-60°C / h and keep it warm for 4 hours;
[0063] (4) Raise the furnace temperature to 930°C to 1000°C at a temperature of 50°C to 60°C / h, and keep it warm for 6 hours.
[0064] (5) Slowly raise the temperature of the furnace to 1080°C-1100°C and keep it warm for 2-3 hours;
[0065] (6) Quenching: Lift out the workpiece and quench it out of the furnace;
[0066] (7) Tempering: Tempering 3 times at 560°C.
[0067] The metallograph...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com