Lithium ion battery
A lithium-ion battery and electrolyte technology, applied in battery electrodes, secondary batteries, circuits, etc., to achieve the effect of improving high-rate charge-discharge characteristics and increasing energy density
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
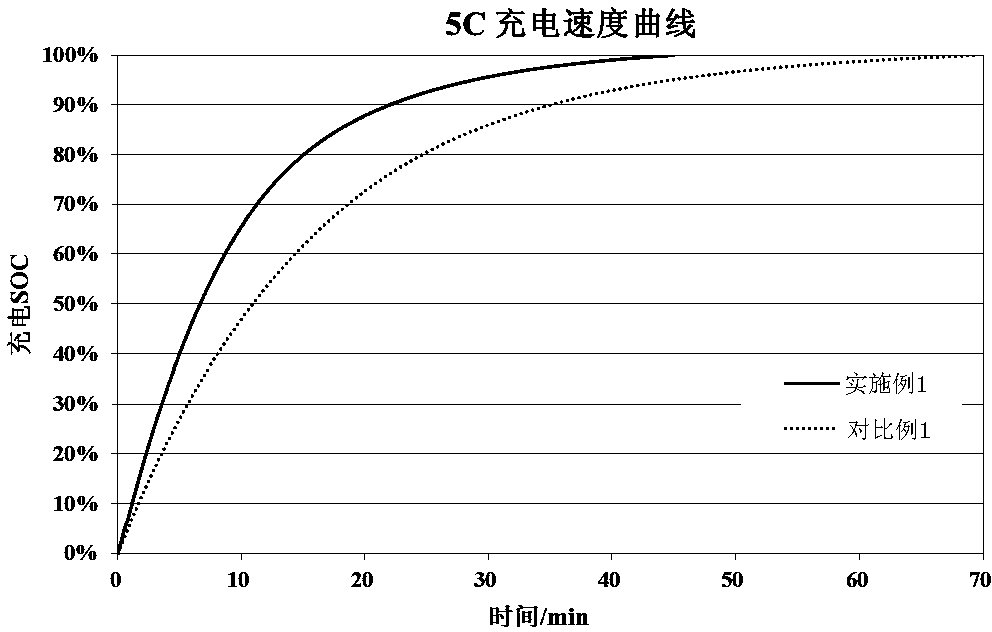
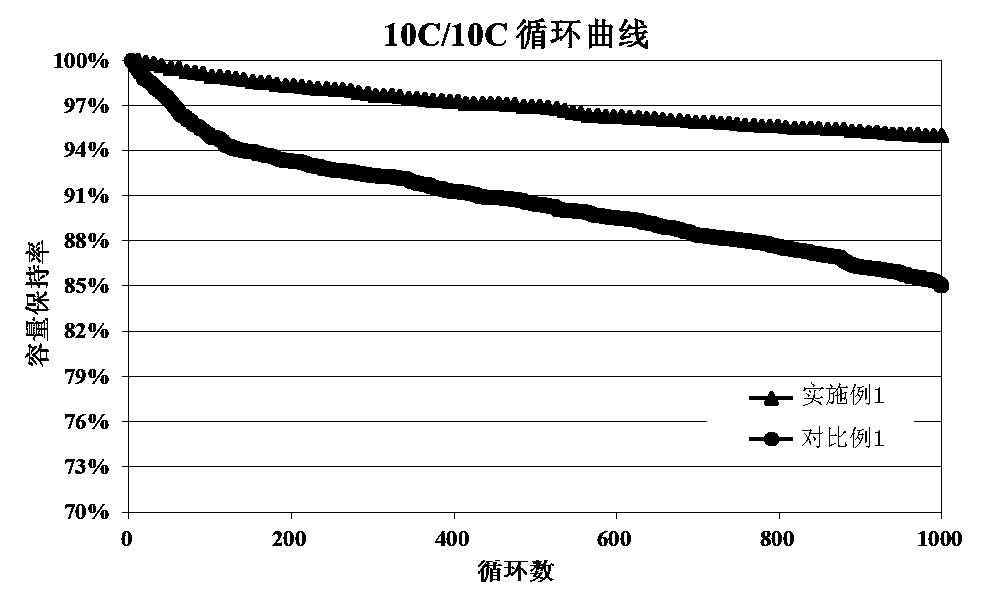
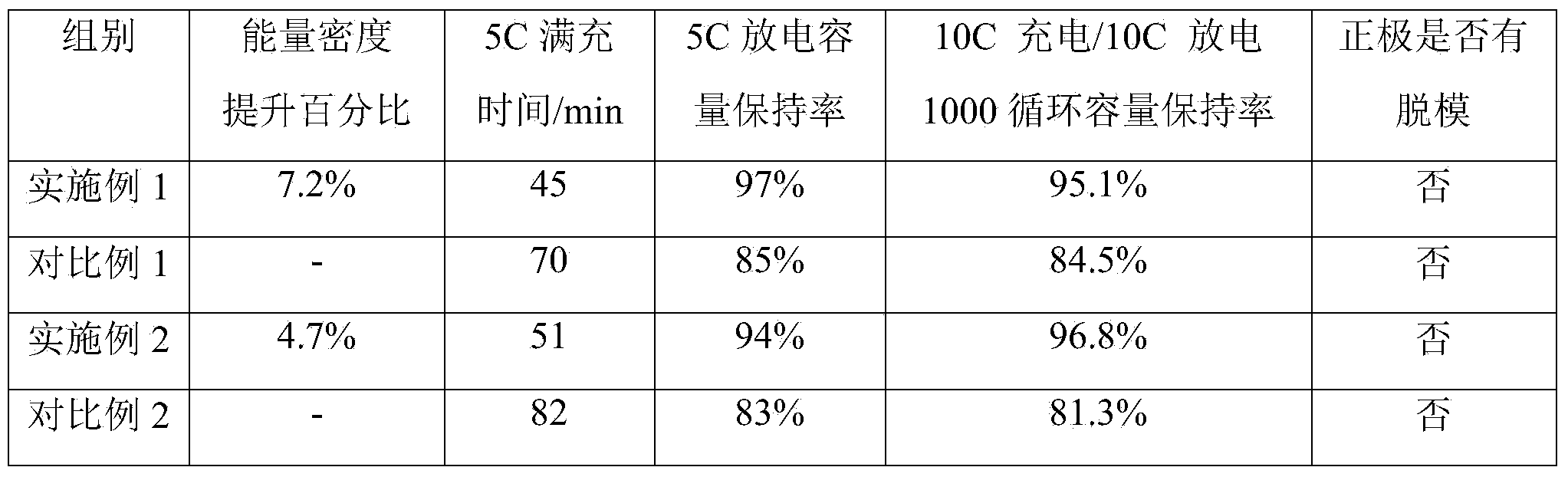
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A lithium ion battery provided in this embodiment includes a positive electrode sheet, a negative electrode sheet, a separator disposed between the positive electrode sheet and the negative electrode sheet, and an electrolyte;
[0037] The positive electrode sheet includes a positive electrode current collector and a positive electrode active material layer disposed on the surface of the positive electrode current collector. In terms of mass percentage, the positive electrode active material layer includes the following components:
[0038] Positive electrode active material nickel cobalt lithium manganese oxide 98.5%;
[0039] Positive electrode conductive agent carbon black 0.3%;
[0040] Positive electrode conductive agent carbon nanotube 0.4%;
[0041] Positive electrode binder polyvinylidene fluoride 0.8%;
[0042] The positive current collector is an aluminum foil with a thickness of 16 μm.
[0043] The negative electrode sheet includes a negative electrode curre...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The difference from Example 1 is that the positive electrode active material is nickel-cobalt-aluminate lithium, and its mass content is 98.8%, and the nickel-cobalt-aluminate lithium is also doped with Mg with a mass percentage of 0.5%; the positive electrode conductor is carbon nanotubes, and its mass content is 0.5%; the positive electrode binder is sodium alginate, and its mass content is 0.7%; the additive includes tris(pentafluorophenyl) boron with a mass ratio of 1.5% accounting for the total mass of the electrolyte Alkane and 2% VC in the mass ratio of the total mass of the electrolyte, and a lithium salt concentration of 1.1 mol / L, and the rest are the same as in Example 1, and will not be repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0068] The difference from Example 1 is that the positive electrode active material is a mixture of lithium cobaltate and lithium manganate, the mass ratio of the two is 5:1, and the mass content of the positive electrode active material is 99.2%, wherein the surface of lithium cobaltate Coated with Al 2 o 3 layer, and Al 2 o 3 The ratio of the mass of the layer to the mass of lithium cobaltate is 1:100, and the lithium manganate is doped with Zr with a mass percentage of 0.3%; the positive electrode conductive agent is a mixture of carbon nanotubes and graphene, and the mass of carbon nanotubes The content is 0.1%, and the mass content of graphene is 0.1%; the positive electrode binder is polyvinyl alcohol, and the mass content of the positive electrode binder is 0.6%; Fluorophenylboron oxalate and VC with a mass ratio of 2% to the total mass of the electrolyte, and a lithium salt concentration of 1.15 mol / L, and the rest are the same as in Example 1, and will not be repea...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com