CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) low-temperature low-noise operational amplifier circuit
An operational amplifier circuit and low-noise technology, applied in the field of CMOS low-temperature and low-noise operational amplifier circuits, can solve problems such as the inability to apply mainstream CMOS circuit design, no adoption, etc., achieve high power supply voltage suppression ratio, overcome circuit oscillation, reduce effect of noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
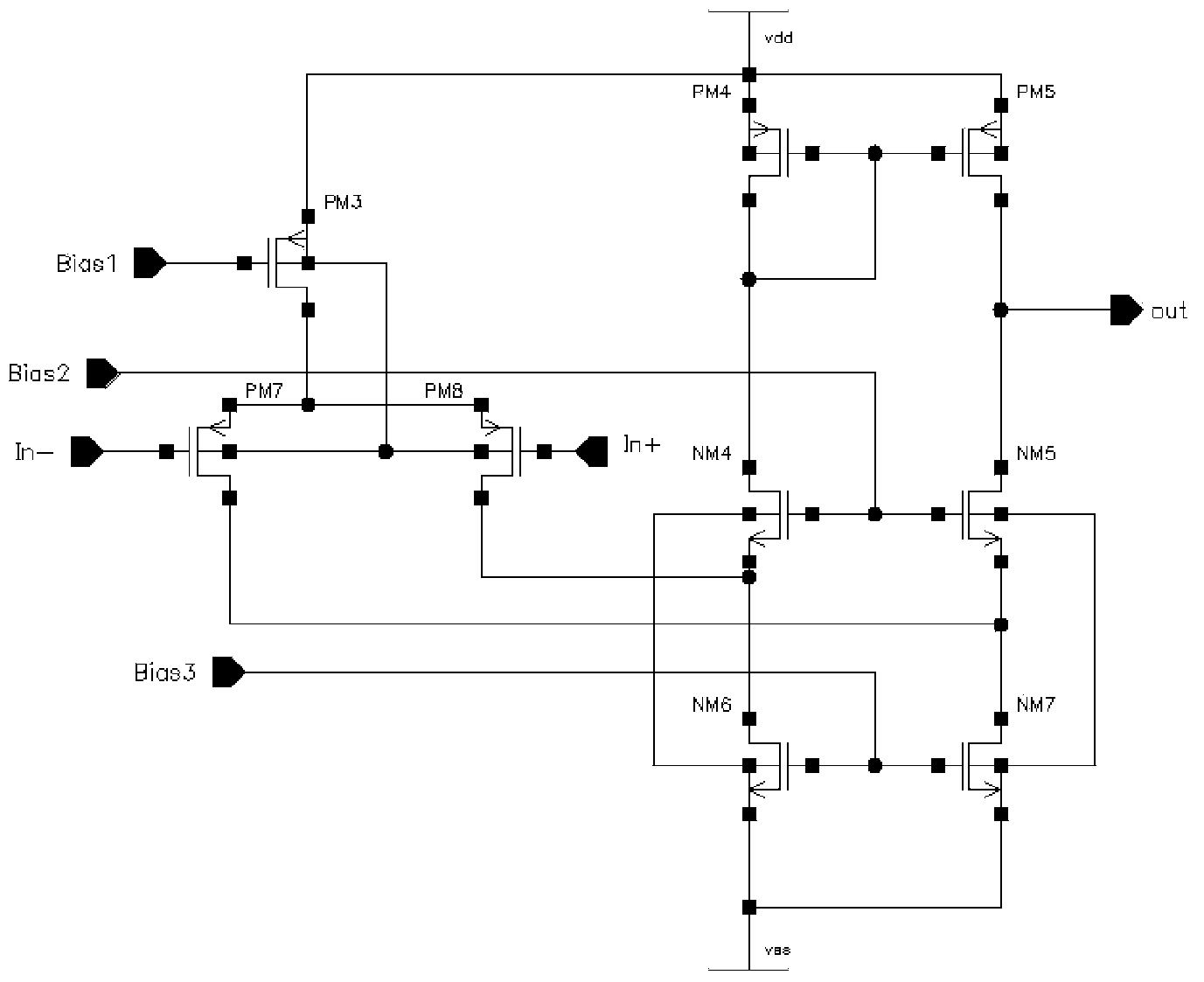
[0020] The total noise of this circuit is mainly determined by the input tubes PM7 and PM8, and the equivalent input noise voltage calculation formula is:
[0021] S v e ( f ) = 8 3 kT g m + K f C ox 2 WL 1 f (in g m = 2 K p W L I ds )
[0022] The first term is channel thermal noise and the second term is 1 / f noise.
[0023] g m For the transconductance of the input ...
Embodiment 2
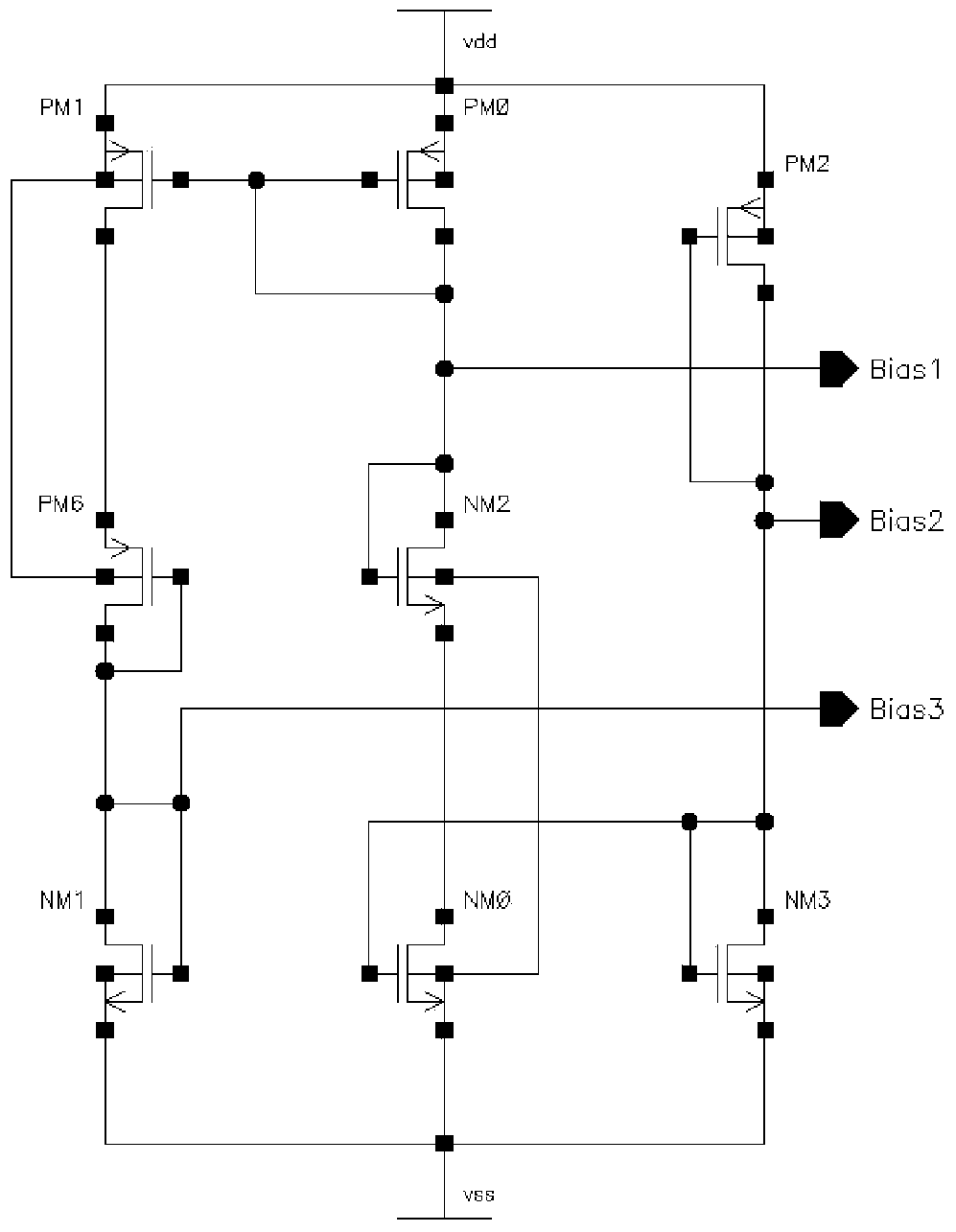
[0027] The bias circuit section of this low temperature low noise CMOS differential operational amplifier is as figure 2 As shown, NM3 and NM0 constitute the first-stage current mirror, PM0 and PM1 constitute the second-stage current mirror, NM1 and the NM6 and NM7 of the enlarged part constitute the current mirror, and PM0 and the PM3 of the enlarged part constitute the current mirror.
[0028] The bias part is composed of eight tubes. PM2 and NM3 connected by diodes form a reference current source. NM3 is mirrored to NM0 to generate one current, and then PM0 is mirrored to PM1 to generate another current. This current source does not use the pair Passive resistors that are particularly sensitive to temperature, so the current source can work normally at room temperature and low temperature. The test results show that the current source has a strong temperature suppression ability, so the entire low-temperature CMOS differential operational amplifier chip has a wide operating...
Embodiment 3
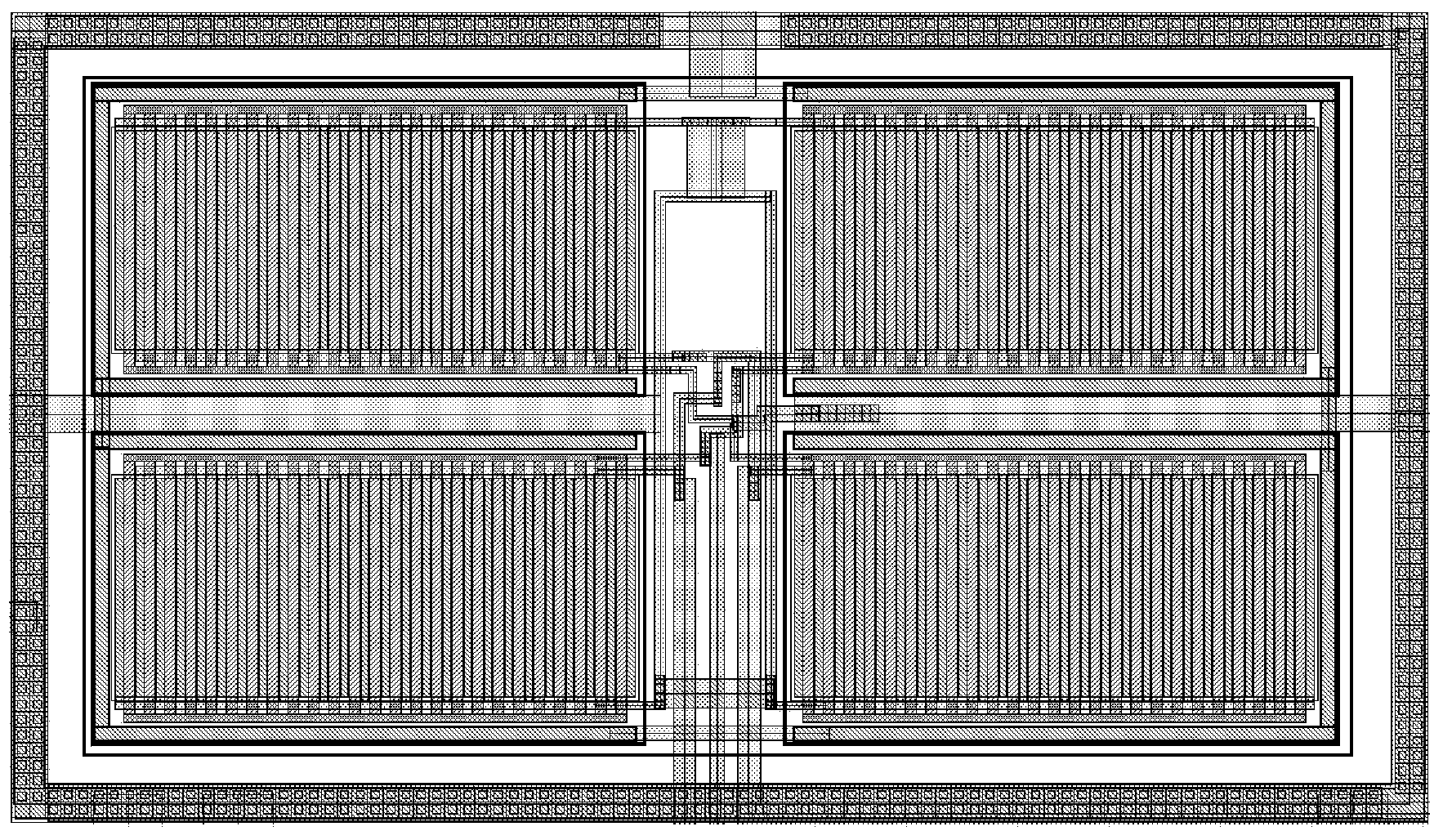
[0032] When drawing the layout of the amplifier, all pairs of tubes use interdigitated transistors, and try to ensure up-down and left-right symmetry, which can reduce the input offset of the CMOS differential operational amplifier at low temperature, especially the input tube of the differential amplifier, which is particularly important. In this circuit, since the differential input pair tube uses a large tube of 1500μm / 1.5μm, in order to achieve up-down and left-right symmetry, 72 41.7μm / 1.5μm tubes are used to form the input pair tube when drawing the layout, as shown in image 3 As shown, this greatly reduces the input offset of the entire differential operational amplifier, and the test results show that the input offset voltage of the low-temperature low-noise CMOS differential operational amplifier is very small, less than 1mV.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com