Molecular marker for detecting DNA methylation of cow mastitis resistance
A technology of molecular markers and methylation, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragments, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as few reports
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Detection of DNA Methylation Molecular Marker Methylation Levels Related to Chinese Holstein Mastitis Resistance
[0028] 1.1 Extraction of genomic DNA from the blood of Chinese Holstein cows to be tested
[0029] The blood of Chinese Holstein cows to be tested is collected from the tail vein, and placed at room temperature for 3-4 hours until the blood coagulates. At this time, the blood is divided into two parts: serum and clot. The serum is clear yellow, and the clot is dark red. Contains DNA, present in blood clots.
[0030] Use Tiangen Blood / Cell / Tissue Genomic DNA Sample Extraction Kit to extract genomic DNA from blood clots, the specific steps are as follows:
[0031] Use ophthalmic scissors to cut 0.2-0.3mL of clot into a sterilized 2mL round bottom centrifuge tube, add 500μL of cell lysate CL;
[0032] Fully homogenize the blood clot with a hand-held homogenizer, shake for 15s, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 1min, and discard the dark red supernatant in...
Embodiment 2
[0072] Example 2 Association analysis and detection application of methylation status of TRAPPC9 gene promoter region and mastitis resistance
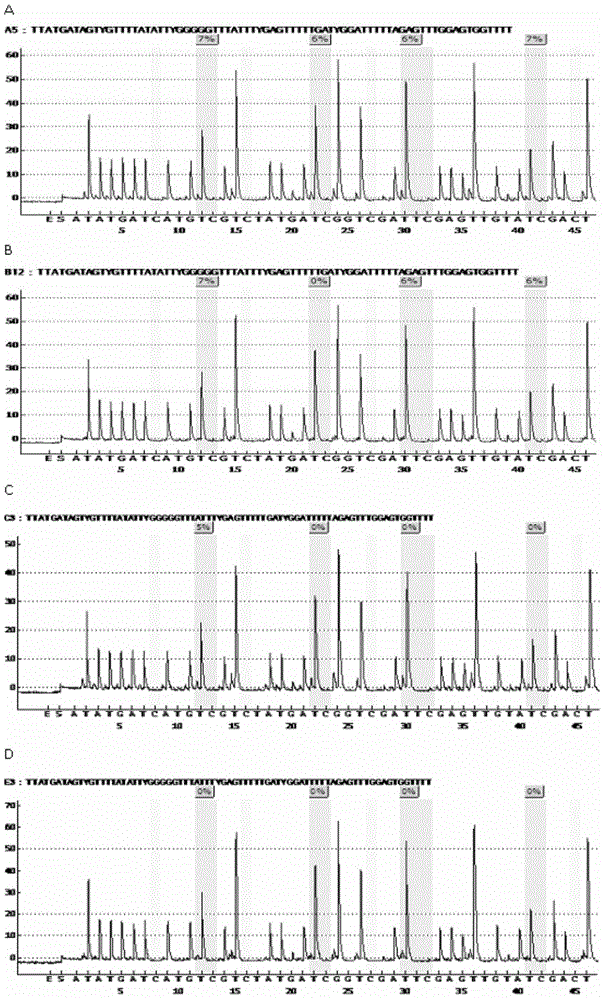
[0073] According to the method of Example 1, 152 Chinese Holstein dairy cows collected from different dairy farms in Beijing were tested for methylation status, and the test results were as follows: figure 1 As shown, it can be seen that each CpG site has a qualitative variation between methylation and unmethylation.
[0074] Using the GLM process of SAS 9.0 software to analyze the relationship between the methylation of each CpG site and the mastitis resistance of Chinese Holstein cattle, the adopted model is as follows:
[0075] y=μ+hys+p+m+e
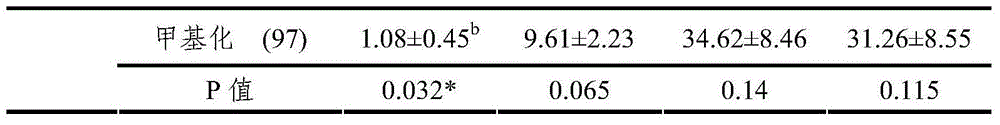
[0076] Among them, y is the phenotype value, μ is the population mean of the phenotype value, hys is the field year-season effect, p is the parity effect, m is the methylation effect, and e is the random residual effect. The analysis results are shown in Table 1.
[0077] Table 1 Correlatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com