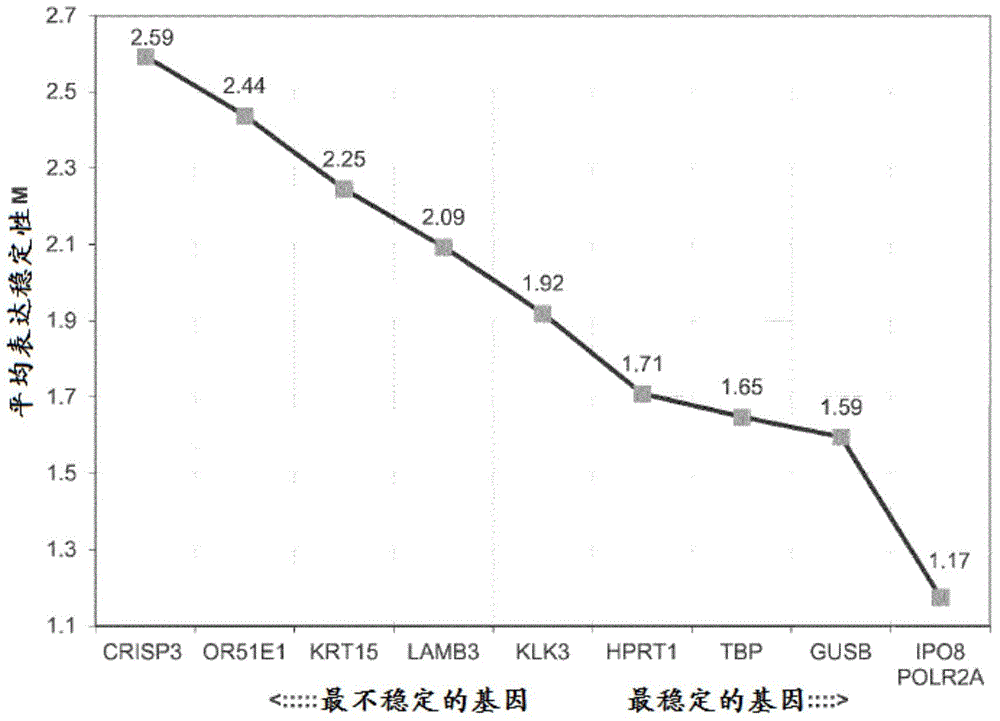
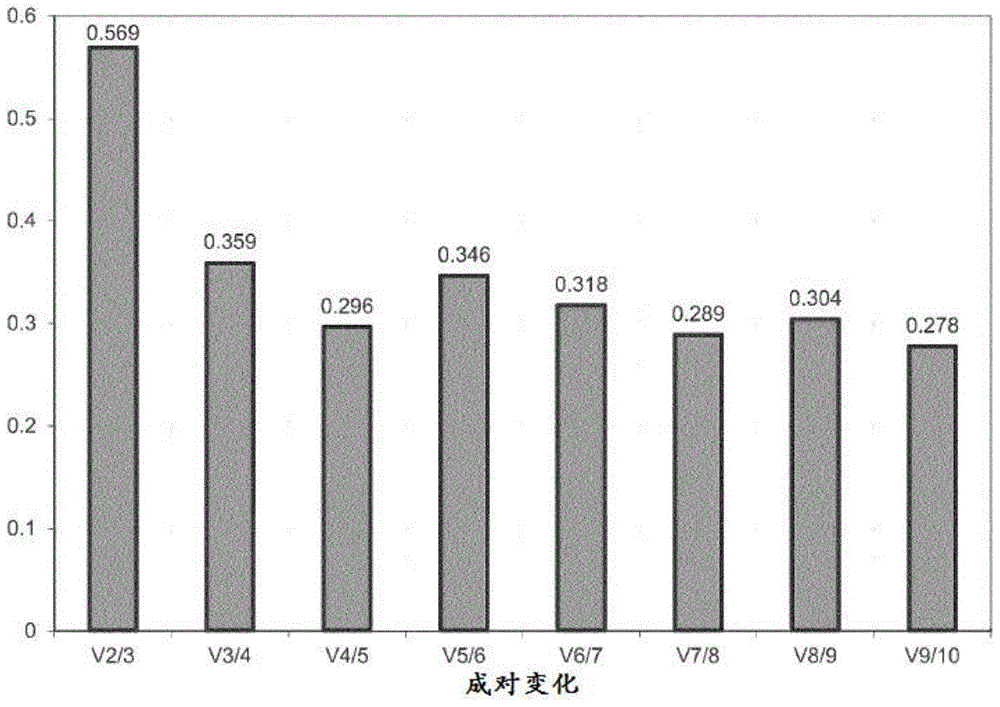
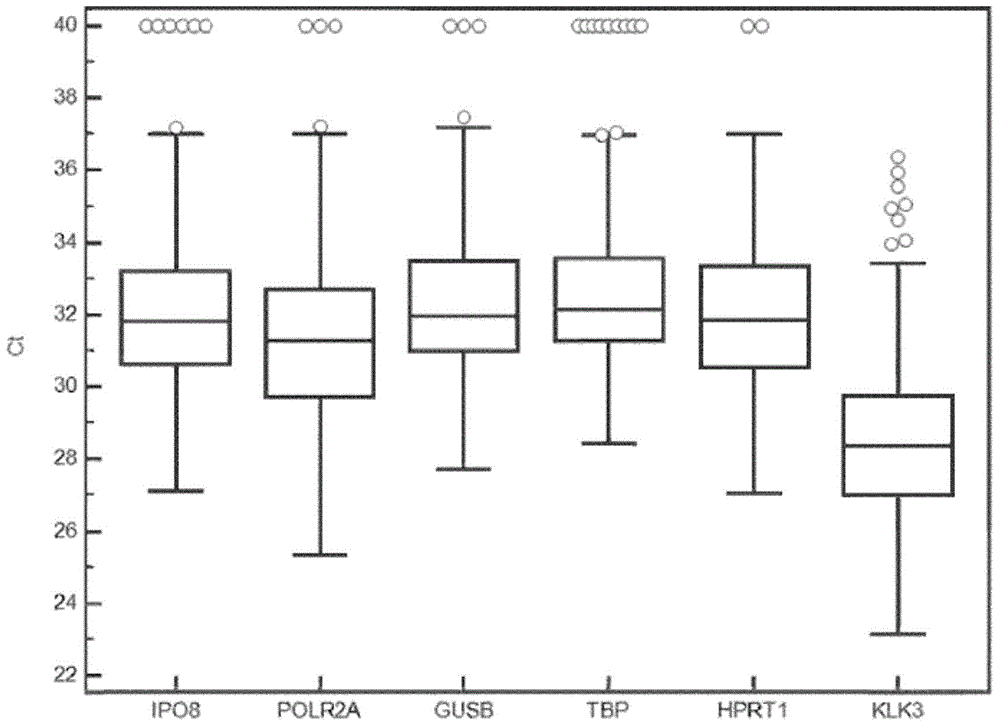
Methods, kits and compositions for providing a clinical assessment of prostate cancer
A prostate cancer and prostate-specific technology, applied in the field of prostate cancer signatures, can solve problems such as lack of effective control markers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0295] Gene expression profiling of whole urine samples
[0296] We determined the technical feasibility of gene expression profiling in whole urine samples from men with or suspected of having prostate cancer. Urine samples were collected from 90 men who underwent a digital rectal examination (DRE) prior to transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy, and the results of the biopsy were used to divide the subjects into two groups: (1) men with prostate cancer and (2) men without prostate cancer, with or without benign prostatic symptoms. Biopsy results were used to assign subjects to one of the two groups described above. Symptoms of benign prostate cancer include: benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HG-PIN), atypical small acinar proliferation (ASAP), and / or atypical prostate cells (Atypia). In all cases, the classification or stratification of samples was based on the interpretation of biopsies assessed by pathologists. ...
Embodiment 2
[0303] Gene expression profiling of urine sediment
[0304]On urine samples obtained after DRE from 77 subjects, the study described in Example 1 was repeated and the genes listed in Table 1 were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR, except that whole urine was not used, but instead Urine samples were centrifuged to pellet cells prior to nucleic acid extraction. The whole process took about 15 minutes in a clinical centrifuge at 2,500 rpm. The obtained urinary sediment containing epithelial cells from the urogenital tract was then extracted as described in Example 1. Table 3B provides the mean normalized expression values of normal subjects and cancer subjects and performance characteristics based on ROC curve analysis for each gene. Genes significantly associated with the presence of prostate cancer cells were either upregulated or downregulated. Genes whose expression levels differ significantly between normal subjects and prostate cancer subjects were determined to be use...
Embodiment 3
[0306] A machine-learning approach for studying genes significantly associated with prostate cancer
[0307] Here, we analyzed normalized gene expression data from 90 whole urine samples from Example 1 using machine learning to select and weight individual genes, gene pairs, or groups according to their ability to distinguish prostate cancer patients from non-prostate cancer individuals Gene. There are a number of different ways to combine genes individually to optimally separate a large number of data sources, one of which is to design class predictions (also known as classifiers) based on a preselected subset of genes. We supplemented this set of single gene signatures with a set of pairwise gene signatures obtained by taking the maximum of two ΔCts (eg "maxERG CACNA1D") or by subtracting the ΔCts of two pairs of genes (eg ERG-SNAI2). Although some selected genes were found to be associated with cancer and / or prostate in Examples 1 and 2, their association with the prosta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com