Method for recognizing slag variety by combining with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy based on least squares support vector machine
A laser-induced breakdown and support vector machine technology, applied in the field of spectral analysis, can solve problems such as time-consuming, limited real-time rapid analysis, and inability to quickly obtain steel product quality information, so as to overcome interference, improve prediction accuracy, and tolerate degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
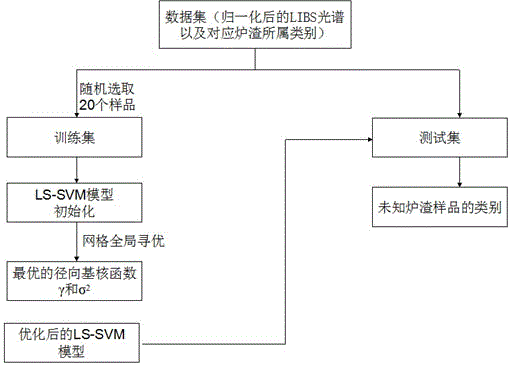
[0020] The LIBS system used in this example includes a dual-wavelength Q-switched single-pulse Nd:YAG laser, an optical system, an adjustable three-dimensional sample stage, an echelle spectrometer (ARYELLE-UV-VIS, LTB400, German) and a computer. The laser energy is 80mJ, the fundamental frequency light wavelength is 1064 nm, the pulse width is 10 ns, the delay time is 1.5 μs, the repetition frequency is 5 Hz, and the spectral range is 220nm-800nm.
[0021] Three kinds of slags (blast furnace slag, converter slag, and flat furnace slag) were selected, and a total of 30 slag samples were used. For the convenience of testing, each slag sample was ground to 200 mesh with a ball mill, and then each sample was pressed into a thin sheet about 2mm thick, with a pressure of 400MPa and last for 5min.
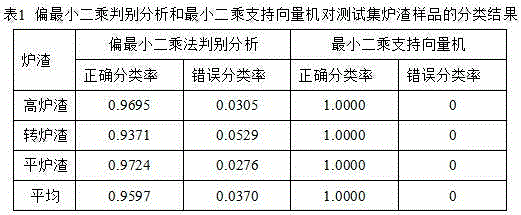
[0022] The LIBS signals of different slag samples were collected by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy. Randomly select 50 measurement points for each slag sample, obtain a measuremen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com