A Method of Evapotranspiration Data Assimilation Based on Distributed Time-varying Gain Hydrological Model
A time-varying gain and hydrological model technology, applied in the field of evapotranspiration estimation, can solve the problems of underestimation of evapotranspiration, accumulation of precision errors, and low precision, and achieve the effects of easy operation, reduced uncertainty, and optimized model simulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029]The technical solution of the present invention will be further specifically described below through specific implementation examples and in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
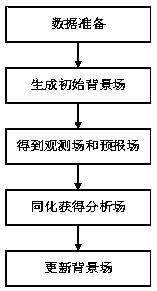
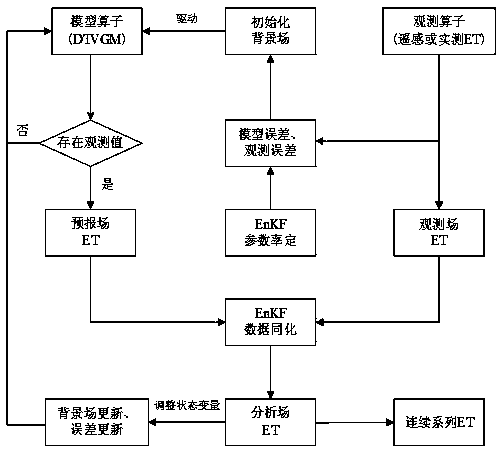
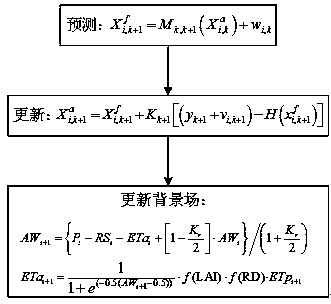
[0030] as attached figure 1 with 2 As shown, a method for assimilating evapotranspiration data based on a distributed time-varying gain hydrological model includes the following steps:
[0031] Step 1, data preparation:
[0032] The daily evapotranspiration of the watershed is obtained as the "observation" of the assimilation system through the inversion of the remote sensing model of evapotranspiration (flux observation data). By calibrating the parameters of the distributed time-varying gain hydrological model, the parameters are optimized to obtain a model with simulation stability. Hydrological model as a model operator;
[0033] Step 2, generate the initial background field:
[0034] On the basis of calibrating the parameters of the distributed time-varying gain hydrological mod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com