Highlight and high-purity water solubility fluorescent molecules and preparing method thereof
A fluorescent molecule and water-soluble technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of high price, achieve low price, low biological toxicity, and facilitate the effect of modification and coupling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Weigh 0.192 g (1 mmol) of citric acid solid powder and dissolve it in 10 mL of deionized water, add 67 μL (1 mmol) of ethylenediamine into the aqueous citric acid solution, and stir evenly with a glass rod. The above solution was transferred to a 20 mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel reaction kettle, the lid of the kettle was tightened, and the reaction was carried out at 140° C. for 6 hours. After the reaction is completed, the reaction kettle is naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain a fluorescent aqueous solution.
[0040] The obtained fluorescent aqueous solution was separated by column chromatography, and the developer was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain IPCA solid. The developer used is a mixed solution of methanol and ethyl acetate, and the volume content of methanol in the mixed solution is 50% to 100% (100% methanol content means that methanol alone can be used as a developer). If the proportion of methanol is low (volume ratio le...
Embodiment 2
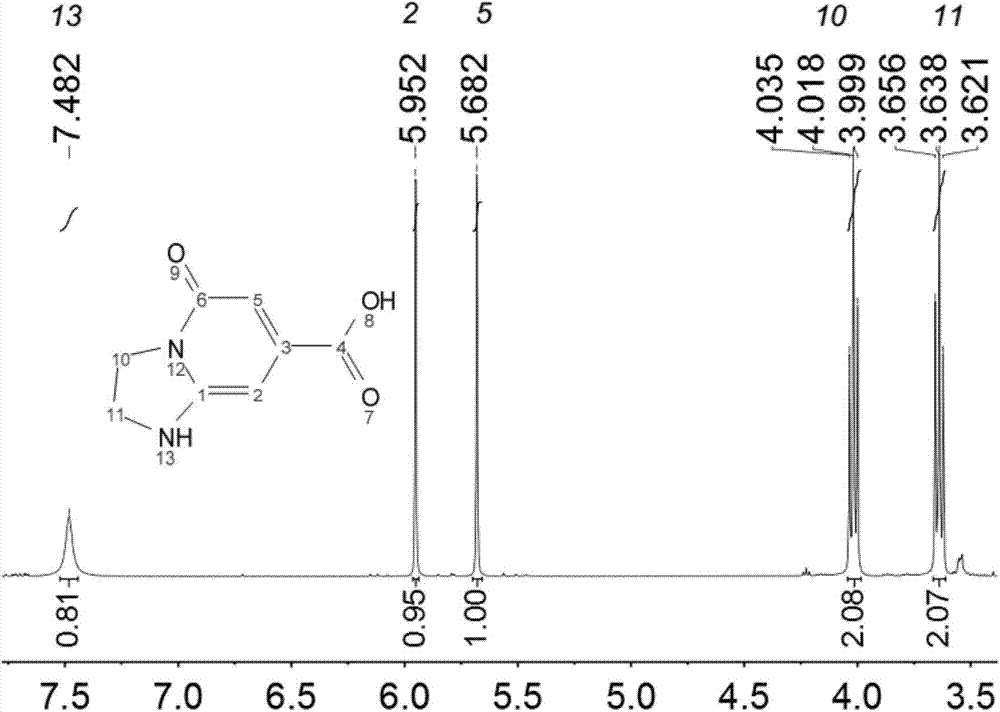
[0048] Weigh 0.192 g (1 mmol) of citric acid solid powder and dissolve it in 10 mL of deionized water, add 67 μL (1 mmol) of ethylenediamine into the citric acid solution, and stir evenly with a glass rod. The liquid was transferred to a 20mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel reaction kettle, the lid of the kettle was tightened, and the reaction was carried out at 140°C for 6 hours. After the reaction is completed, the reaction kettle is naturally cooled to room temperature to obtain a fluorescent aqueous solution. Ethyl acetate was selected as the extractant, and the fluorescent aqueous solution was extracted, and the extractant was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain IPCA solid. From the NMR spectrum ( Figure 9 ) analysis, the product of the present embodiment and the IPCA proposed by column chromatography have the same nuclear magnetic signal peak, and there are few miscellaneous peaks, which proves that the sample purity is higher, and the productive rate...
Embodiment 3
[0050] As in Example 1, the fluorescent aqueous solution can also be obtained by changing the feed ratio / hydrothermal temperature / hydrothermal time during synthesis. When other conditions remain unchanged, such as changing the feeding ratio (the molar ratio of acid / amine is changed between 0.25 and 4:1), the properties of the fluorescent aqueous solution are changed ( Figure 10 ). As the proportion of acid increases, the fluorescence quantum yield of the sample gradually decreases; at the same time, if the proportion of acid is too low, the absorption value of the sample decreases, which means that the reaction yield decreases. In summary, it is considered that the feeding ratio of 1:1 is more appropriate.
[0051] Such as changing the water temperature (between 100 and 200°C, Figure 11 ), the quantum yield of the obtained product decreases gradually with the increase of the reaction temperature. At the same time, we found that when the hydrothermal temperature is 150°C, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com