Method of manufacturing semiconductor device
A manufacturing method and semiconductor technology, which can be applied to semiconductor lasers, light guides, structures of active regions, etc., and can solve problems such as limiting the thickness of compound semiconductor layers.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
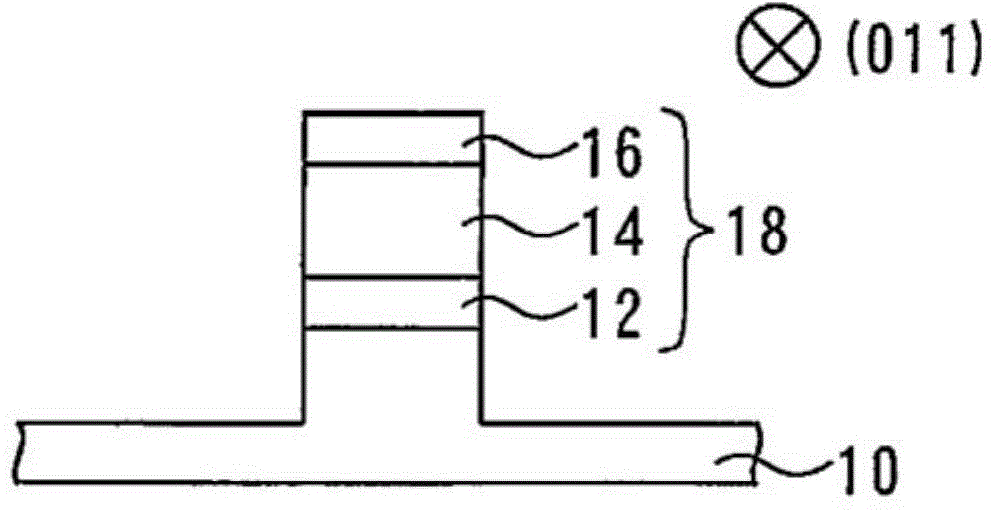
[0039] According to the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, a semiconductor device having a compound semiconductor layer functioning as a current blocking layer on the left and right of the laser portion having a raised stripe shape is formed. First, a laser portion is formed. figure 1 is a cross-sectional view showing the laser unit 18 . Substrate 10 is formed of InP. An active layer 12 is formed at a portion of the substrate 10 . The active layer 12 is formed as a multiple quantum well structure in which InGaAs quantum well layers and InGaAs barrier layers are stacked alternately and repeatedly. An upper semiconductor layer 14 made of InP is formed on the active layer 12 .
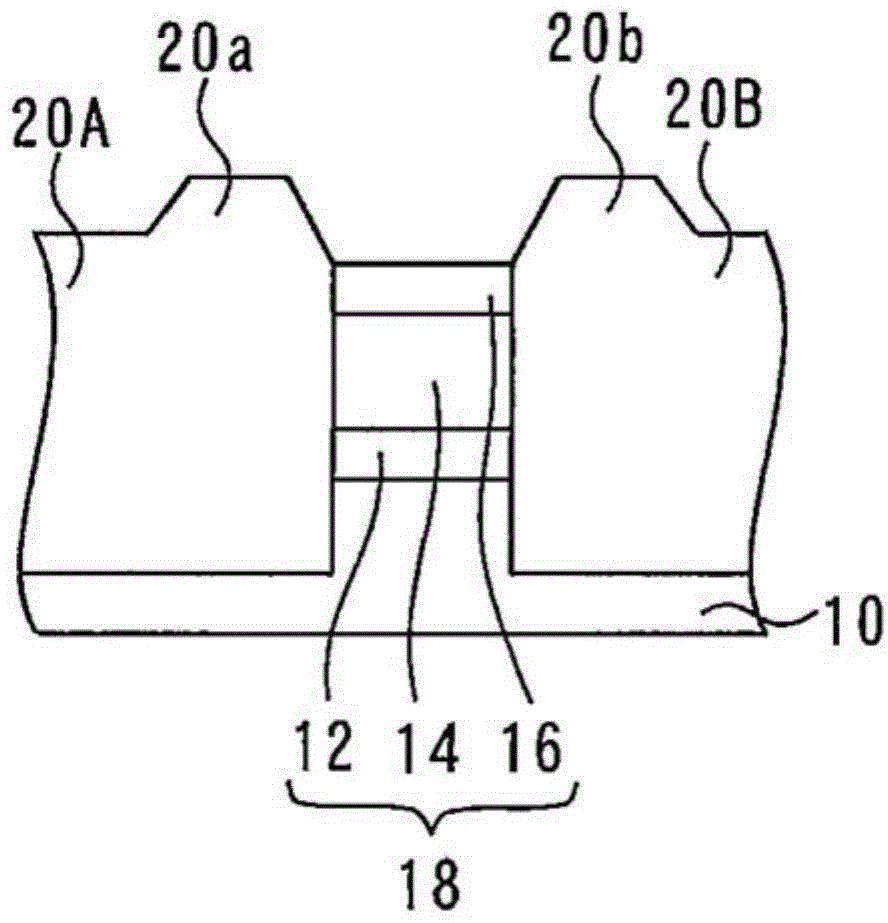
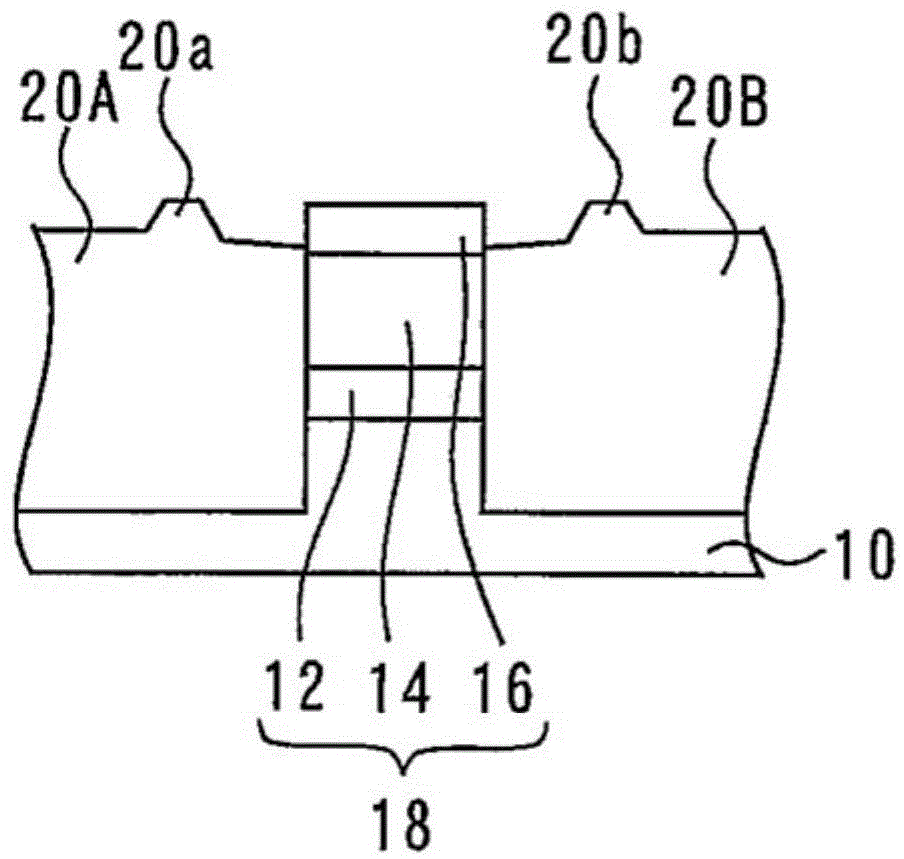
[0040] A mask 16 is formed on the upper semiconductor layer 14 . Mask 16 is formed of InGaAs. The active layer 12 , the upper semiconductor layer 14 , and the mask 16 constitute a laser section 18 . will form figure 1 The process of th...
Embodiment approach 2
[0073] In Embodiment 1, a current blocking layer is formed as a compound semiconductor layer, but in Embodiment 2, an optical modulator is formed as a compound semiconductor layer. That is, the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to Embodiment 2 is a method of manufacturing a laser diode with an optical modulator. First, through the laser portion forming process, a Figure 10 The laser section 18 is shown.
[0074] Then, through the semiconductor layer forming process, a Figure 11 The compound semiconductor layer 60 is shown. The compound semiconductor layer 60 constitutes an optical modulator in contact with the (011) plane or the (0-1-1) plane of the laser unit 18 . The compound semiconductor layer 60 has a cladding layer 62 formed on the substrate 10 , an active layer 64 formed on the cladding layer 62 , and a cladding layer 66 formed on the active layer 64 . These layers are formed by the MOCVD method, and therefore, convex portions 66 a are forme...
Embodiment approach 3
[0080] In the method of manufacturing a semiconductor device according to Embodiment 3, a laser diode, an optical modulator, and an optical waveguide are formed on a substrate. First, through the laser portion forming process, a Figure 14 The laser section 18 is shown. Then, the light modulator 100 is formed on the substrate 10 . The optical modulator 100 has a mask 102 formed of InGaAs on the uppermost layer.
[0081] Then, through the semiconductor layer forming process, a Figure 15 The compound semiconductor layer 104 is shown. The compound semiconductor layer 104 is in contact with the (011) plane or the (0-0-1) plane of the laser portion 18 , and is in contact with the (011) plane or the (0-0-1) plane of the optical modulator 100 . The compound semiconductor layer 104 has a cladding layer 106 made of InP, an active layer 108 made of InGaAsP / InGaAsP formed on the cladding layer 106 , and a cladding layer 110 made of InP formed on the active layer 108 . The compound ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com