Aptamer electrochemical sensor used for kanamycin A detection and production and application methods of aptamer electrochemical sensor
A technology of nucleic acid aptamer and kanamycin, which is applied in the field of biological analysis, can solve problems such as the influence of test results and the need to verify the tolerance, and achieve the effect of simple design and strong versatility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
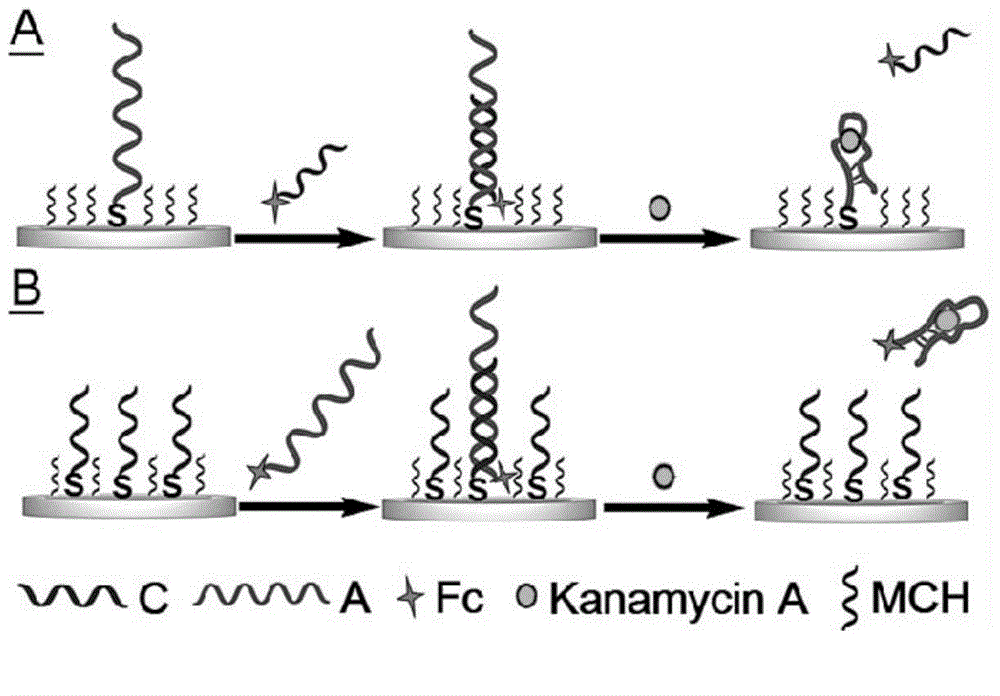
[0034] Embodiment 1: the two-step method preparation of SD-EAB A and B that is used for kanamycin A detection.
[0035] SD-EAB A( figure 1 A ) preparation: 1 μM capture probe 1 (A-SH) and 100 μM TCEP in buffer A (10 mM phosphate buffer, 1 M NaCl, 5 mM MgCl 2 , pH 7.0), mix well, and let stand for reduction for 1 hour. Immerse the clean electrode in the reducing solution, place it at 37°C, and react overnight. Wash with buffer B (10mM phosphate buffer, 1M NaCl, pH 7.0) three times, and then put into 2mM MCH for blocking at 37°C for 1 hour. After washing with buffer B three times, it was immersed in buffer A containing 0.5 μM signal probe 2 (C-Fc) and incubated at 37° C. for 2 hours, and washed with buffer B three times. The prepared sensor was stored in the hybridization solution at 4°C for future use.
[0036] SD-EAB B( figure 1 B ) preparation: the above capture probe 1 (A-SH) was replaced with capture probe 3 (C-SH), the above signal probe 2 (C-Fc) was replaced with s...
Embodiment 2
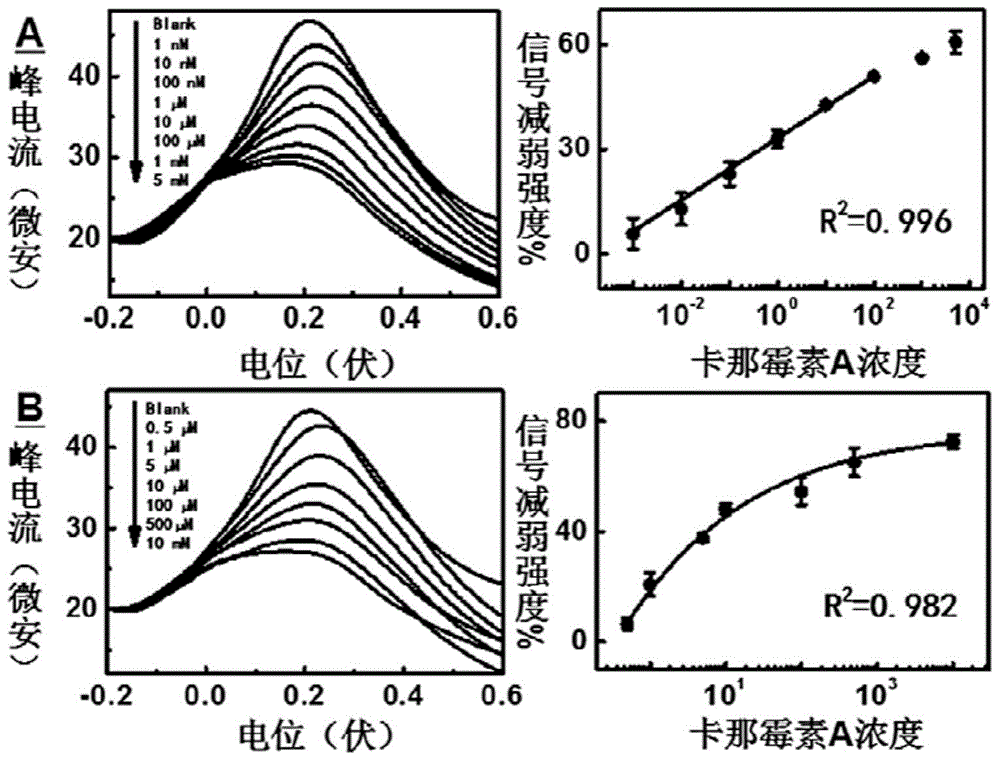
[0037] Embodiment 2: Utilize SD-EAB A and SD-EAB B to detect the kanamycin of different concentrations respectively.
[0038] Use electrochemical equipment to scan the two sensors with square wave voltammetry, and measure the oxidation peak corresponding to ferrocene near 0.2V. Detection of Namycin A. Kanamycin A was detected by SD-EAB A and SD-EAB B, respectively. get results like figure 2 As shown, the kinetic interval of the SD-EAB A sensor in the present invention is 1 nM to 10 mM, which is 2-5 orders of magnitude wider than that of the kanamycin A sensor reported in the prior art. The logarithm of the concentration of Kanamycin A has a good linear relationship with the corresponding current change in the range of 1nM to 100μM, the correlation coefficient is 0.996, and the detection limit is 1nM, which is better than other kanamycins based on nucleic acid aptamers reported. The A sensor is 5-10 times more sensitive, comparable to immunological and spectroscopic methods...
Embodiment 3
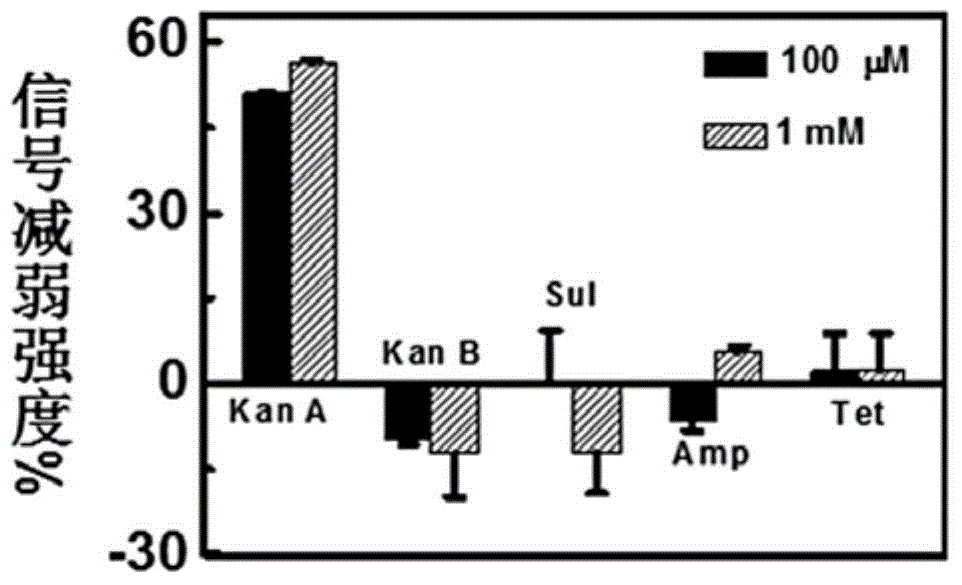
[0039] Embodiment 3: SD-EABA among the present invention is carried out target selectivity assay.
[0040] Antibiotics with similar or completely different chemical structures to kanamycin A were tested with SD-EAB A in the same manner. SD-EAB A has excellent selectivity to the structural analog of kanamycin A (kanamycin B) and other types of antibiotics including ampicillin, sulfidexoxine and tetracycline. When the concentration of the antibiotic tested was 100 μM, the corresponding current signal decreases were: kanamycin A 51.2%, sulfidesoxine 0±9.4%, tetracycline 2.2±6.8%. In the presence of kanamycin B and ampicillin, an increase in the current signal was detected, corresponding to an increase in the current signal of 9.8±1.0% and 6.6±1.6%, respectively. Even at a high concentration (1 mM), SD-EAB still has a high degree of specific recognition for kanamycin A.
[0041] When SD-EAB A interacts with kanamycin A and its structural analogue kanamycin B, it shows completely...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com