Heat treatment method for strength of 28CrMoNiV steel capable of improving industrial steam turbine rotor forge piece
A heat treatment method and technology of industrial steam turbines, applied in the field of production of industrial steam turbine steel forgings, can solve problems such as insufficient strength and unsatisfactory use, and achieve the effect of reducing residual stress
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
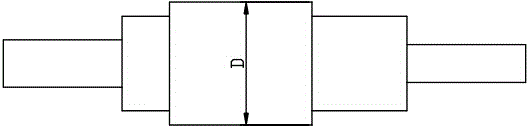
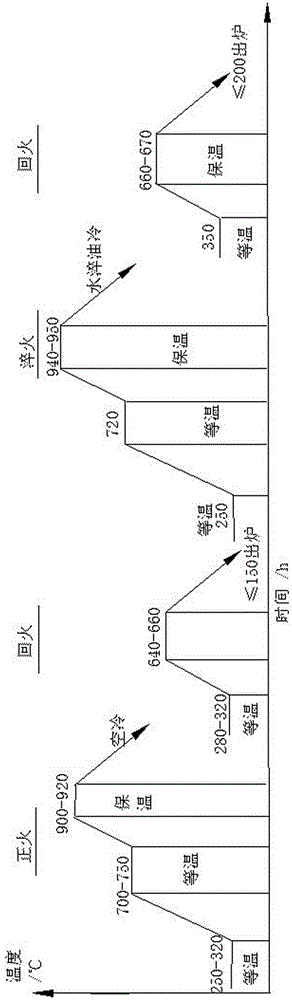
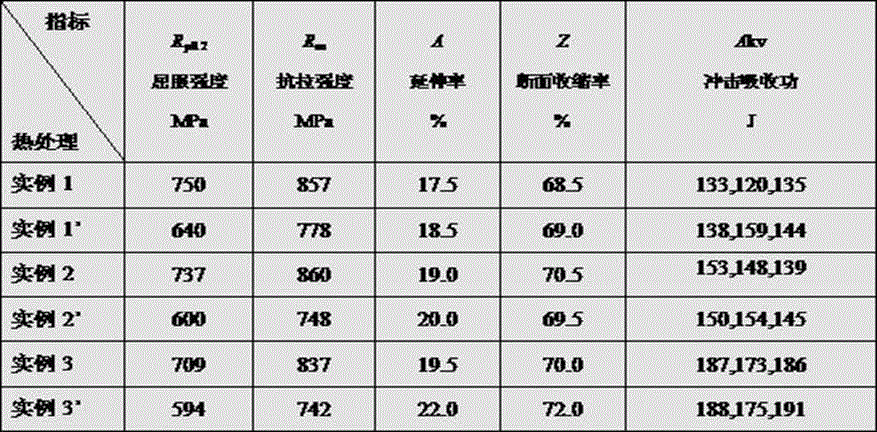
[0018] Embodiment 1: as figure 1 As shown, the heat treatment method described in this example to improve the strength of 28CrMoNiV steel for industrial steam turbine rotor forgings uses a shaft diameter of 400 mm, a chemical composition of C: 0.25-0.30%, Si: ≤0.30%, Mn: 0.30-0.80%, P: ≤0.012%, S: ≤0.012%, Cr: 1.10~1.40%, Ni: 0.50~0.75%, Mo: 0.80~1.00%, V0.25~0.35%, Cu: ≤0.20%, Al: ≤0.01 %, the rest is Fe; the steel type is a forging of 28CrMoNiV. The heat treatment process is carried out by normalizing + tempering + quenching and tempering, such as figure 2 As shown, normalize first, and preheat for 10 hours at a preheating temperature of 250-320°C. Normalizing heating adopts a staged heating method, and the first stage is from 250-320°C to no more than 60°C / h Heating to a temperature of 700-750°C, holding for 3 hours after reaching the temperature, heating to 900-920°C in the second stage, holding time for 8 hours, and air-cooling to 320-380°C when out of the furnace; At...
Embodiment 2
[0019] Example 2: The heat treatment method described in this example to improve the strength of 28CrMoNiV steel for industrial steam turbine rotor forgings, the shaft diameter is 500mm, the chemical composition is C: 0.25-0.30%, Si: ≤0.30%, Mn: 0.30-0.80% , P: ≤0.012%, S: ≤0.012%, Cr: 1.10~1.40%, Ni: 0.50~0.75%, Mo: 0.80~1.00%, V0.25~0.35%, Cu: ≤0.20%, Al: ≤ 0.01%, the rest is Fe; the steel type is 28CrMoNiV forgings. The heat treatment process is carried out by normalizing + tempering + quenching and tempering, such as figure 2 As shown, normalize first, and preheat for 10 hours at a preheating temperature of 250-320°C. Normalizing heating adopts a staged heating method, and the first stage is from 250-320°C to no more than 60°C / h Heating to a temperature of 700-750°C, and keeping it warm for 3 hours after reaching the temperature, the second stage is rapidly heated to 900-920°C, the holding time is 10 hours, and air-cooled to 320-380°C after being out of the furnace; At ...
Embodiment 3
[0020] Example 3: The heat treatment method described in this example to improve the strength of 28CrMoNiV steel for industrial steam turbine rotor forgings uses a shaft diameter of 600 mm and a chemical composition of C: 0.25-0.30%, Si: ≤0.30%, Mn: 0.30-0.80% , P: ≤0.012%, S: ≤0.012%, Cr: 1.10~1.40%, Ni: 0.50~0.75%, Mo: 0.80~1.00%, V0.25~0.35%, Cu: ≤0.20%, Al: ≤ 0.01%, the rest is Fe; the steel type is 28CrMoNiV forgings. The heat treatment process is carried out by normalizing + tempering + quenching and tempering, such as figure 2As shown, normalize first, and preheat for 10 hours at a preheating temperature of 250-320°C. Normalizing heating adopts a staged heating method, and the first stage is from 250-320°C to no more than 60°C / h Heating to a temperature of 700-750°C, and keeping it warm for 3 hours after reaching the temperature, the second stage is rapidly heated to 900-920°C, and the holding time is 12 hours, and air-cooled to 320-380°C after being out of the furnac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com