Forward-flyback topology switched mode power supply
A switching mode power supply and current technology, which is applied in the direction of electronic switches, electrical components, and adjustment of electrical variables, can solve the problems of increasing the number of components and manufacturing costs, and achieve the effect of reducing resistance loss and capacitive coupling loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
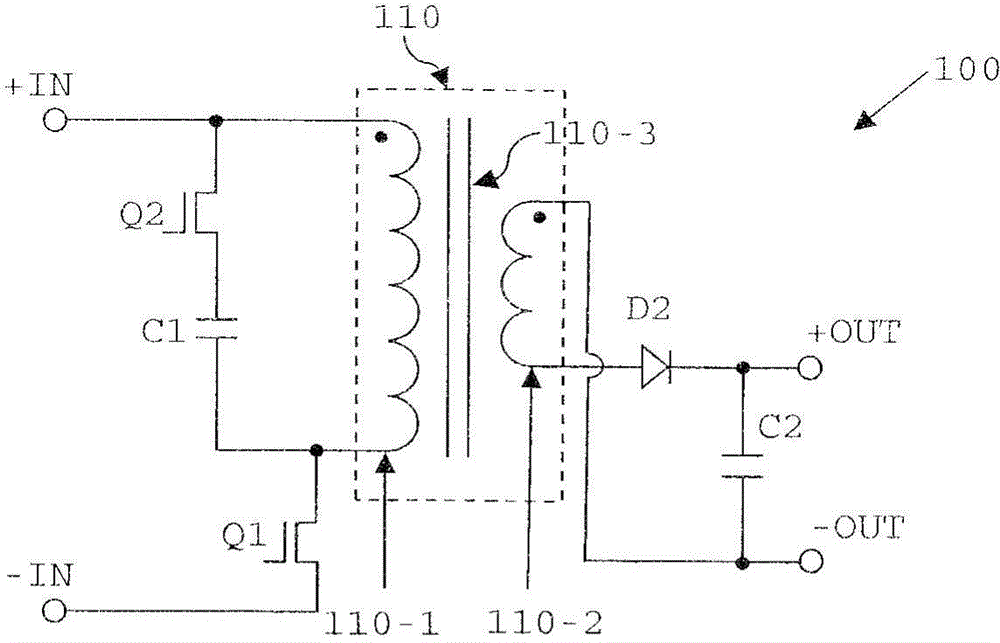
[0044] Figure 4A A switched mode power supply according to a first embodiment of the invention is shown. Figure 4A The SMPS 400 shown in has a forward-flyback topology converter with an active clamp on the primary side. For example, the SMPS of this embodiment can be used to enable a radio frequency power amplifier (RFPA) to deliver an output voltage of 10-32V or 17-32V.
[0045] More specifically, the flyback converter 400 includes a flyback transformer 410 having a primary winding 410-1 and a secondary winding 410-2 with Turns ratio N=n p / n s Wound transformer core 410-3, where n p and n s are the turns of the primary winding 410-1 and the secondary winding 410-2, respectively. Transformer core 410-3 may be formed from any suitable material (including, for example, powdered iron or other material with high magnetic permeability), and may be shaped such that transformer 110-3 has The gap (for example, an air gap) of the magnetizing energy provided.
[0046] The pr...
Embodiment 2
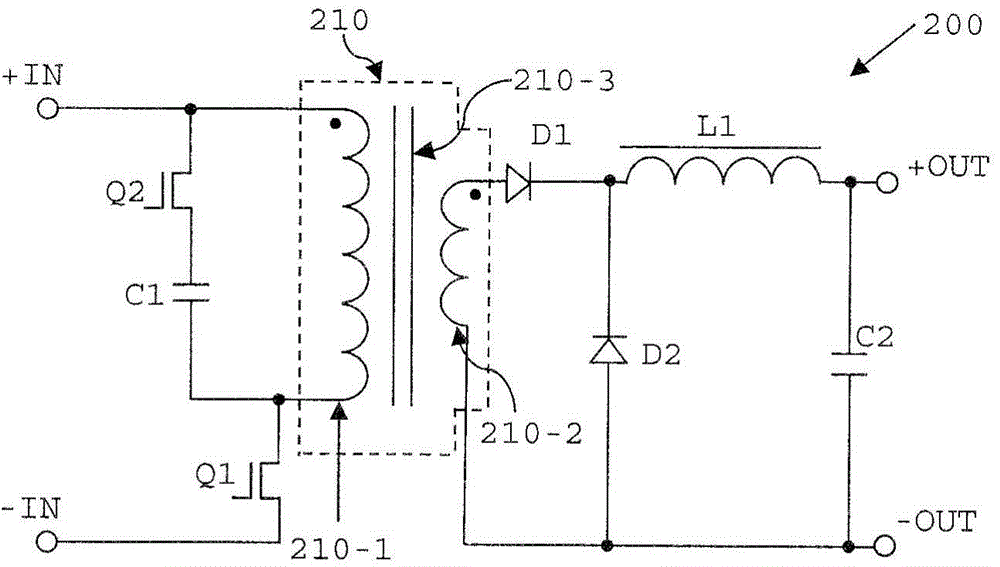
[0063] will now refer to Figure 7A and Figure 7B A switched mode power supply according to a second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0064] Figure 7A The SMPS 500 shown in FIG. 2 differs from the SMPS 400 of the first embodiment only in that the cathodes of diodes D1 and D2 are connected to opposite ends of inductor L1. Therefore, with Figure 4A Contrary to the SMPS 400, the cathode of the diode D2 is connected to the output terminal +OUT of the SMPS 500 instead of being indirectly connected to +OUT through the inductor L1. In this alternate embodiment, power is delivered to the output of the SMPS through Q4 and D2 (while bypassing choke L1) during the flyback phase, and power is delivered to the output of the SMPS via choke L1 during the forward phase. output. Routing current on the secondary side to bypass choke L1 can provide the advantage of reducing losses during the flyback phase.
[0065] The switched-mode power supplies of the first an...
Embodiment 3
[0067] will now refer to Figure 8A and 8B A switched mode power supply according to a third embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0068] Figure 8A The SMPS 600 shown in , differs from the SMPS 400 of the first embodiment only in that it is provided in the form of synchronous rectifiers Q5 and Q6 instead of the passive rectifiers of SMPS 400 (i.e., diodes D1 and D2). High-side rectifier on the secondary side. The switched-mode power supplies of the first and third embodiments are otherwise identical, and repeated descriptions will be omitted for simplicity.
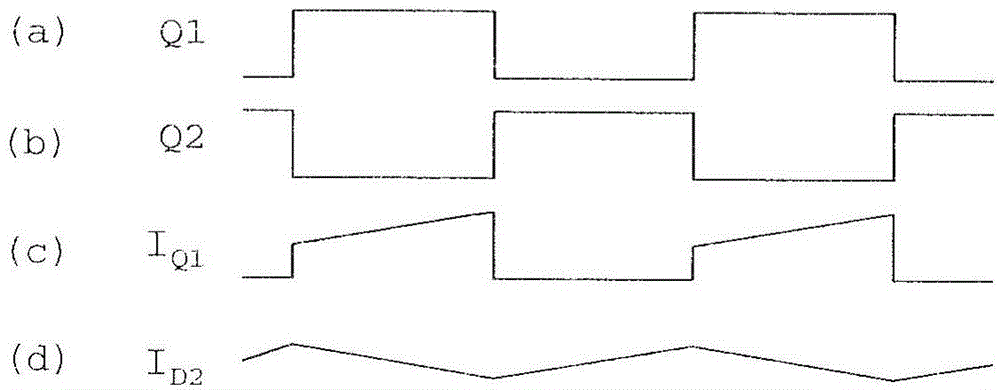
[0069] The SMPS 600 of the third embodiment operates in the same manner as the first embodiment, except for the above-mentioned fully synchronous rectification provided on the secondary side, as Figure 8B The trajectories (a) to (e) in are shown. More specifically, a control signal generator (not shown) may be provided on the primary or secondary side of the transformer 410 for generating signals...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com