Method used for removing antibiotics in breeding industry wastewater via anaerobic self-electrolysis
A technology for breeding wastewater and antibiotics, which is applied in the field of environmental pollution biological treatment and bioenergy, can solve the problems of pollution load, large animal antibiotics, and difficulty in breeding wastewater, and achieves mild operating conditions, low maintenance costs, and strong safety. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] A method for removing antibiotics by anaerobic self-electrolysis of aquaculture wastewater, the specific operation steps are as follows:
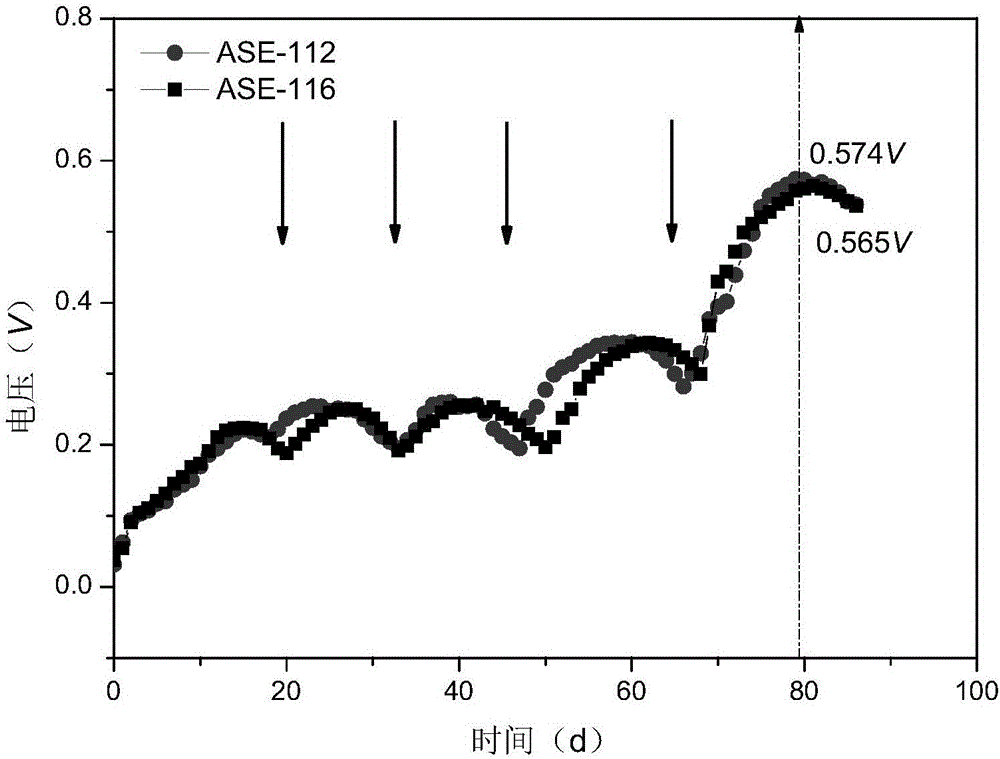
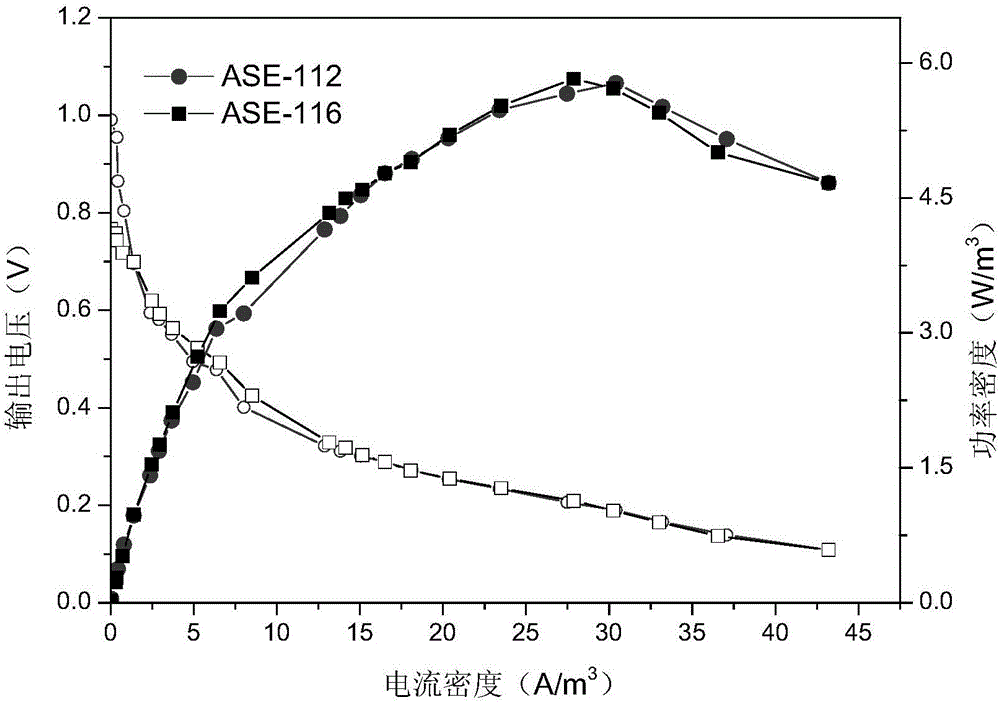
[0030] (1) Mix the simulated aquaculture wastewater and the anaerobic granular sludge supernatant at a volume ratio of 1:1, and start the anaerobic self-electrolysis reactor in batch mode under the conditions of external resistance 1000Ω and constant temperature of 30±1°C. The anaerobic self-electrolysis reactor mainly consists of two parts with a total volume of 1200mL. The upper part is a cylindrical glass tube, the outer wall of the glass tube has a small hole with a diameter of 1mm, and the opening rate is 15%, the lower part is an inverted cone, the bottom of the cylinder is provided with a water inlet, and the top side is provided with a water outlet. The outlet diameter is about 4mm. The inner side of the reactor constitutes the anode chamber, and the outer side is wrapped with cation exchange membrane and cathode material in...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The antibiotic removal status of four different antibiotics in the anaerobic self-electrolysis system and the impact on the anaerobic self-electrolysis of aquaculture wastewater, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0042] (1) Under the conditions of an external resistance of 1000Ω and an operating temperature T of 30±1°C, the reactor is operated in a continuous flow mode, and the output voltage is continuously stable for at least three HRTs;
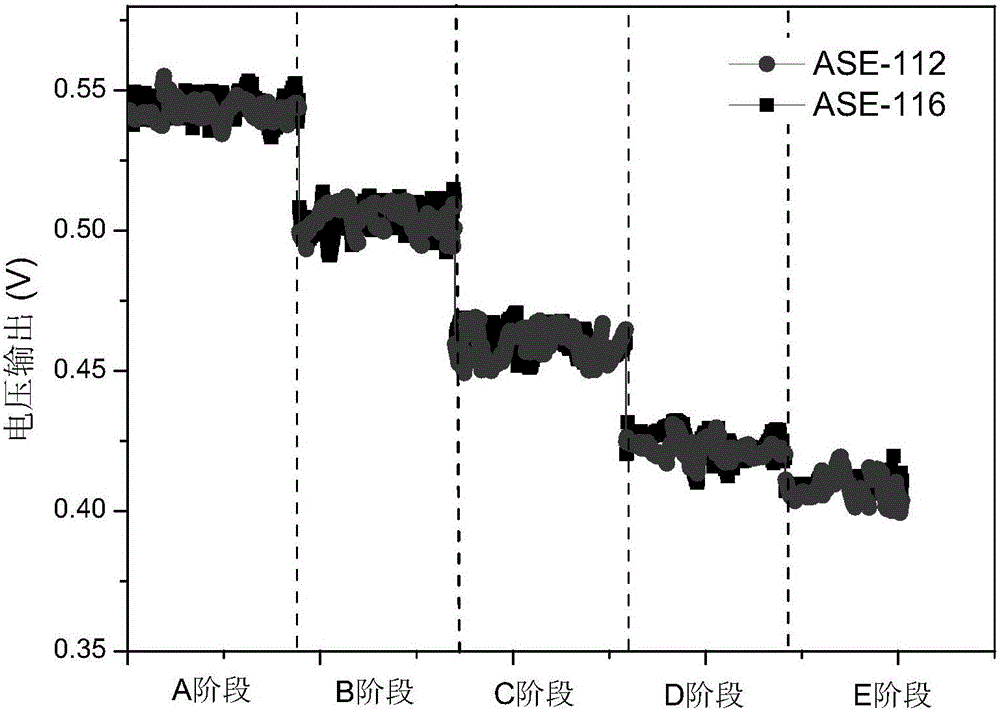
[0043] (2) Four typical aureomycin (tetracyclines), sulfamethazine (sulfonamides), roxithromycin (macrolides), norfloxacin (fluoroquinolones) Add exogenous antibiotics to the artificial simulated breeding wastewater, run the anaerobic self-electrolysis reactor on the artificial simulated breeding wastewater without antibiotics as stage A; The self-electrolysis reactor is stage B; the anaerobic self-electrolysis reactor is stage C with the artificial simulated breeding wastewater containing aureomycin (15 μg / L) and ...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The removal of antibiotics with different concentration gradients in the anaerobic autoelectrolysis system and the effect on the anaerobic autoelectrolysis of simulated aquaculture wastewater, the specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0061] (1) Under the conditions of an external resistance of 1000Ω and an operating temperature T of 30±1°C, the reactor is operated in a continuous flow mode, and the output voltage is continuously stable for at least three HRTs.
[0062] (2) The four types of antibiotics with three different concentration gradients of high, medium and low were sequentially added to the simulated aquaculture wastewater as influent. Among them, the artificial simulated breeding wastewater without antibiotics is run in an anaerobic self-electrolysis reactor as stage A; / L) and norfloxacin (18μg / L) artificially simulated breeding wastewater to run the ASE reactor as stage F, with aureomycin (15μg / L), sulfamethazine (10μg / L), erythromycin The ASE r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com