Method for obtaining extracellular water-soluble monascus yellow pigment through high-carbon source fermentation and application of method
A monascus yellow pigment and water-soluble technology, applied in the field of Monascus fermentation, can solve the problems of no market report, reducing the ratio of monascus red and orange pigment, and complicated product purification process, so as to eliminate adverse effects, optimize metabolism, Promising effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Preparation of seed liquid: inoculate the seeds of Monascus ruber (Monascus ruber) WQ15 (preservation number is CGMCC No.10910) streaked on the plate into sterilized seed medium (glucose 1g, yeast extract powder 0.15g , fish meal peptone 0.5g, KCl 0.025g, KH 2 PO 4 0.2g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 (0.5mg, fixed to 50mL with distilled water, and the pH is natural) to cultivate and proliferate, 50ml seed culture medium inoculates 5 single bacterium colonies of cultivating 6 days, cultivates 30h at 30 ℃, 180rpm, makes the seed culture medium have mature spores, obtains seed liquid.
[0033] (2) High carbon source fermentation: the seed liquid that step (1) obtains is inoculated into the basic fermentation medium (glucose 1.25g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.125g, KH 2 PO 4 0.125g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.0125g, KCl 0.0125g, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.25mg, ZnSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.25mg, MnSO 4 ·H 2(0.75mg, be fixed to 25mL with distilled water, pH is natural), 30 ℃, 180rpm ferment and cultivate 3 days; Th...
Embodiment 2
[0037] (1) Preparation of seed liquid: same as step (1) of Example 1.
[0038] (2) High-carbon source fermentation: basically the same as step (2) of Example 1, the difference is only that glycerol is added in this example, replacing the glucose added in Example 1, and the amount of added glycerol is calculated per liter Add 300g of glycerol to the basic fermentation medium.
[0039] (3) conventional fermentation: with embodiment 1 step (3).
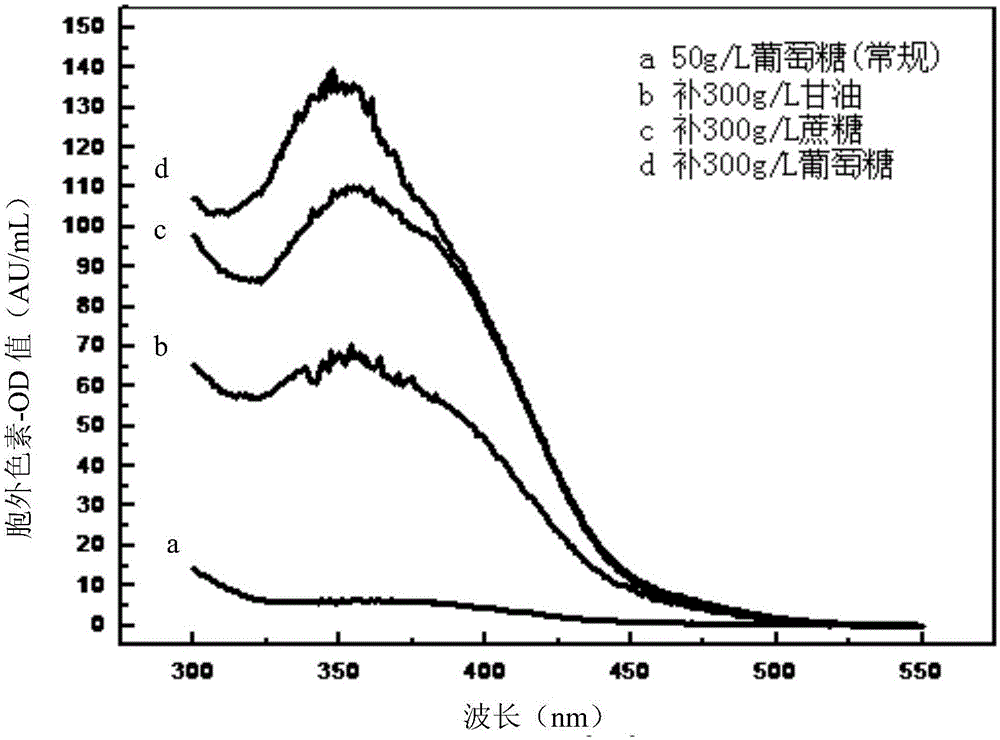
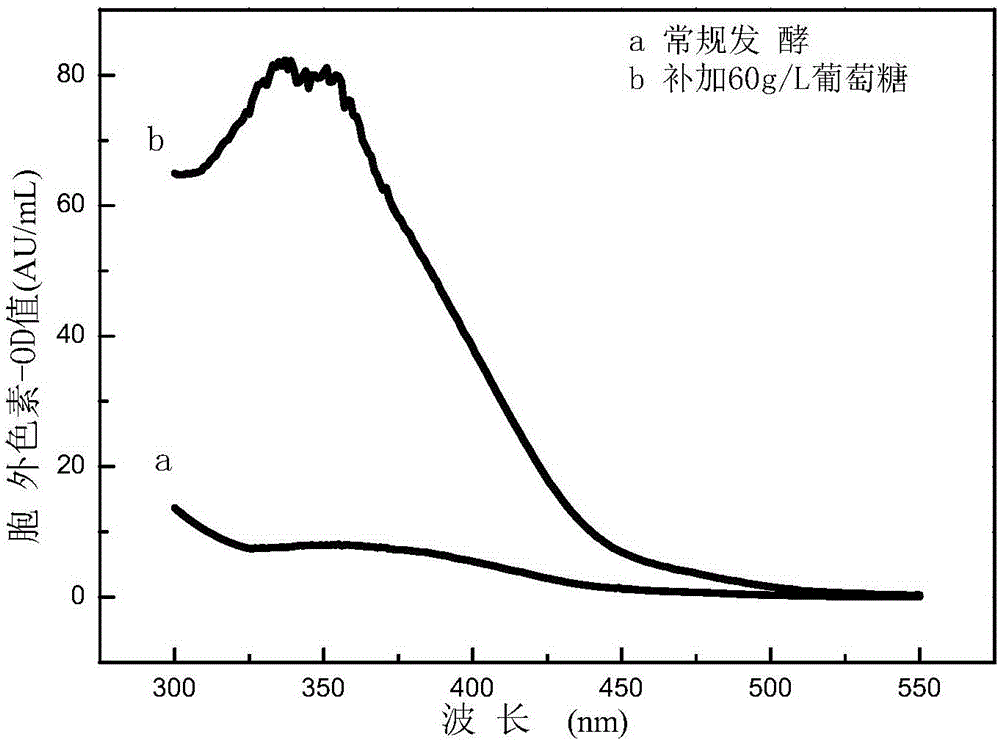
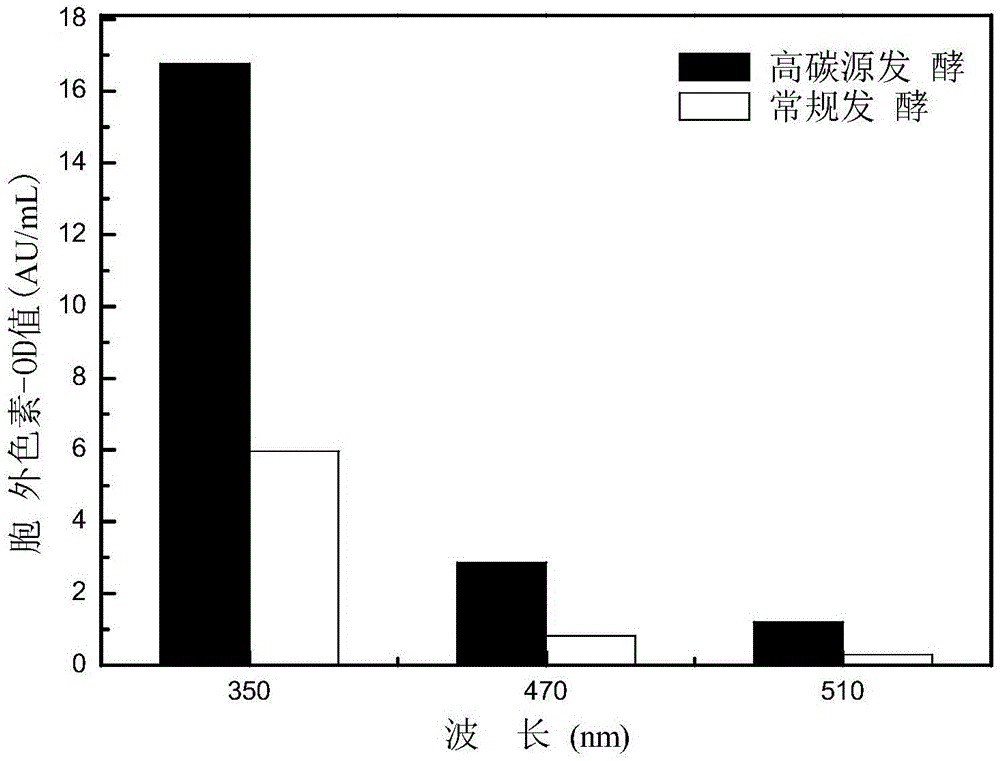
[0040] The result is as figure 1 As shown, the absorbance of the high-carbon source fermentation extracellular liquid at the characteristic wavelengths of 350, 470, and 510nm measured by an ultraviolet spectrophotometer was 68.27, 4.98, and 0.65 AU / mL, respectively, and the yellow hue of the fermented extracellular red yeast rice was 105.03, indicating that the yellow The purity of the pigment is high, and the output of extracellular yellow pigment is the same as that of conventional fermentation (10.00AU 350 / mL) 6.83 times.
Embodiment 3
[0042] (1) Preparation of seed liquid: same as step (1) of Example 1.
[0043] (2) High-carbon source fermentation: basically the same as step (2) of Example 1, the only difference is that what is added in this example is sucrose, which replaces the glucose added in Example 1, and the amount of sucrose added is calculated per liter Calculated by adding 300g sucrose to the basic fermentation medium.
[0044] (3) conventional fermentation: with embodiment 1 step (3).
[0045] The result is as figure 1 As shown, the absorbance at the characteristic wavelengths of 350, 470, and 510 nm of the high-carbon source fermentation extracellular liquid was measured by a spectrophotometer to be 108.15, 5.29, and 1.04 AU / mL, respectively, and the yellow hue of the fermented extracellular red yeast rice was 104.00, indicating that the yellow pigment High purity, extracellular yellow pigment production is conventional fermentation (10.00AU 350 / mL) 10.81 times.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Absorbance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com