Current measuring device
A technology of current measuring device and signal processing circuit, which is applied in the direction of measuring device, only measuring current, measuring electrical variables, etc., can solve the problems of proportional error temperature characteristics, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the fluctuation range and stabilizing output characteristics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
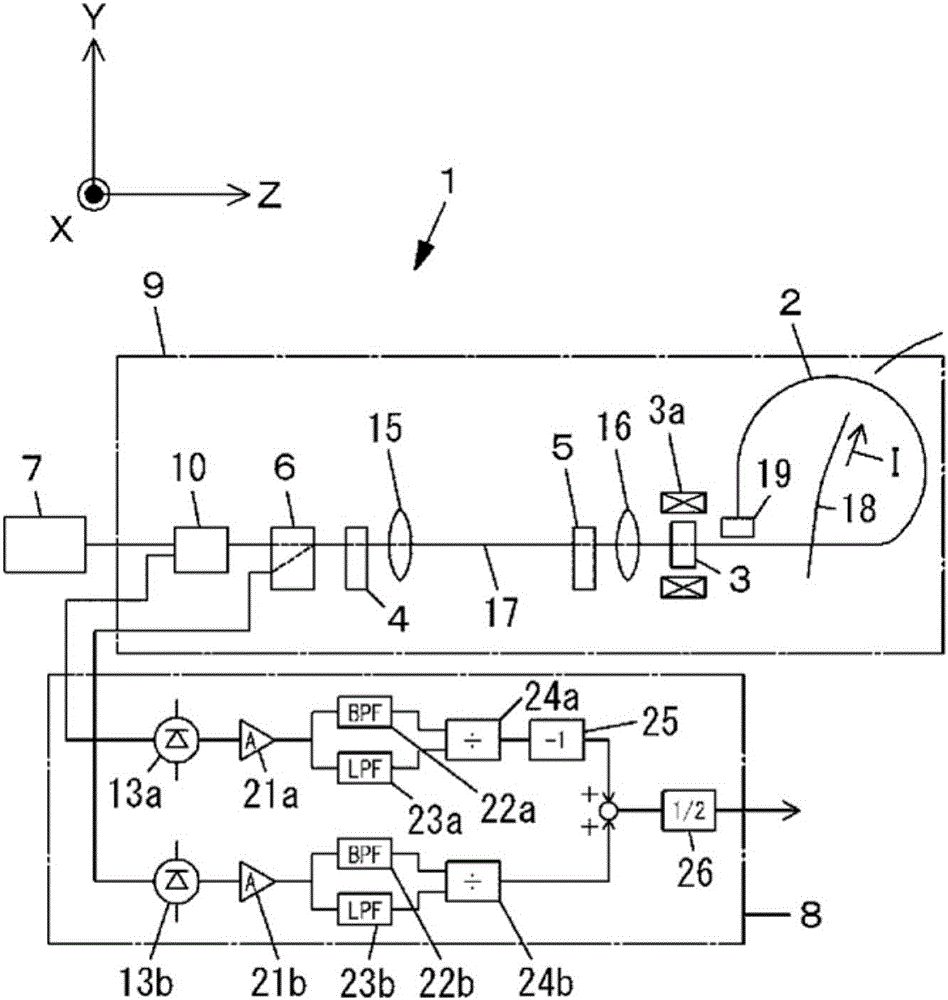
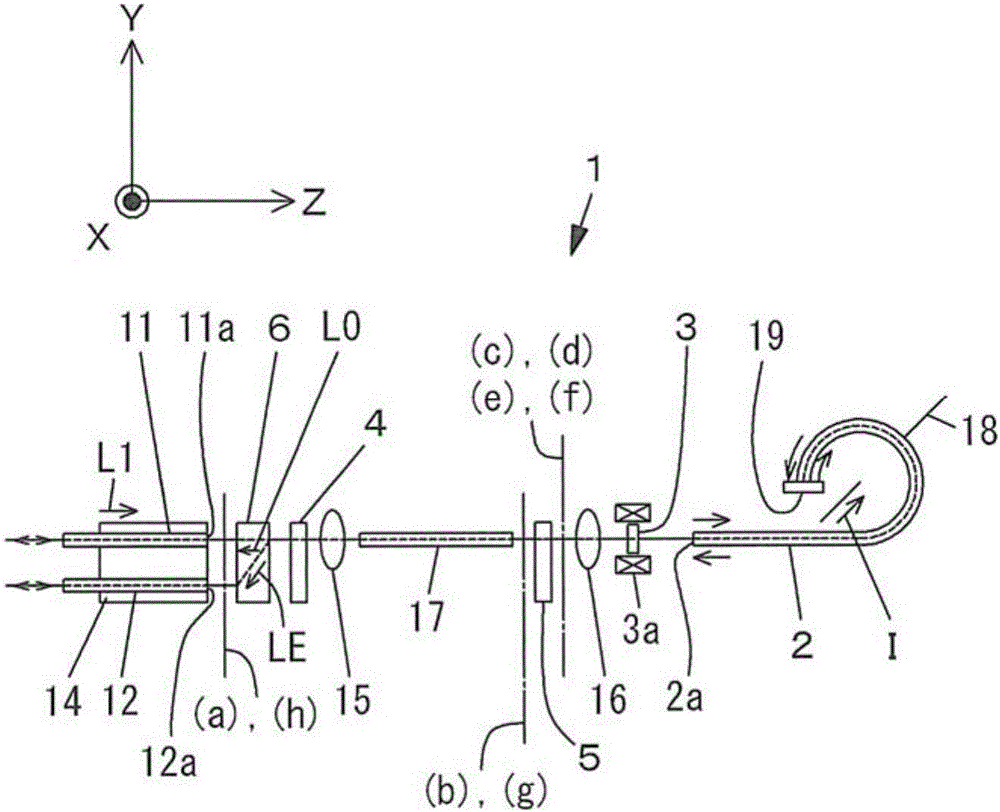
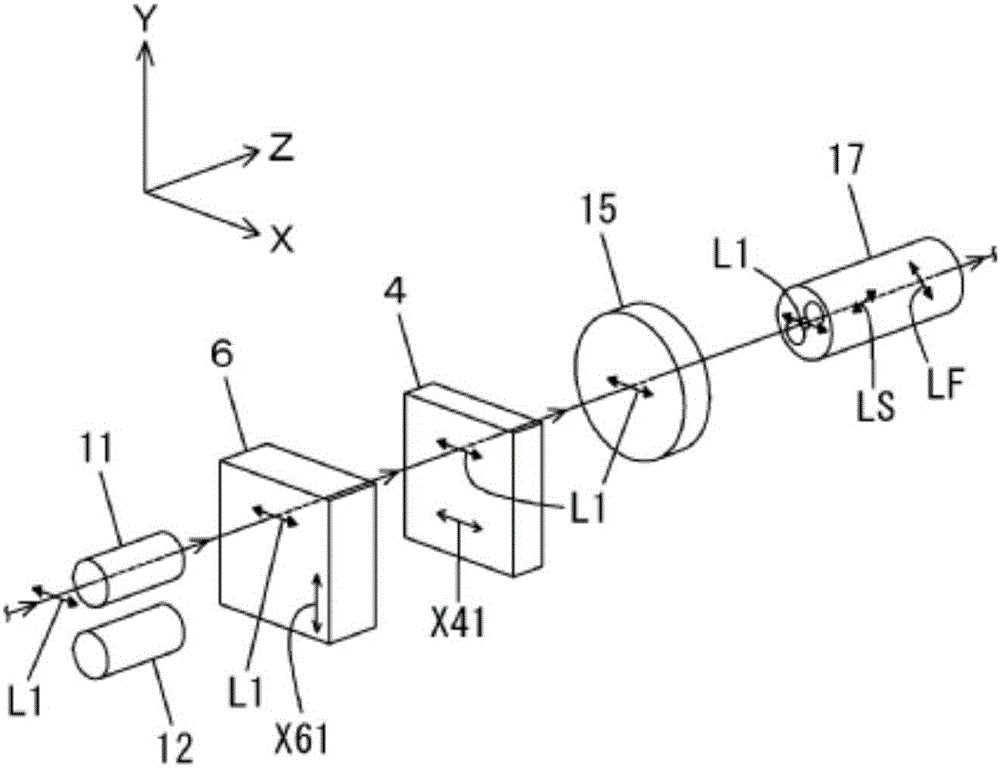
[0158] as figure 2 The Faraday rotator 3, indicated for use in opto-isolators, uses features such as Figure 14 An example of a magnetic garnet showing the temperature characteristics of the Faraday rotation angle. A Faraday rotator with a Faraday rotation angle set to 22.5°+1.0° at a temperature of 23° C. was used. That is, α=1.0° is set, and the total Faraday rotation angle at the time of magnetic saturation when the circularly polarized lights LC1 and LC2 transmit back and forth is set to 47.0°. The temperature-proportional error characteristics in the measured value of the measured current I output from the signal processing circuit of the current measuring device 1 having such a Faraday rotator 3 are shown in Table 1 and Figure 24 . In addition, the Faraday rotation angle in Table 1 refers to the total Faraday rotation angle at the time of magnetic saturation when the circularly polarized lights LC1 and LC2 transmit back and forth. In addition, the proportional erro...
Embodiment 2
[0163] The temperature dependence of the rotation angle of the reciprocating magnetic garnet was expressed by the following quadratic formula (mathematical formula 1), and the minimum value of the variation width of the proportional error of the phase coefficient a and the coefficient b was calculated. In addition, the coefficient c is set such that the proportional error fluctuation range takes the minimum value. Table 2 shows the relationship between the variation range of the proportional error and coefficient a and coefficient b. In addition, as shown in Table 2, the relationship between the Faraday rotation angle adjustment part α° and the coefficient a and coefficient b at a temperature of 23° C. when the proportional error fluctuation range is the minimum value is shown in Table 3.
[0164] Mathematical formula 1
[0165] θF=a·T2+b·T+c In addition, T: temperature [°C]
[0166] Table 2
[0167]
[0168] table 3
[0169]
[0170] Table 2 and Table 3 have a point...
Embodiment 3
[0180] Based on the research results in Table 2, the development of a magnetic garnet for reducing the proportional error by a Faraday rotator was carried out. As a result, a magnetic garnet having a temperature dependence shown in Mathematical Formula 3 below was obtained. The Faraday rotation angle at a temperature of 23° C. is 24.22°, that is, α=1.72°. The temperature dependence of the obtained magnetic garnet is shown in Figure 29 .
[0181] Mathematical formula 3
[0182] θF=-1.64.·10-4·T2-0.0185·T+48.95 In addition, T: temperature [°C]
[0183]The total Faraday rotation angle at the time of magnetic saturation when circularly polarized light LC1 and LC2 are reciprocally transmitted is 48.44°. The temperature-proportional error characteristics in the measured value of the measured current I output from the signal processing circuit of the current measuring device 1 having such a Faraday rotator 3 are shown in Table 5 and Figure 30 .
[0184] table 5
[0185]
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com