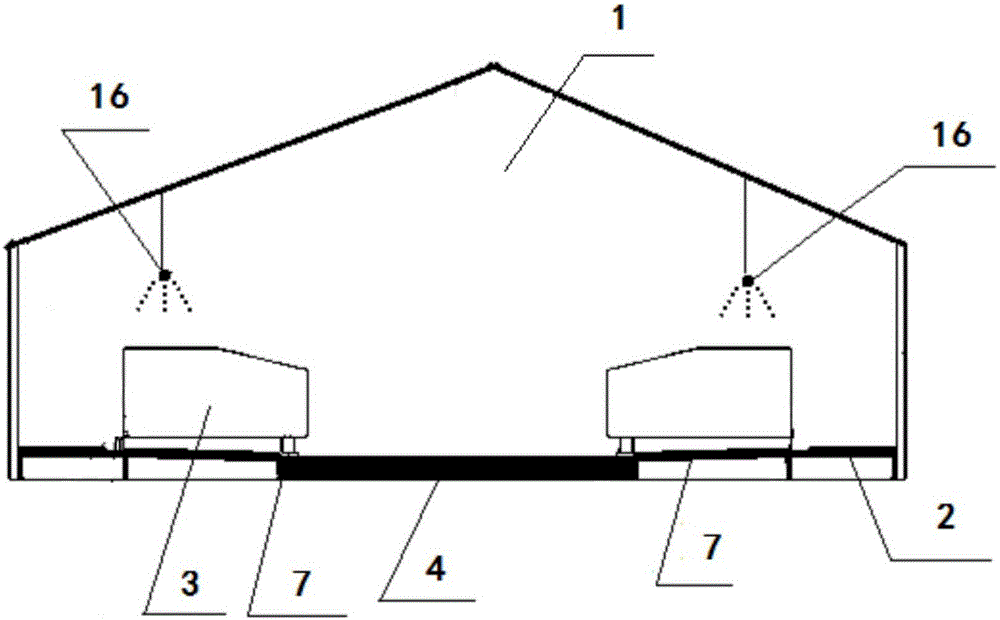
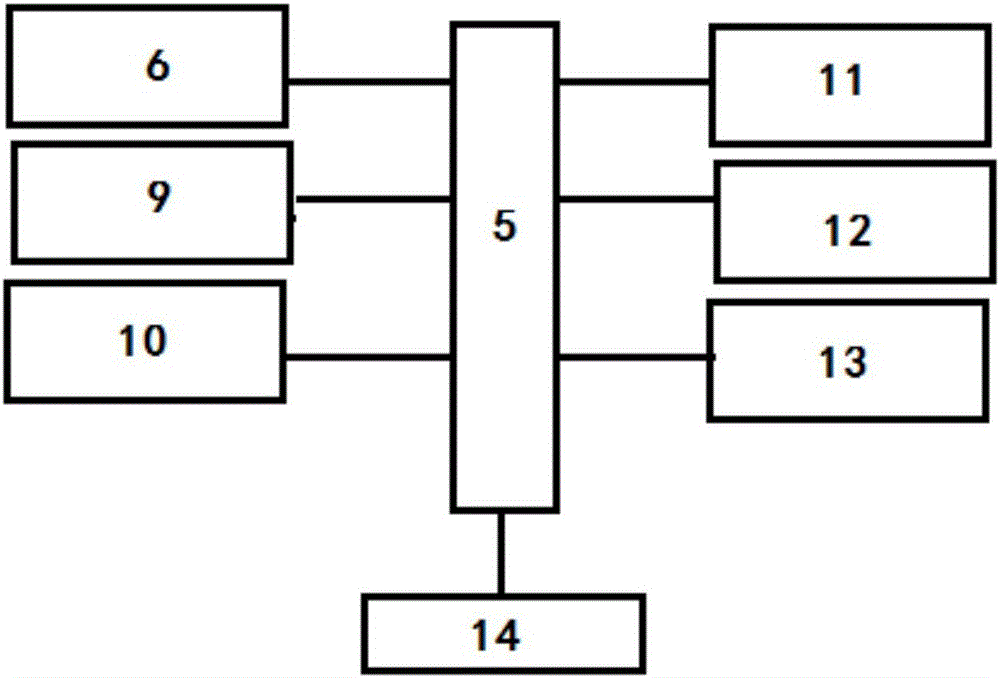
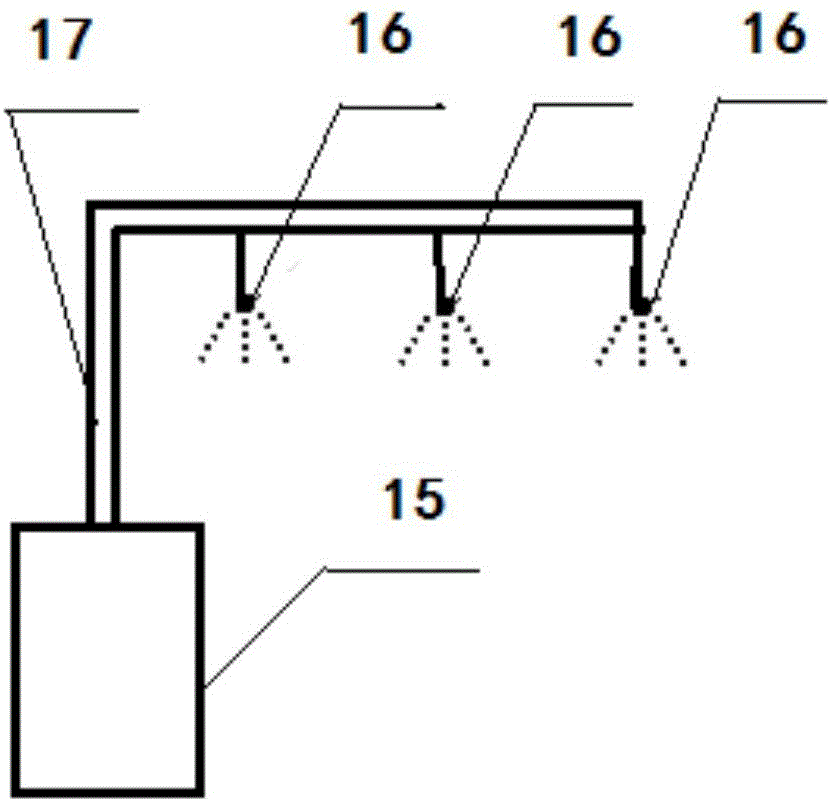
Chicken farm and chicken breeding method
A breeding method and farm technology, applied in chicken farms and chicken breeding fields, can solve the problems of low survival rate of laying hens, low feed conversion rate, low egg production, etc., and achieve high survival rate of laying hens, feed The effect of high conversion rate and high egg production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A chicken breeding method, using the above-mentioned farm, comprises the following steps:
[0038] Step 1. Cultivate chicks: choose healthy chicks that are lively and of uniform size, and place the chicks at 36.5°C for cultivation. From the second day onwards, reduce the temperature by 0.5°C every day until the temperature is 25°C; when the chicks are 4 weeks old, press the following quality Percentage configuration feed for feeding: 62% corn, 3.2% wheat bran, 30% soybean meal, 1.3% calcium hydrogen phosphate, 1.2% stone powder, 0.3% salt, 1% multivitamins for laying hens, 1% disease-resistant auxiliary materials; The auxiliary materials are composed of the following components in parts by weight: 6 parts of ferrous fumarate, 7 parts of ferrous lactate, 3 parts of methionine chelated zinc, 3 parts of zinc propionate, 10 parts of methionine chelated manganese, 1.5 parts of copper sulfate, 0.2 parts of cobalt acetate, 6 parts of potassium iodide premix, 26 parts of magnes...
Embodiment 2
[0043] A chicken breeding method, using the above-mentioned farm, comprises the following steps:
[0044] Step 1. Cultivate chicks: choose healthy chicks that are lively and neat in size, and place the chicks at 36°C for cultivation. From the second day onwards, reduce the temperature by 0.5°C every day until the temperature is 25°C; when the chicks are 3 weeks old, press the following quality Percentage configuration feed for feeding: 62% corn, 3.2% wheat bran, 30% soybean meal, 1.3% calcium hydrogen phosphate, 1.2% stone powder, 0.3% salt, 1% multivitamins for laying hens, 1% disease-resistant auxiliary materials; The auxiliary materials are composed of the following components in parts by weight: 5 parts of ferrous fumarate, 8 parts of ferrous lactate, 2 parts of methionine chelated zinc, 4 parts of zinc propionate, 8 parts of methionine chelated manganese, 2 parts of copper sulfate, 0.1 part of cobalt acetate, 8 parts of potassium iodide premix, 24 parts of magnesium sulfa...
Embodiment 3
[0049] A chicken breeding method, using the above-mentioned farm, comprises the following steps:
[0050] Step 1. Cultivate chicks: choose healthy chicks that are lively and neat in size, and place the chicks at 37°C for cultivation. From the second day onwards, reduce the temperature by 0.5°C every day until the temperature is 25°C; when the chicks are 6 weeks old, press the following quality Percentage configuration feed for feeding: 62% corn, 3.2% wheat bran, 30% soybean meal, 1.3% calcium hydrogen phosphate, 1.2% stone powder, 0.3% salt, 1% multivitamins for laying hens, 1% disease-resistant auxiliary materials; The auxiliary materials are composed of the following components in parts by weight: 8 parts of ferrous fumarate, 5 parts of ferrous lactate, 4 parts of methionine chelated zinc, 2 parts of zinc propionate, 12 parts of methionine chelated manganese, 1 part of copper sulfate, 0.3 parts of cobalt acetate, 5 parts of potassium iodide premix, 28 parts of magnesium sulf...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com