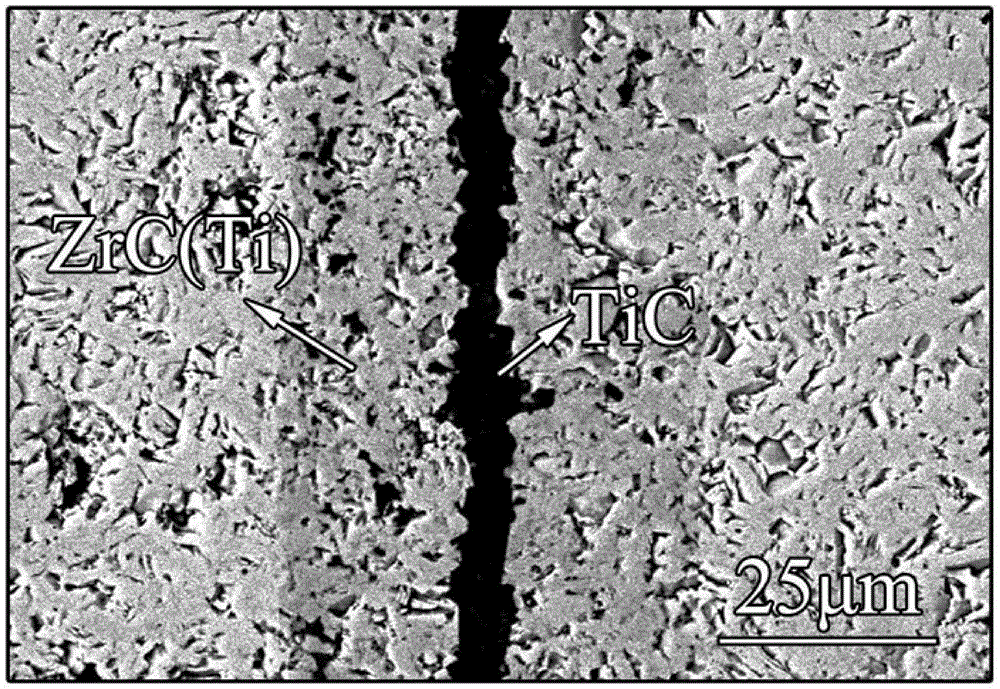
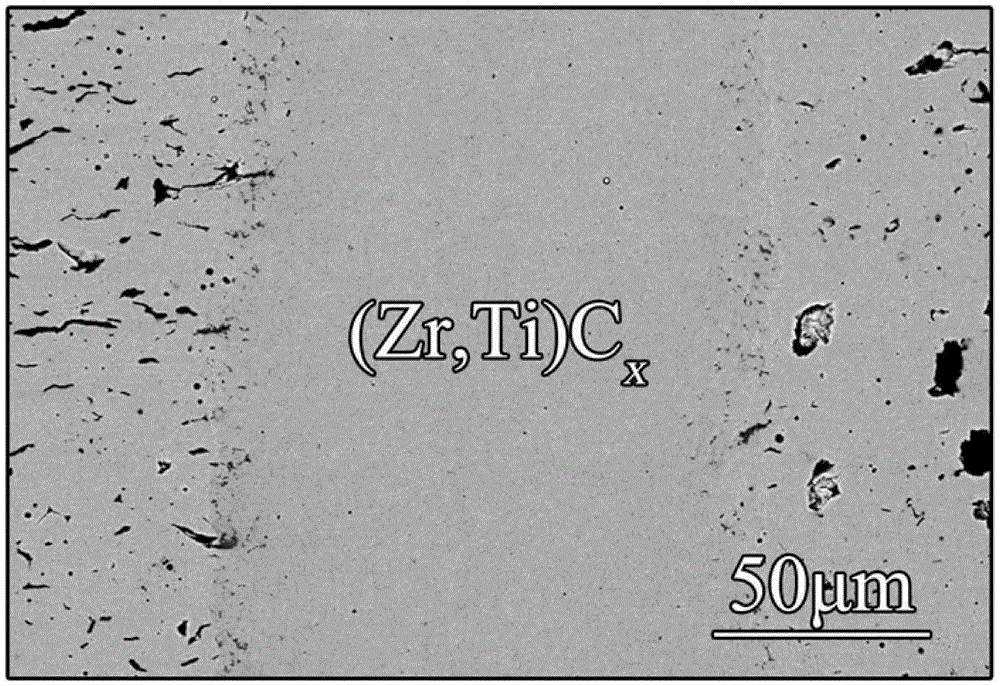
High-temperature-application-based composite active middle layer diffusion bonding method for implementing interstitial carbide or nitride ceramic seamless connection
A technology of nitride ceramics and active intermediate layer, which is applied in the field of composite active intermediate layer diffusion connection, can solve the problem that the single-layer active metal intermediate layer cannot form a homogeneous mutual-dissolution joint, and achieve lower connection temperature, higher operating temperature, and higher efficiency Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0012] Specific Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, a composite active interlayer diffusion connection method based on high-temperature application to realize seamless connection of interstitial carbide or nitride ceramics is carried out according to the following steps:
[0013] 1. Surface cleaning: use two or more types of diamond grinding discs from 500# to 1500# to grind the two ceramic base materials to be connected step by step, and then use two or more types of diamond grinding discs from 1500# to 2000# Among them, two or more types of water-grinding sandpaper are finely ground step by step, and finally the two ceramic base materials to be connected after fine grinding are polished, placed in acetone, ultrasonically cleaned for 15min to 30min, and then placed in absolute ethanol. Ultrasonic cleaning for 10 to 15 minutes, and finally placed in a drying oven to dry, that is, two ceramic base materials after surface cleaning are obtained; wherein the ceramic base materials ar...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0018] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that M in the MCx single-phase ceramic described in step 1 is Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb or Ta, and x is: 0.55≤x≤ 1; M in the MNx single-phase ceramics described in step 1 is Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb or Ta, and x is: 0.55≤x≤1; in the MNx / MNx composite phase ceramics described in step 1 M is Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb or Ta, and x is: 0.55≤x≤1; M in the MCx / MCx composite ceramics described in step 1 is Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb or Ta, x is 0.55≤x≤1; in the MNx / MCx multiphase ceramics described in step 1, M in MNx is Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb or Ta, x is: 0.55≤x≤1, M in MCx is Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb or Ta, and x is: 0.55≤x≤1. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0019] Embodiment 3: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2 in that: the water-abrasive paper described in step 1 is silicon carbide water-abrasive paper or alumina water-abrasive paper. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com