Production method of high-toughness high-isotropy large-section hot working die steel
A hot-working die steel and production method technology, applied in the field of steel casting, can solve problems such as low die life and die cracking, and achieve the effects of uniform quality, optimized time difference, and elimination of carbides and segregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045]A production method of high toughness, high isotropic large section hot work die steel:
[0046] Step 1: After electroslag remelting, the annealed steel ingot (the material type is H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1)) is placed in a heating furnace and heated to 1260 ° C. After the center reaches the set temperature, it is kept for 5 hours to complete the first homogenization.
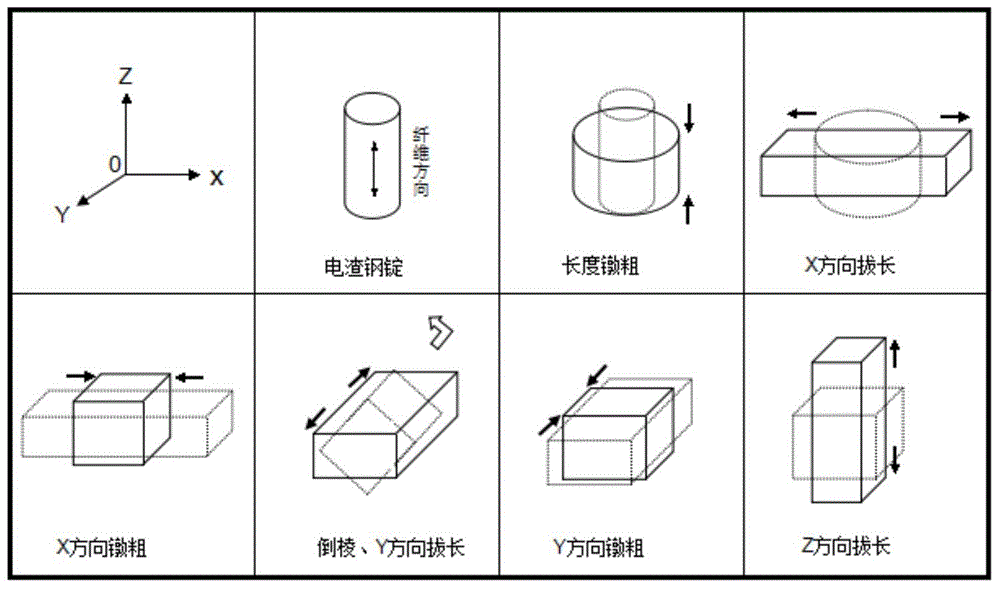
[0047] Step 2: Start three-direction strong forging at an initial forging temperature of 1260°C and a final forging temperature of 900°C. The forging sequence is as follows figure 1 As shown, that is, steel ingot upsetting → X direction upsetting → Y direction chamfering upsetting → Z direction elongation, the upsetting deformation rate of each direction is above 40%, except for the finishing pass, the compression of each pass The down rate is above 15%.
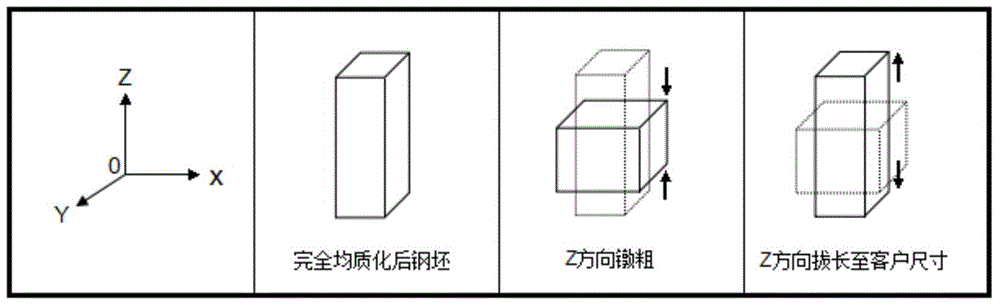
[0048] Step 3: The steel billet that has been strongly forged in three directions continues to be heated to the homogenization temperature. After the center of ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A production method of high toughness, high isotropic large section hot work die steel:
[0053] Step 1: After electroslag remelting, the annealed steel ingot (the material type is H13 (4Cr5MoSiV1)) is placed in a heating furnace and heated to 1300 ° C. After the center reaches the set temperature, it is kept for 8 hours to complete the first homogenization.
[0054] Step 2: Start three-direction strong forging at an initial forging temperature of 1300°C and a final forging temperature of 900°C. The forging sequence is: steel ingot upsetting → X direction upsetting → Y direction chamfering upsetting → Z direction elongation, The upsetting deformation rate in each direction is above 50%; except for the finishing pass, the reduction rate of each pass is above 20%.
[0055] Step 3: The steel billet that has been strongly forged in three directions continues to be heated to the homogenization temperature. After the center of the billet reaches 1300 ° C, it is kept for 20 ho...
Embodiment 3
[0059] A production method of high toughness, high isotropic large section hot work die steel:
[0060] Step 1: After electroslag remelting, the annealed steel ingot (the material type is H418 (4Cr5Mo2V)) is placed in a heating furnace and heated to 1280 ° C. After the center reaches the set temperature, it is kept for 6 hours to complete the first homogenization.
[0061] Step 2: Start three-direction strong forging at an initial forging temperature of 1260°C and a final forging temperature of 900°C. The forging sequence is: steel ingot upsetting → X direction upsetting → Y direction chamfering upsetting → Z direction elongation, The upsetting deformation rate in each direction is above 50%; except for the finishing pass, the reduction rate of each pass is above 20%.
[0062] Step 3: The steel billet that has been strongly forged in three directions continues to be heated to the homogenization temperature. After the center of the billet reaches 1280 ° C, it is kept for 20 hou...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com