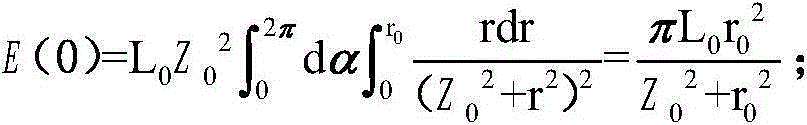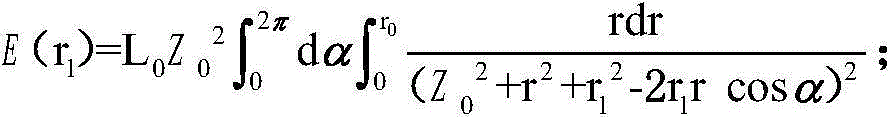Instrument for testing stray light of finite-conjugate-distance microscope objective and testing precision adjustment method
A technology of microscope objective lens and conjugate distance, applied in the field of optical testing, can solve the problems of inaccessibility, inability of black body target plate, influence of stray light measurement results of microscope objective lens, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
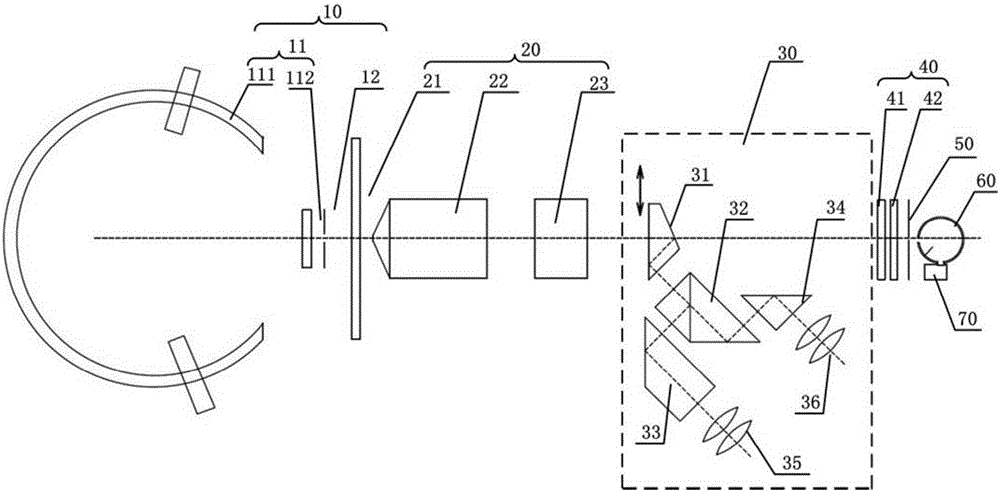
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, the infinity conjugate distance microscope objective lens stray light tester of the present invention comprises in turn:
[0038] A light source 10 for providing uniformly illuminated light;
[0039] The imaging device 20 is used to receive the light emitted by the light source 10 and form an image; the imaging device 20 includes an infinity conjugate distance microscopic objective lens 22 and a tube lens 23 combined for imaging, and is located at the infinity conjugate distance microscopic objective lens 22 front focus The black body target plate 21 that is used to provide black spots for the infinite conjugate distance microscope objective lens 22;
[0040] The trinocular observation device 30 is used for observing to ensure that the position of the black spot is placed correctly during measurement;
[0041] A filter device 40, the light emitted by the imaging device 20 is filtered by the filter device 40 and then output in the visible lig...
Embodiment 2
[0053] On the basis of Embodiment 1, Embodiment 2 provides a method for adjusting the test accuracy of the stray light tester for the infinite conjugate distance microscope objective lens. The uniformity of light affects the test accuracy of the stray light tester for the infinite conjugate distance microscope objective lens: the greater the uniformity of light, the higher the test accuracy. Therefore, by adjusting the uniformity of the light to make it larger, the test accuracy of the stray light tester for the infinite conjugate distance microscope objective lens can be improved. However, the uniformity of light is directly proportional to the transmission distance, and the energy of light is inversely proportional to the transmission distance. Then, let the distance Z between the integrating sphere expand the light source 111 and the cosine diffuse transmission sheet 112 0 , the opening diameter r of the expanding light source 111 of the integrating sphere 0 , cosine diff...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com