Silicon carbide porous ceramic material and preparation method of silicon carbide porous ceramic material
A technology of porous ceramics and silicon carbide, applied in the field of material science, can solve the problems of high energy consumption, complex components and processes, and achieve the effect of low energy consumption and high promotion value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Specific steps are as follows:
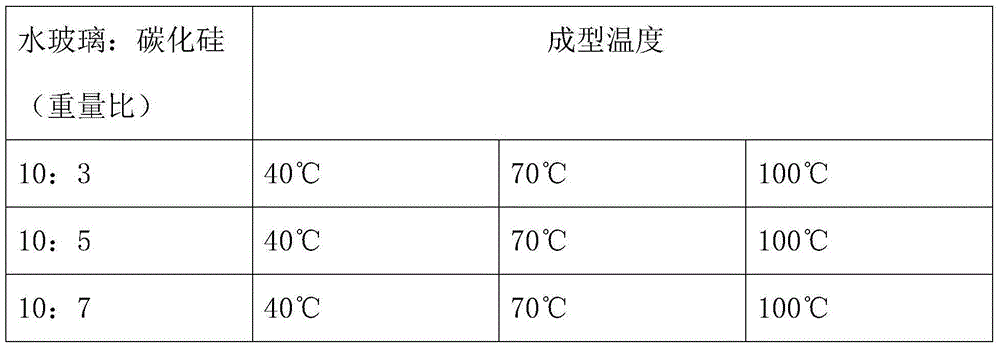
[0033] 1) Mix the raw materials according to the ratio shown in Table 1, first mechanically stir, and then ball mill to prepare the slurry; the silicon carbide powder is green silicon carbide;
[0034] 2) dipping the above-mentioned slurry on the formwork to obtain a preform; the formwork adopts open polystyrene foam;
[0035] 3) Forming at low temperature according to the temperature shown in Table 1, and the heating time is 24 hours.
[0036] 4) Insulate at 160°C for 4 hours to cure completely.
[0037] Table 1 Proportion and molding temperature of silicon carbide porous ceramic slurry
[0038]
[0039] testing method:
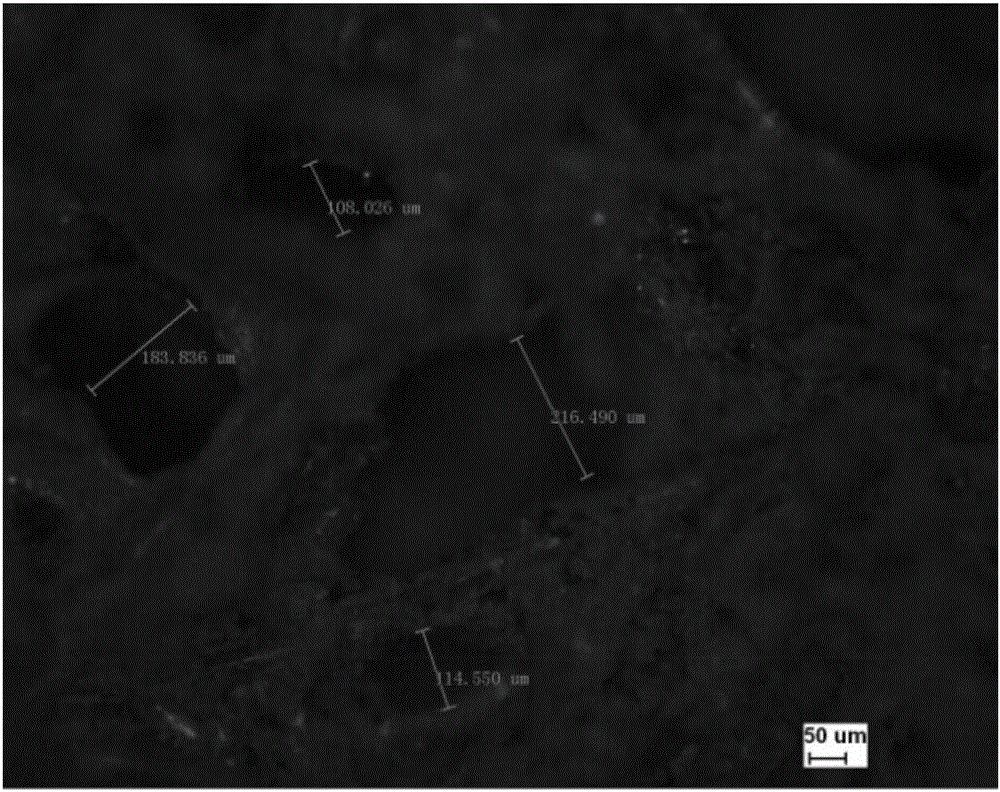
[0040] The measurement of open porosity is to put the sample in water first, read the change of the reading in the measuring cylinder, which is the sum of the volume of the sample and the closed volume, then seal the opening of the sample with silicone grease, and place it in water. The change in the reading in ...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is that water is added on the basis of embodiment 1.
[0054] Specific steps are as follows:
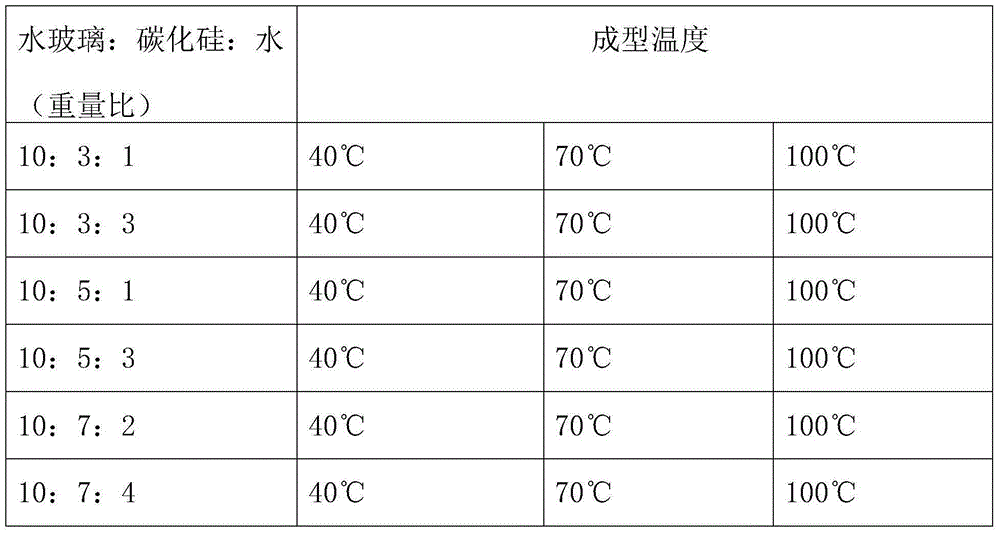
[0055] 1) Mix the raw materials according to the ratio shown in Table 5, first mechanically stir, and then ball mill to prepare the slurry; the silicon carbide powder is black silicon carbide;
[0056] 2) dipping the above-mentioned slurry on the formwork to obtain a preform; the formwork adopts open polyurethane foam;
[0057] 3) Forming at low temperature according to the temperature shown in Table 5, and the heating time is 36 hours.
[0058] 4) Insulate at 160°C for 4 hours to cure completely.
[0059] Table 5 Proportion and molding temperature of silicon carbide porous ceramic slurry
[0060]
[0061] Test Results:
[0062] Table 6 Test results of sample porosity and strength of water glass: silicon carbide: water = 10:3:1
[0063] Molding temperature
Open porosity
Flexural strength / MPa
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com