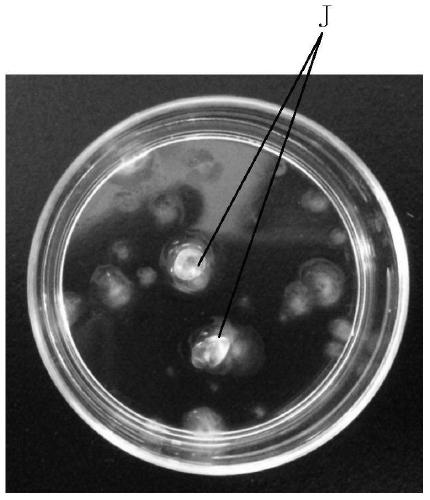
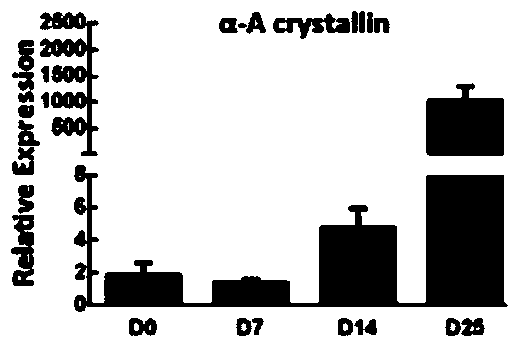
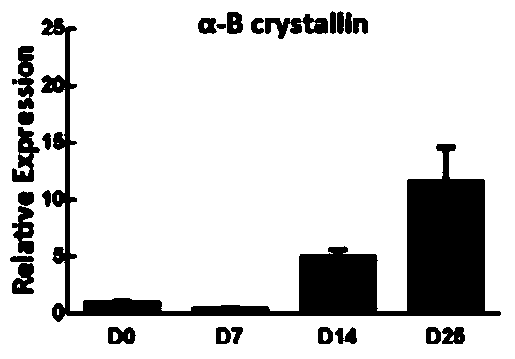
A method for directed differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into lens bodies in vitro
A technology of pluripotent stem cells and directed differentiation, which is applied in the field of preparation of in vitro induced lens body, can solve the problems of lens body limitation, inability to transition human lens, inability to form good shape and optical function, and achieve wide application prospects, The effect of good light transmission
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] A method for inducing directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into lens bodies, comprising the following steps:
[0055] (1) Directed induction of pluripotent stem cells into primary neuroectodermal cell clusters
[0056] The six-well plate was first coated with Matrigel solution and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO 2 Place it in an incubator with saturated humidity for 50 minutes, then suck off the coating solution, and wash it once with DMEM / F12 medium; then seed the pluripotent stem cells on a six-well plate and culture them with mTesR (human embryonic stem cell medium) cultured in liquid for 5 days to obtain primary neuroectoderm cell mass;
[0057] The matrigel solution was embryonic stem cell matrigel (BD matrigel TM hESC-qualified Matrix) was dissolved in DMEM / F12 culture medium, and the volume ratio of embryonic stem cell matrigel was 0.8%; the human growth factor contained in mTesR culture medium was 90ng / ml noggin;
[0058] Under the microscope, it ca...
Embodiment 2
[0068] A method for inducing directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into lens bodies, comprising the following steps:
[0069] (1) Directed induction of pluripotent stem cells into primary neuroectodermal cell clusters
[0070] The six-well plate was first coated with Matrigel solution and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO 2 Place it in an incubator with saturated humidity for 1 hour, then absorb the coating solution, and wash it once with DMEM / F12 medium; then inoculate pluripotent stem cells on a six-well plate and culture them with mTesR medium for 6 days to obtain primary Neuroectodermal cell mass;
[0071] The matrigel solution was embryonic stem cell matrigel (BD matrigel TM hESC-qualified Matrix) was dissolved in DMEM / F12 culture medium, and the volume ratio of embryonic stem cell matrigel was 1.0%; the human growth factor contained in mTesR culture medium was 100ng / ml noggin;
[0072] Under the microscope, it can be observed that the obtained primary ectoderm ...
Embodiment 3
[0082] A method for inducing directed differentiation of pluripotent stem cells into lens bodies, comprising the following steps:
[0083] (1) Directed induction of pluripotent stem cells into primary neuroectodermal cell clusters
[0084] The six-well plate was first coated with Matrigel solution and incubated at 37°C in 5% CO 2Place it in an incubator with saturated humidity for 10 minutes, then absorb the coating solution, wash it once with DMEM / F12 medium; then inoculate pluripotent stem cells on a six-well plate and culture them with mTesR medium for 7 days to obtain primary neurons. Ectodermal cell mass;
[0085] The matrigel solution was embryonic stem cell matrigel (BD matrigel TM hESC-qualified Matrix) was dissolved in DMEM / F12 culture medium, and the volume ratio of embryonic stem cell matrigel was 1.2%; the human growth factor contained in mTesR culture medium was 110ng / ml noggin;
[0086] Under the microscope, it can be observed that the obtained primary ectode...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com