Refining technology for producing long carbon chain dicarboxylic acid by using biological fermentation process
A long carbon chain dibasic acid and bio-fermentation technology, which is applied in the separation/purification of carboxylic acid compounds, organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of poor thermal stability, high ash and iron salt content, and low purity, and achieve The effect of expanding development space, high monoacid content, and high thermal stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
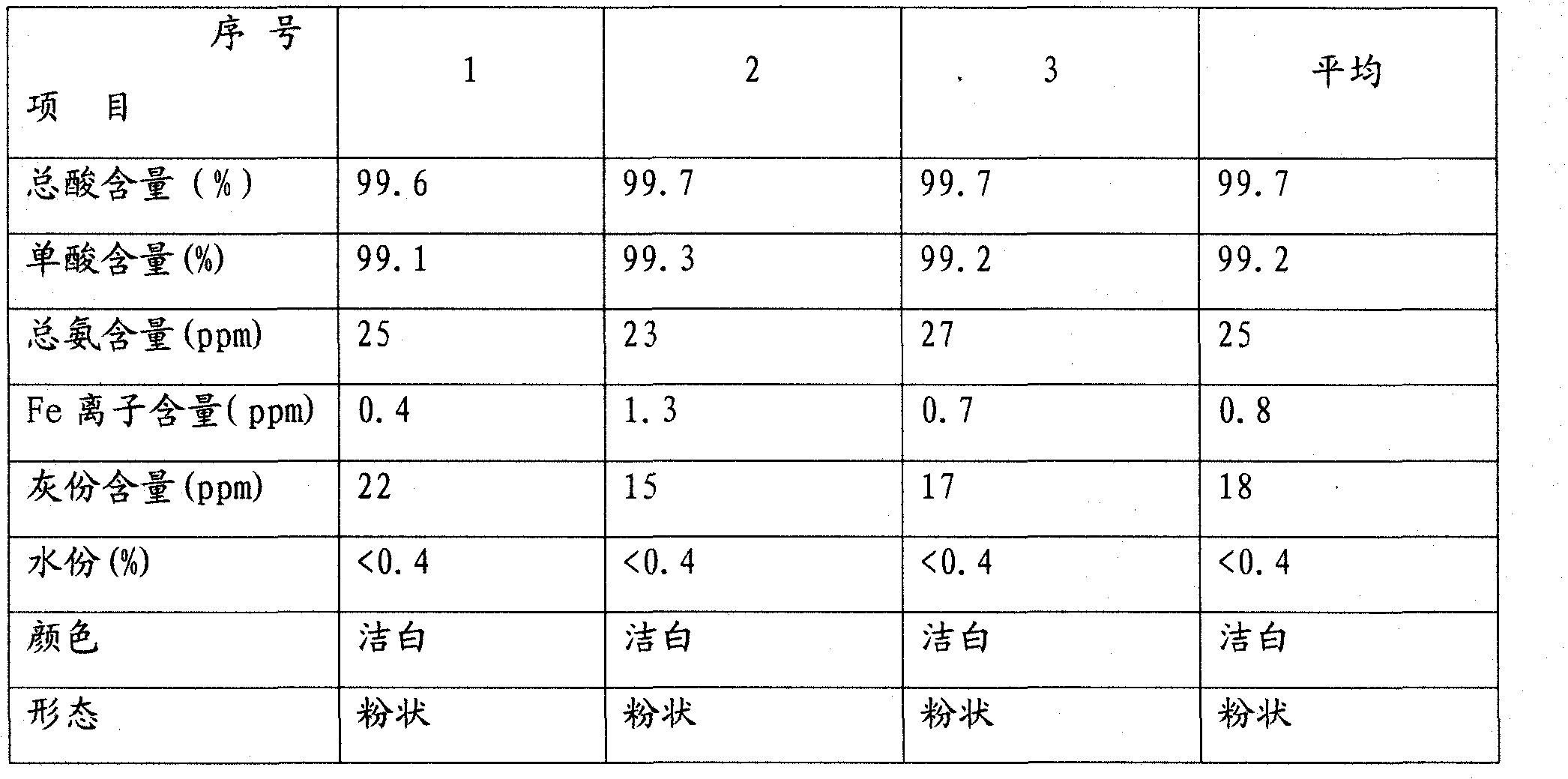
Embodiment 1
[0017] A refining process for producing long-carbon-chain dibasic acids by biological fermentation. The refining process steps include:
[0018] (1) Decolorization and filtration: put the dibasic acid crude product into the decolorization tank, the water content is 5wt%, add 0.05wt% activated carbon, and the mass ratio of the solvent and the dibasic acid is 3.0: 1 when converted into a content of 100%. At a temperature of 85°C, decolorize for 20 minutes and then filter through a plate and frame filter press to obtain a dibasic acid clear solution. The solvent is 90% acetic acid solution.
[0019] (2) Primary crystallization and separation: Put the dibasic acid clear solution obtained in step (1) into a primary crystallization tank, cool down to 75°C, keep it warm for 1 hour, then cool down to 25°C, after the material is completely crystallized, put the crystallization The material is separated by centrifuge.
[0020] (3) High-temperature water crystallization and separation:...
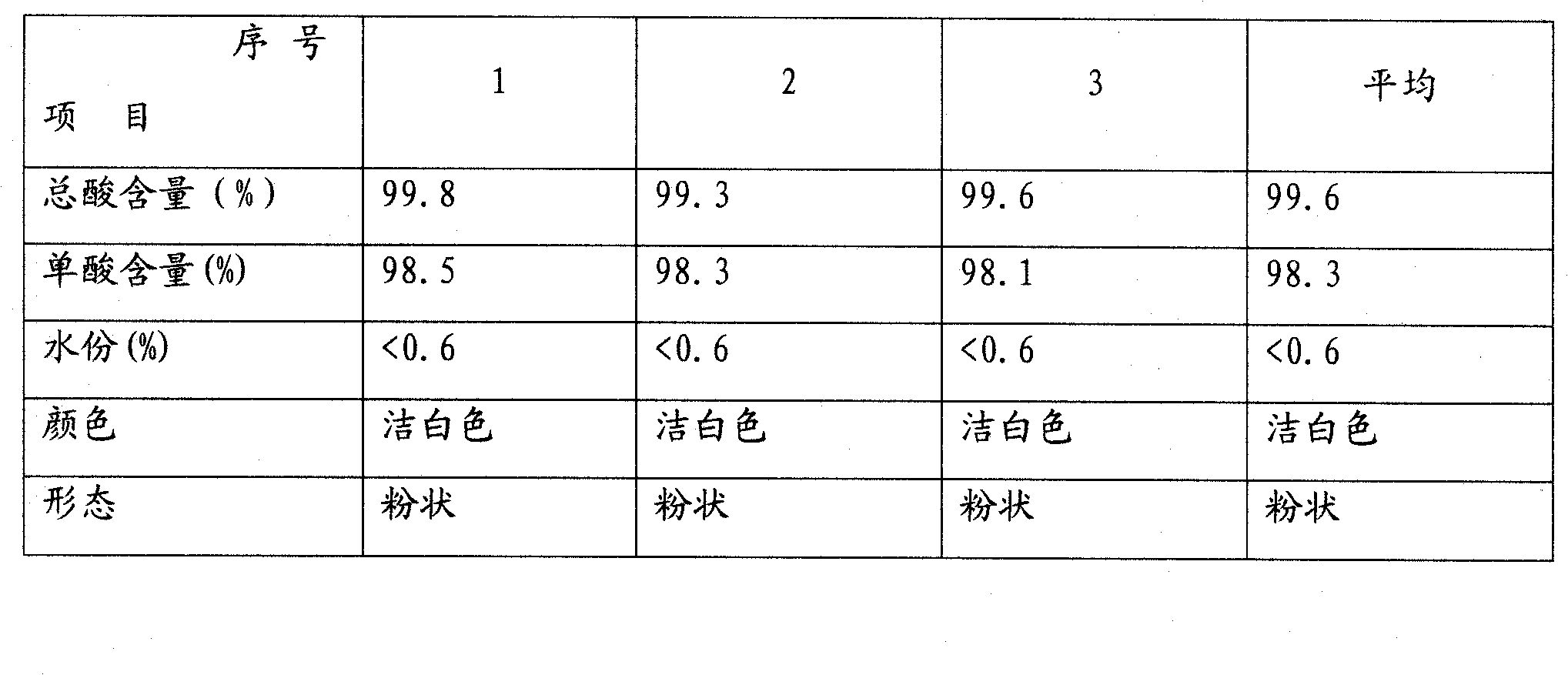
Embodiment 2
[0023] A refining process for producing long-carbon-chain dibasic acids by biological fermentation. The refining process steps include:
[0024] (1) Color filtration: Put the dibasic acid crude product into the decolorization tank, the water content is 8wt%, add 0.1wt% activated carbon, the mass ratio of the solvent and the dibasic acid is 2.5: 1 when converted into a content of 100%. At a temperature of 90°C, decolorize for 60 minutes and then filter through a plate and frame filter press to obtain dibasic acid clear liquid. The solvent is 99% acetic acid solution.
[0025] (2) Secondary crystallization and separation: Put the dibasic acid clear liquid obtained in step (1) into a primary crystallization tank, cool down to 80°C, keep it warm for 1.5 hours, then cool down to 30°C, after the material is completely crystallized, put the crystallization The material is separated by centrifuge.
[0026] (3) Warm water crystallization and separation: put the crystallization materi...
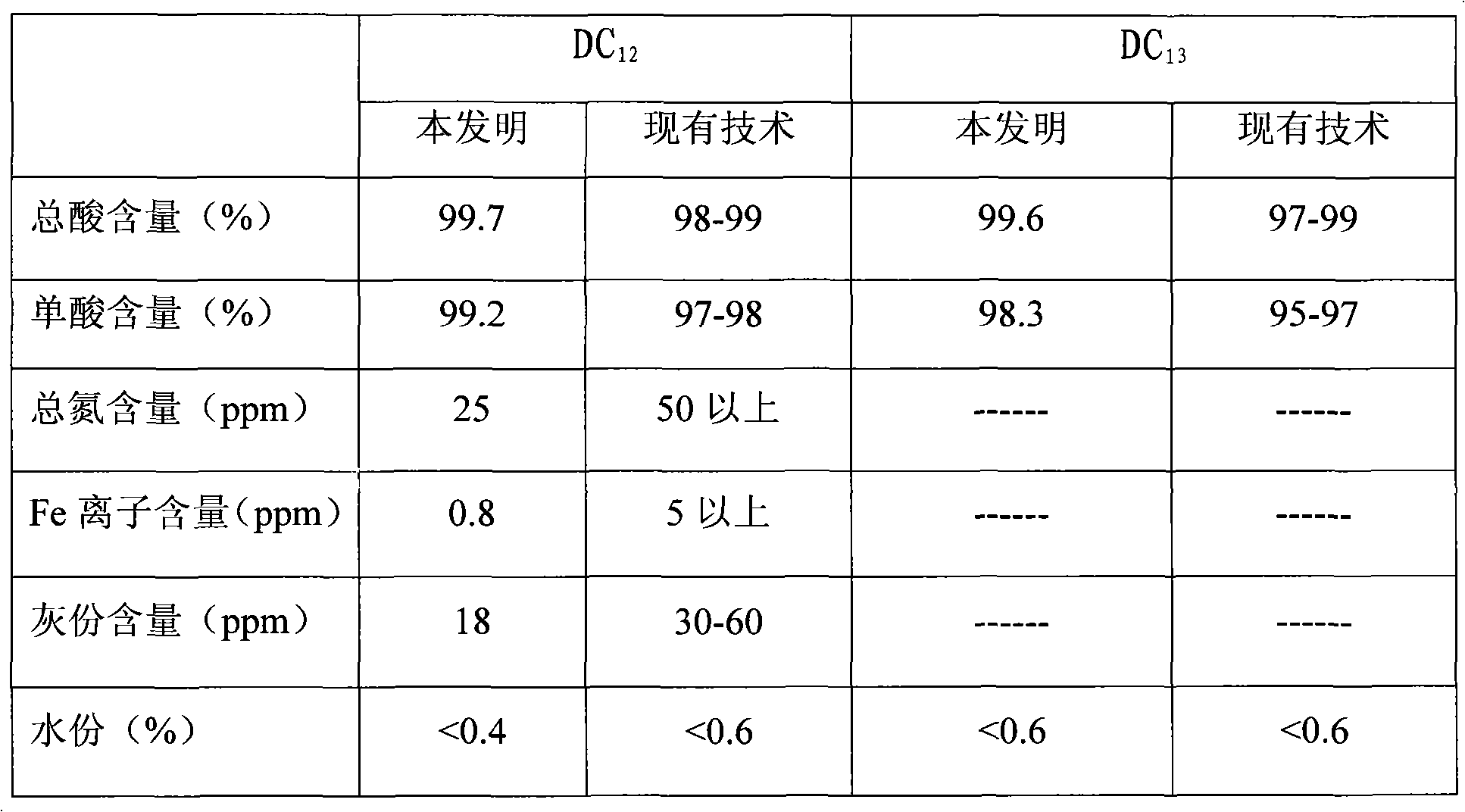
Embodiment 3
[0030] A refining process for producing long-carbon-chain dibasic acids by biological fermentation. The refining process steps include:
[0031] (1) Decolorization and filtration: put the dibasic acid crude product into the decolorization tank, the water content is 12wt%, add 0.2wt% activated carbon, the mass ratio of the solvent and the dibasic acid converted into a content of 100% is 2.0:1, At a temperature of 100°C, decolorize for 90 minutes and then filter through a plate and frame filter press to obtain dibasic acid clear liquid. The solvent is 95% acetic acid solution.
[0032] (2) Primary crystallization and separation: Put the dibasic acid clear solution obtained in step (1) into a primary crystallization tank, cool down to 85°C, keep it warm for 2 hours, then cool down to 35°C, after the material is completely crystallized, put the crystallization The material is separated by centrifuge.
[0033] (3) High-temperature water crystallization and separation: put the cry...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com