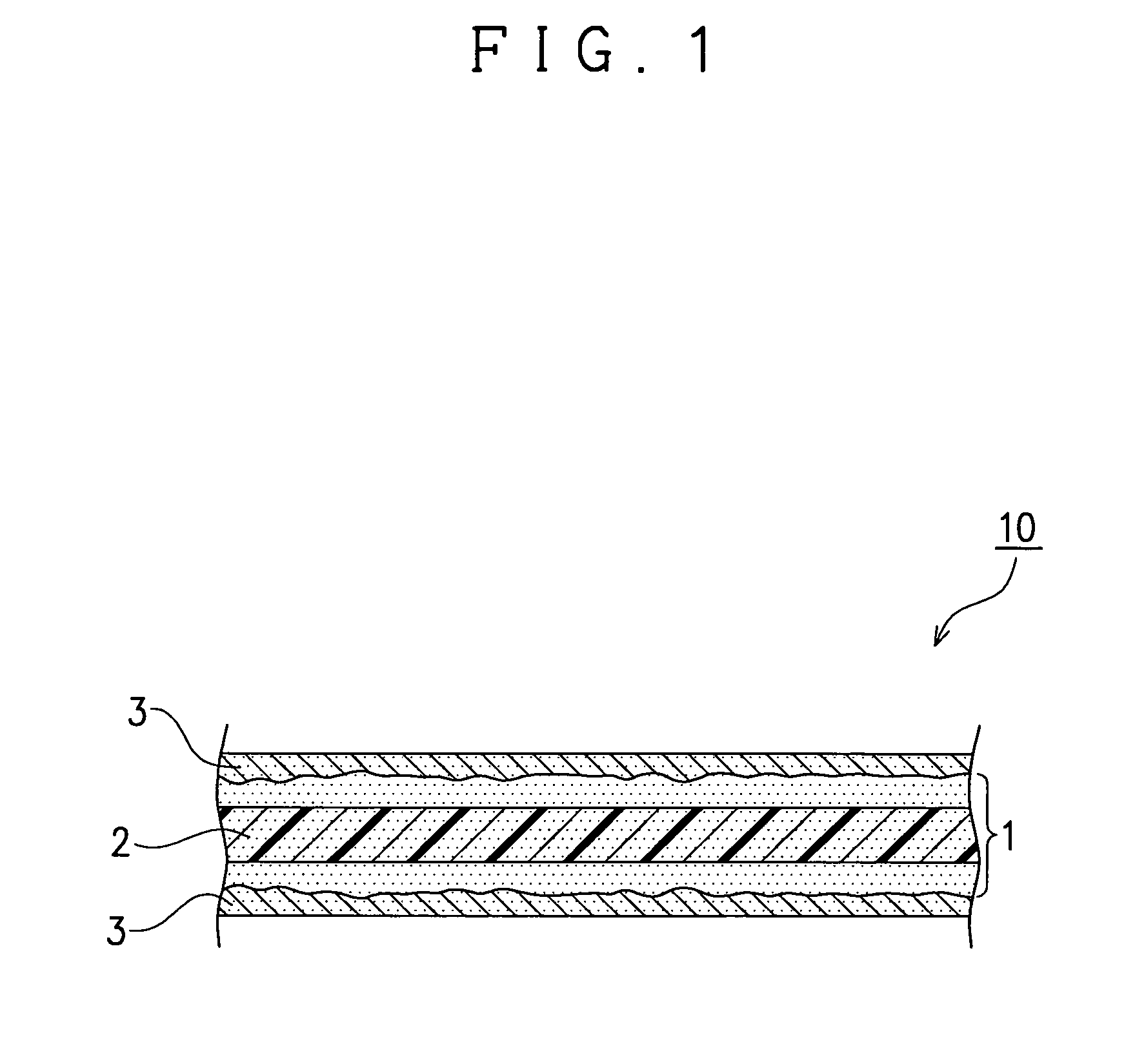
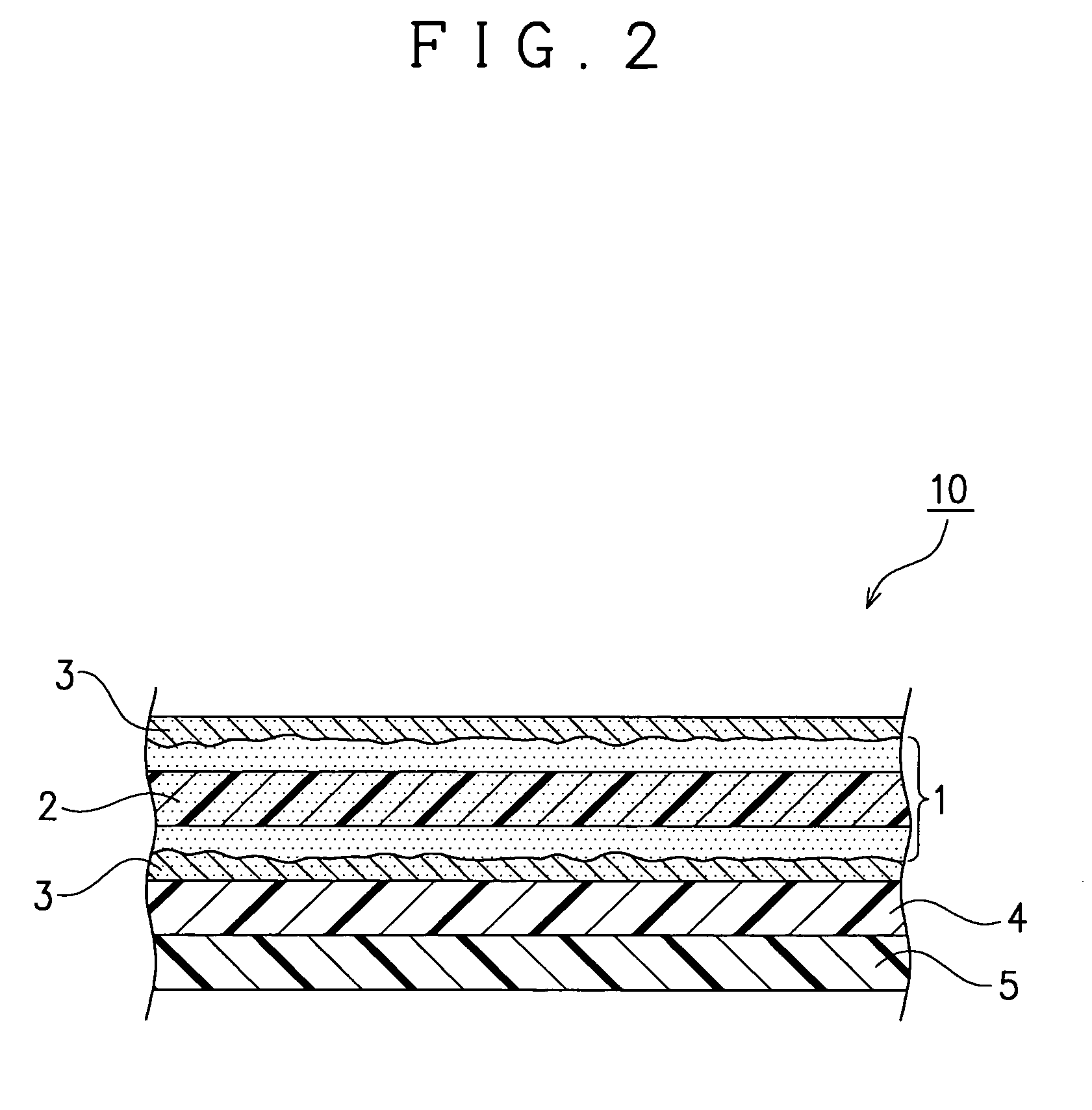
Resin sheet, liquid crystal cell substrate, liquid crystal display device, substrate for an electroluminescence display device, electroluminescence display device, and a substrate for a solar cell
a technology of liquid crystal cells and substrates, applied in the direction of synthetic resin layered products, identification means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of plastic substrates posing a problem of misalignment and relatively low mechanical strength, so as to suppress thermal shrinkage and expansion, improve impact resistance, and prevent misalignment of electrodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
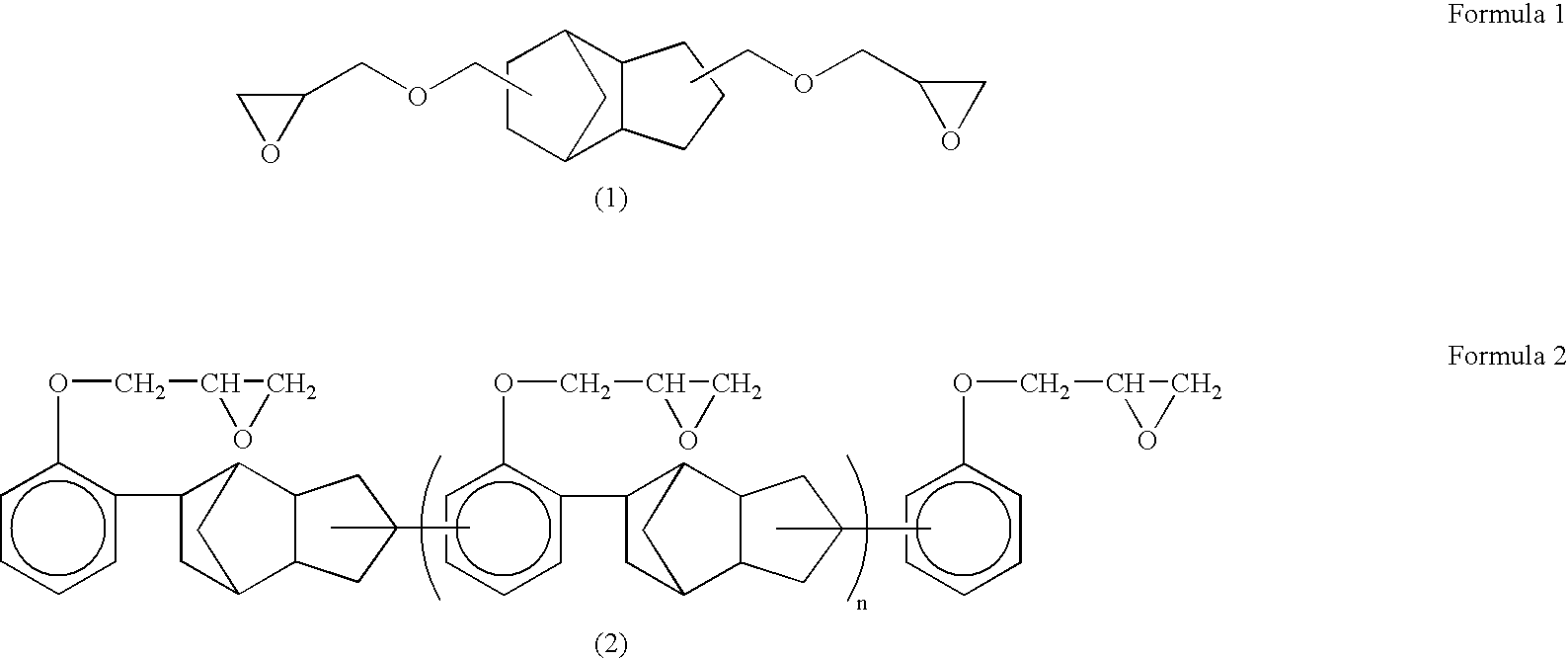
[0082] An epoxy resin liquid was prepared by stirring and mixing: 35.9 parts by weight (hereinafter referred only to parts) of 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3,4-epoxycyclohexane carboxylate represented by the following formula (3) and 10.1 parts of a dicyclopentadiene type epoxy resin (“EXA-7230”, trade name (epoxy equivalent of 259); manufactured by Dainippon Ink And Chemicals, Incorporated) represented by the following formula (4); as a curing agent, 52.9 parts of methylnadic anhydride; and as a curing accelerator, 1.1 parts of tetra-n-butylphosphonium o,o-diethylphosphorodithioate represented by the following formula (5).
[0083] Then, the aforesaid epoxy resin liquid was impregnated into a glass fiber cloth-like material (“NEA2116F S136”, trade name; manufactured by Nitto Boseki Co., Ltd., a refractive index of 1.513, a thickness of 90 μm), and left to stand for 60 minutes under a condition of a reduced pressure (200 Pa).
[0084] Then, a hard-coat layer having a thickness of 2 μm was...
example 2
[0087] A resin sheet was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that, of the resins for forming an overcoat layer, the other oxetane resin (“ARON OXETANE OXT-121”, trade name; manufactured by Toagosei Co., Ltd.) was used as an oxetane resin.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| light transmittance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| light transparency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com