Method for improving carbon dioxide displacement yield by using surfactants
A technology of surfactants and carbon dioxide, applied in chemical instruments and methods, mixing methods, production fluids, etc., can solve the problem of expanding the swept volume, harsh conditions for the use and selection of surfactants, and unclear improvement of oil recovery and other issues to achieve good recovery and enhanced recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0022] Embodiment, surfactant-carbon dioxide composite oil displacement agent and its preparation
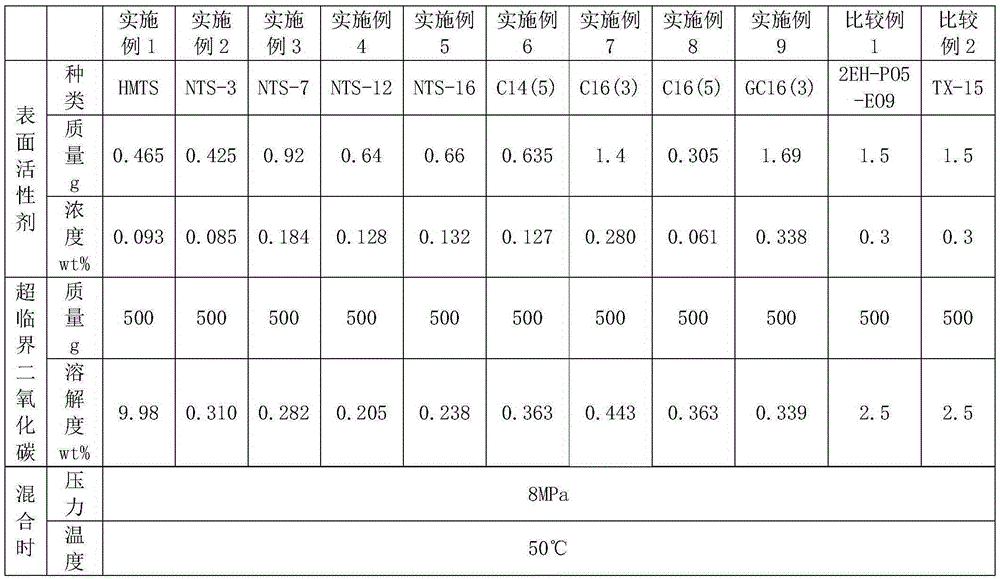
[0023] Each parameter in the method of the present invention is adjusted according to the description in Table 1, and specific examples 1-9 of the method for enhancing the recovery of carbon dioxide flooding by using surfactants are provided.
[0024] The specific method is: mix surfactant and supercritical carbon dioxide according to the ratio of (0.00061:1) to (0.00338:1) in mass ratio to obtain surfactant-carbon dioxide composite oil displacement agent (fluid), and then the composite flooding The oil agent is injected into the oil reservoir.
[0025] Considering the critical point of carbon dioxide (pressure 7.4MPa, temperature 31.2° C.), the selected pressure is 8 MPa and the temperature is 50° C. during the mixing of the examples. Of course, other values above the critical point of carbon dioxide can theoretically complete the preparation of surfactant-carbon dioxide com...
experiment example 1
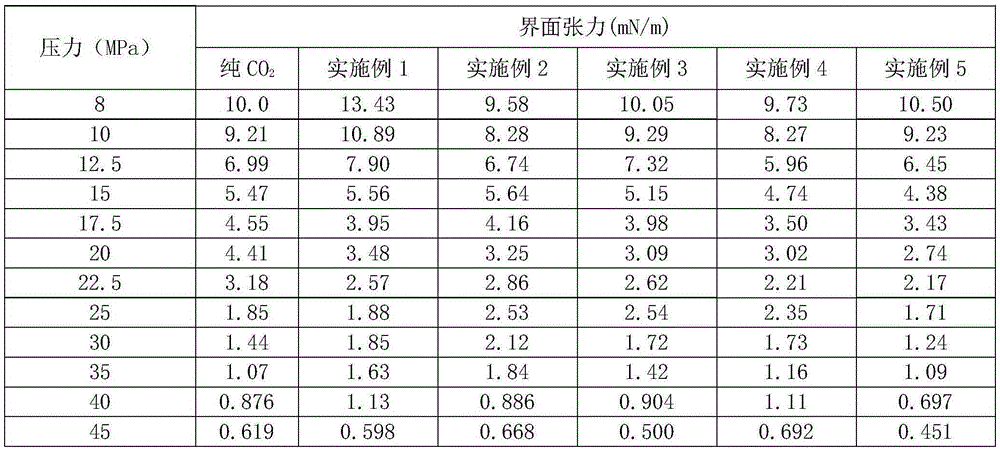
[0033] Experimental example 1. Interfacial tension experiment with crude oil
[0034] Use a high-pressure carbon dioxide interfacial tension meter to measure the interfacial tension between carbon dioxide and crude oil after adding a surfactant at 86°C (the oil layer temperature of the No. 8 Oil Production Plant of Daqing Oilfield), and set the pressure when the interfacial tension is zero to be the minimum miscible pressure for one contact. Test Methods as below:
[0035] (1) Turn on the high-pressure carbon dioxide injection system, turn on the oil container heating and pipeline heating.
[0036] (2) Turn on the heating in the kettle and turn on the photographic light source.
[0037] (3) Start the software, capture the image, correct the image magnification, and adjust the image definition.
[0038] (4) Add the surfactant to be tested into the heating and stirring apparatus, add a certain amount of carbon dioxide (to a container pressure slightly higher than 8MPa), and st...
experiment example 2
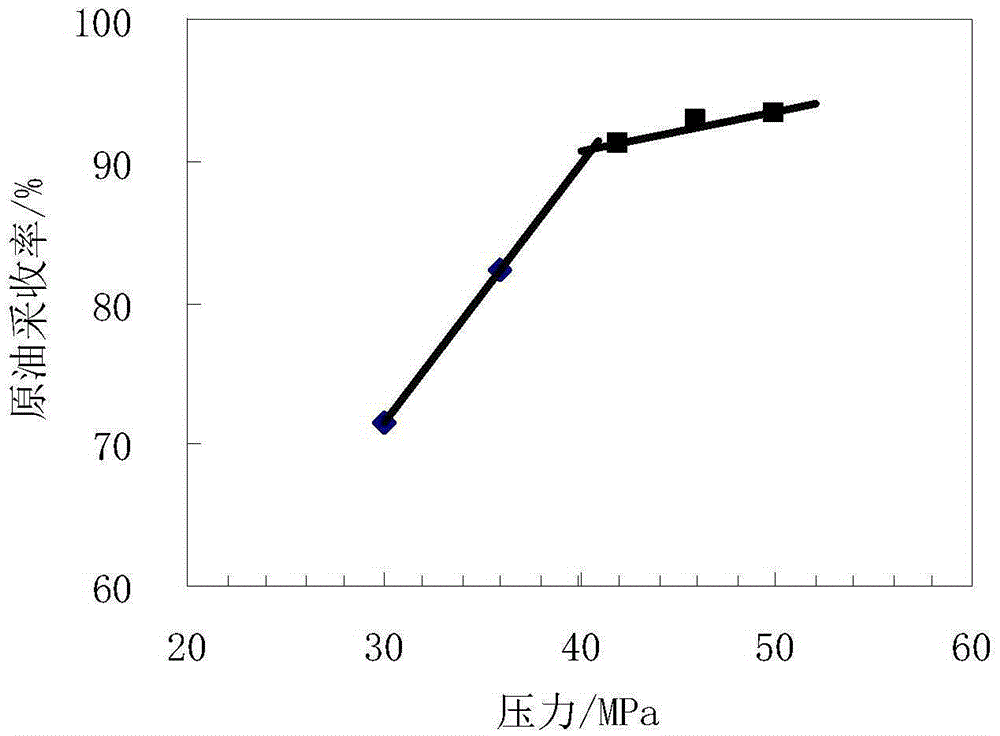
[0053] Experimental example 2: Slim tube displacement experiment with crude oil
[0054] The supporting device of the thin tube displacement experiment was used to measure the oil recovery rate of carbon dioxide flooding under different pressure conditions at 86°C, and the minimum miscible pressure of multiple contact was defined as the pressure when the oil recovery rate exceeded 90%. The data in Table 5 were used to simulate The minimum miscible pressure is calculated together, see Table 6, and the test method is as follows:
[0055] (1) According to the high-pressure physical properties of formation oil, natural gas and degassed crude oil were used to prepare formation oil at 85.9 °C, and its high-pressure physical properties were measured.
[0056] (2) After heating the thin tube to a constant temperature, evacuate it, press the prepared saturated oil sample into the thin tube model with a constant pressure pump, stop the pump when the pump is 2PV, and record the volume of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com