Sintering method and apparatus for rare earth neodymium-iron-boron magnet
A technology of rare earth NdFeB and NdFeB, which is applied in the direction of magnetic objects, magnetic materials, inductors/transformers/magnets, etc., can solve the problems of difficult cooling of graphite boxes, improve material utilization, prevent sticking, reduce The effect of oxidation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
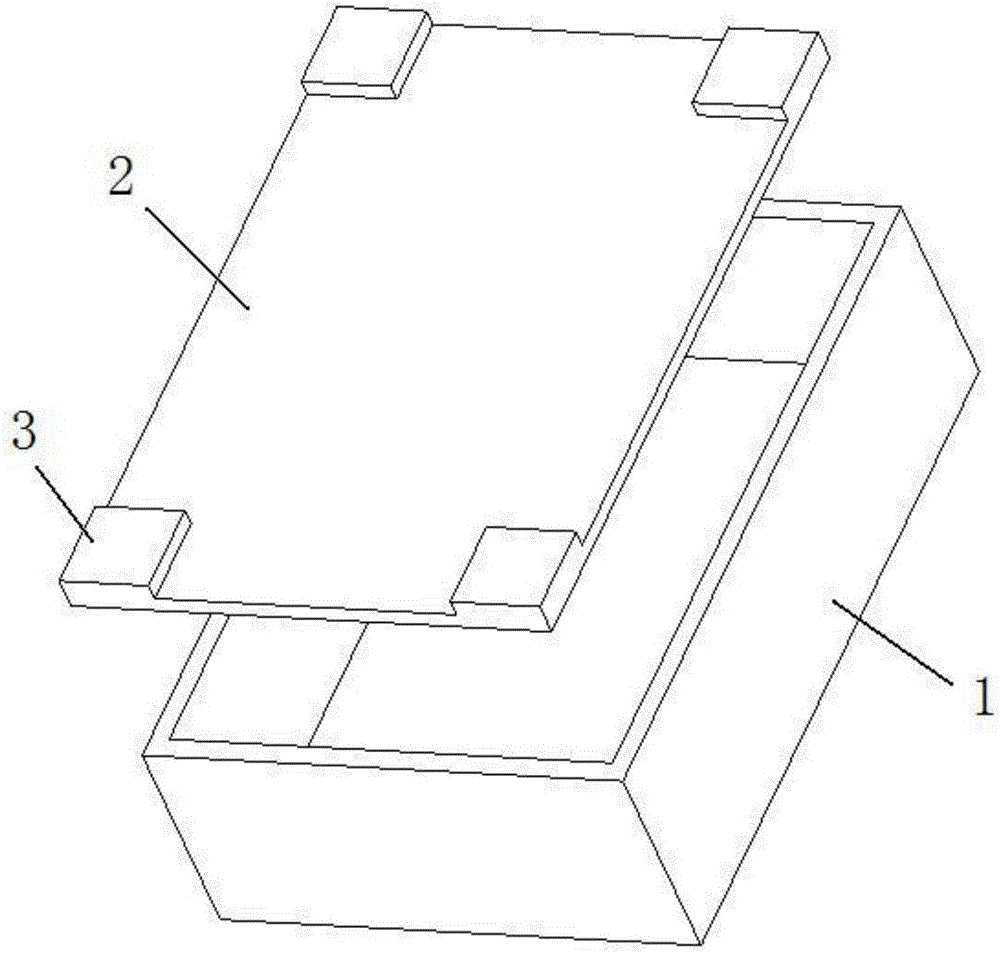
[0028] (1) The specification of graphite box 1 is 280mm×210×60mm, and the four corners of graphite box cover plate 2 have a height of 8mm (such as figure 1 shown).
[0029] (2) The graphite box 1 and the graphite box cover plate 2 were baked in an oven at 60° C. for 24 hours.
[0030] (3) Evenly spread a layer of high-temperature-resistant zirconia powder with an average particle size of 20um on the bottom of the graphite box 1.
[0031] (4) Place the rare earth NdFeB magnet product 4 in the graphite box 1, and evenly spread a layer of high-temperature-resistant zirconia powder with an average particle size of 20um on the contact surface between the product and the product.
[0032] (5) NdFeB waste powder with a particle size of 3.8um is placed in the gap of the graphite box 1 .
[0033] (6) Put the loaded product into the sintering furnace model VS-300RPA (rated furnace capacity 300Kg), the vacuum degree is 5×10 -2 pa, the temperature is 1060-1100°C, the sintering time is ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] This example is based on Example 1. When the products are superimposed and fired, the high-temperature-resistant zirconia powder with an average size of 20um is compared with that without it. After sintering with zirconia powder, there is no sticking between the products The junction and integrity are good and the magnetic properties remain basically unchanged. The products without zirconia powder are bonded to each other.
Embodiment 3
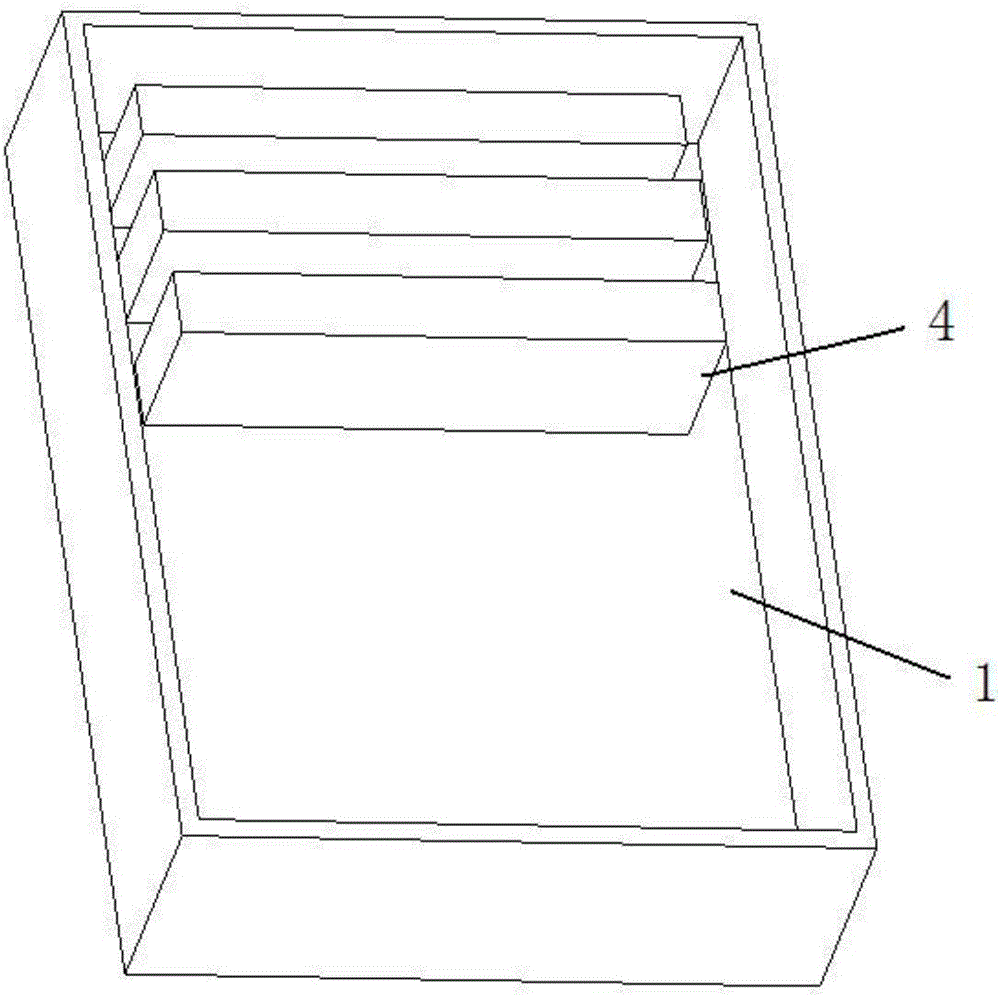
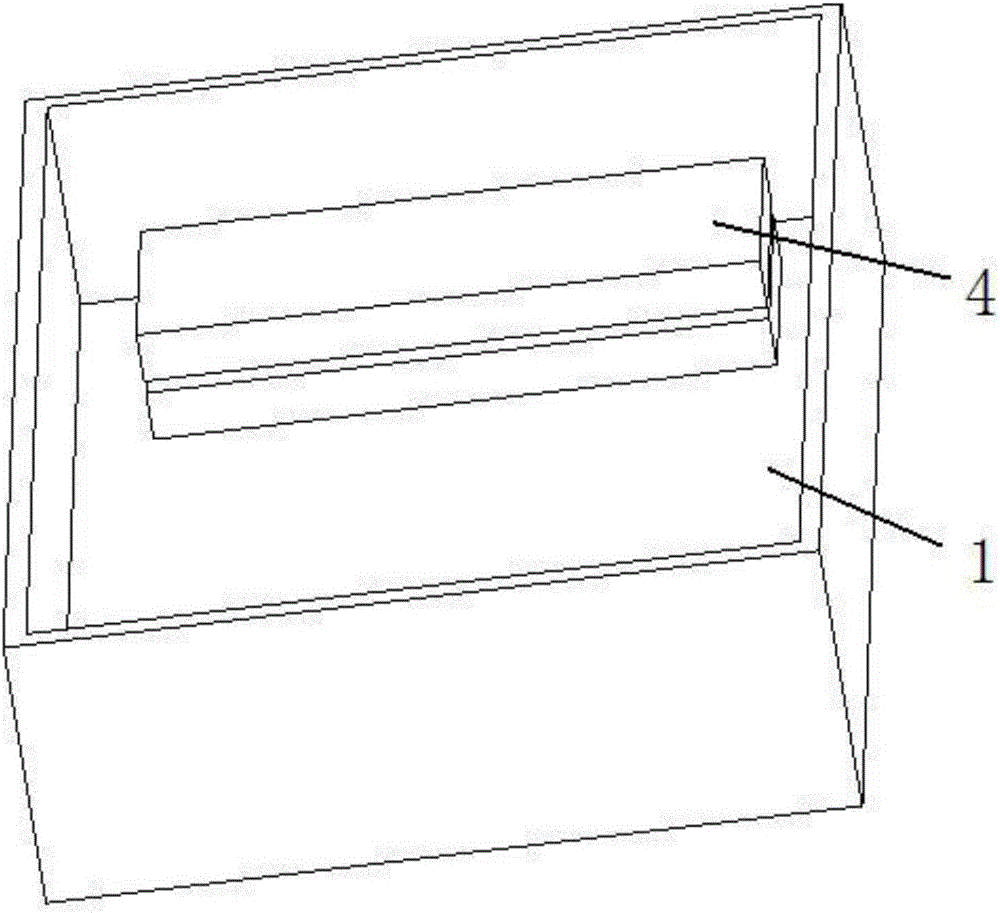
[0041] The present embodiment is on the basis of embodiment one and embodiment two, and product charging is compared, wherein: figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of the superimposed product loading and firing structure in this embodiment, image 3 Schematic diagram of the loading and firing structure for traditional stacked products. Carry out dimension detection, and the measurement results are shown in Table 2. Comparing the two groups of measurement data, it can be known that after using the method of this embodiment, the machining allowance reserved for each surface of the product can reduce the dimensional deformation by about 0.6mm on average, which can reduce the dimensional deformation due to The ratio of cracking and corner loss caused by sintering improves the product yield.
[0042] Table 2: Size detection after sintering in different loading and firing methods (unit: mm)
[0043]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com