Wireless charging receiver end and manufacturing method thereof
A technology of wireless charging and manufacturing method, which is applied in the direction of circuits, inductors, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of increased internal resistance of coils, waste of copper foil, and increased AC resistance, and achieve overall thickness reduction, reduced loss, and increased effect of diameter
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
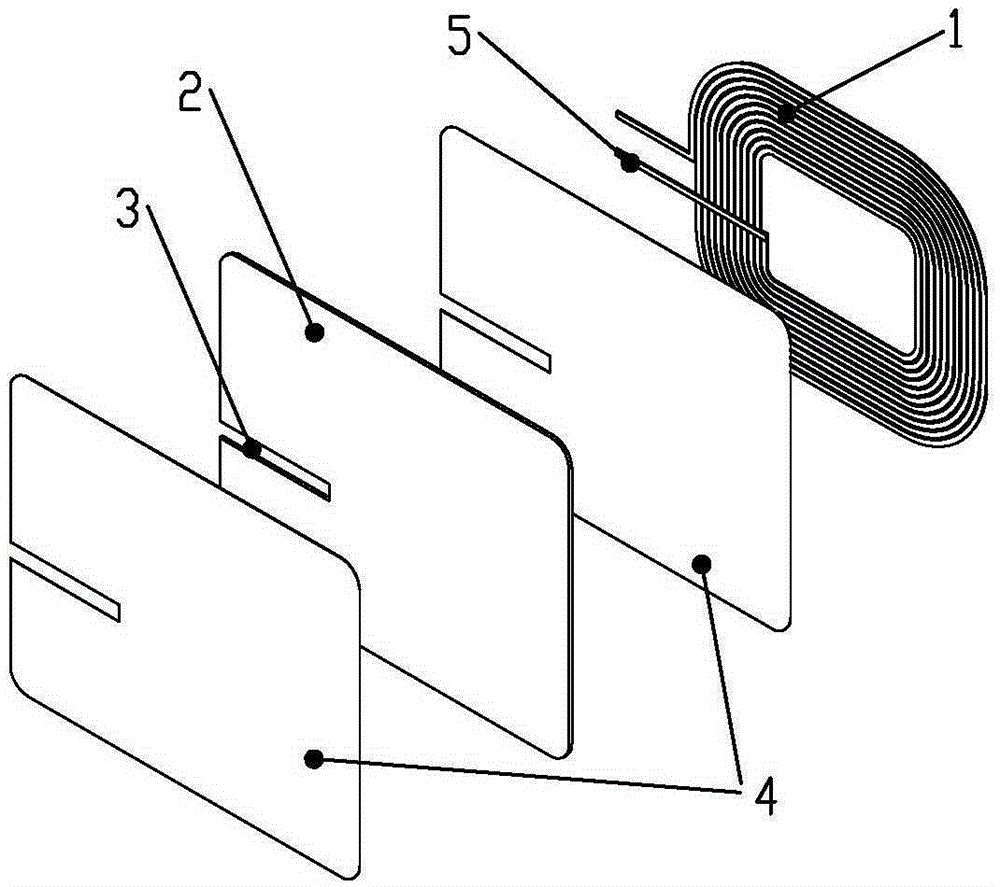
[0041] Method Embodiment 2: A method for manufacturing a wireless charging receiving end. In this embodiment, a planar coil is fabricated on a single-sided FPC, including the following steps:
[0042] A. Processing of receiving coil
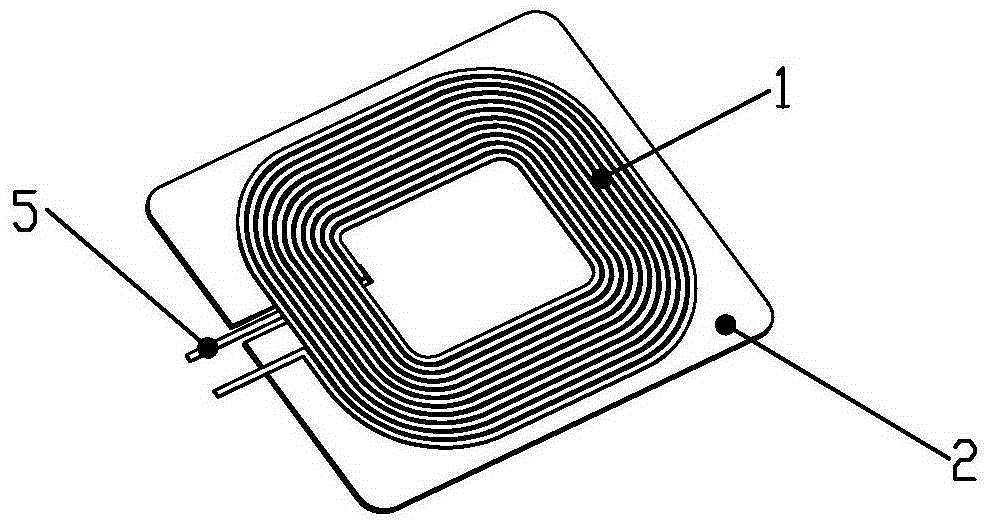
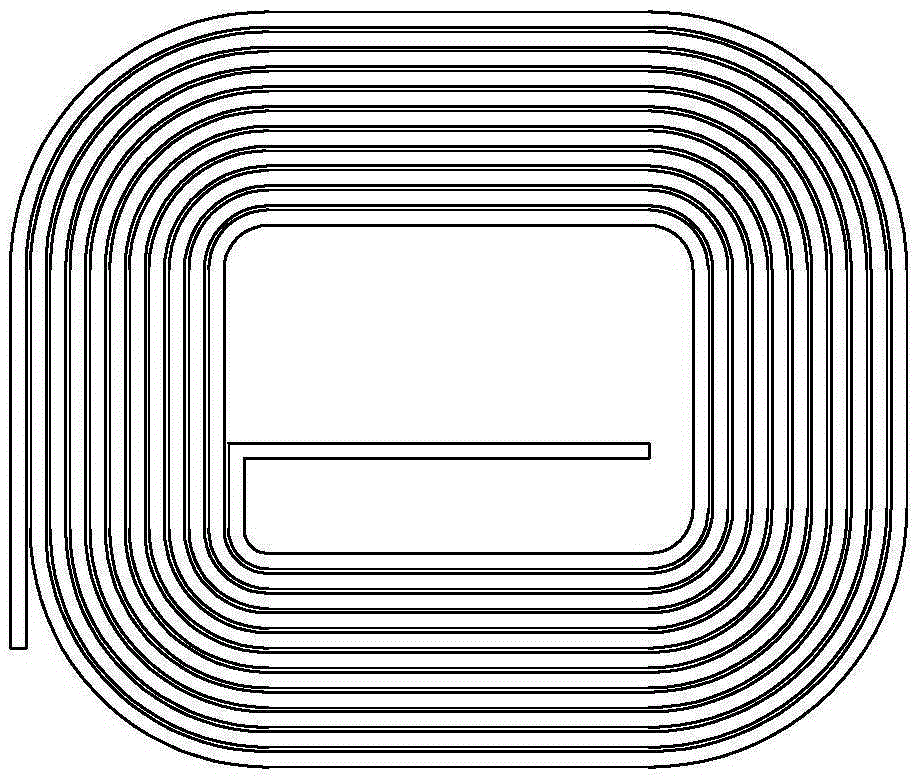
[0043] A1. Process the planar coil and the inner and outer lead-out lines on the single-sided flexible circuit board FPC, wherein the outer lead-out lines are directly set at the lead-out position and extend outward from the outermost circle of the planar coil (such as Figure 4 shown);
[0044] A2. Cut the three edges where the inner lead wire and the coil are not connected;
[0045] A3. Insulate the part where the cut inner lead wire is in contact with the coil main body;
[0046] A4. Fold the inner lead wire after insulation treatment to the surface of the coil. The bending angle can be any angle according to the needs, preferably 90° or 45°, so that the outgoing wire directions of the inner and outer lead wires are consistent;
[0047] B. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com