Method for repairing lead-polychlorinated biphenyl combined pollution soil through halophytes kochia scoparia (L.) Schrad.
A polychlorinated biphenyl and compound pollution technology, applied in the field of phytoremediation, achieves low technical requirements, strong adaptability, and the effect of improving soil degradation and productivity decline
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
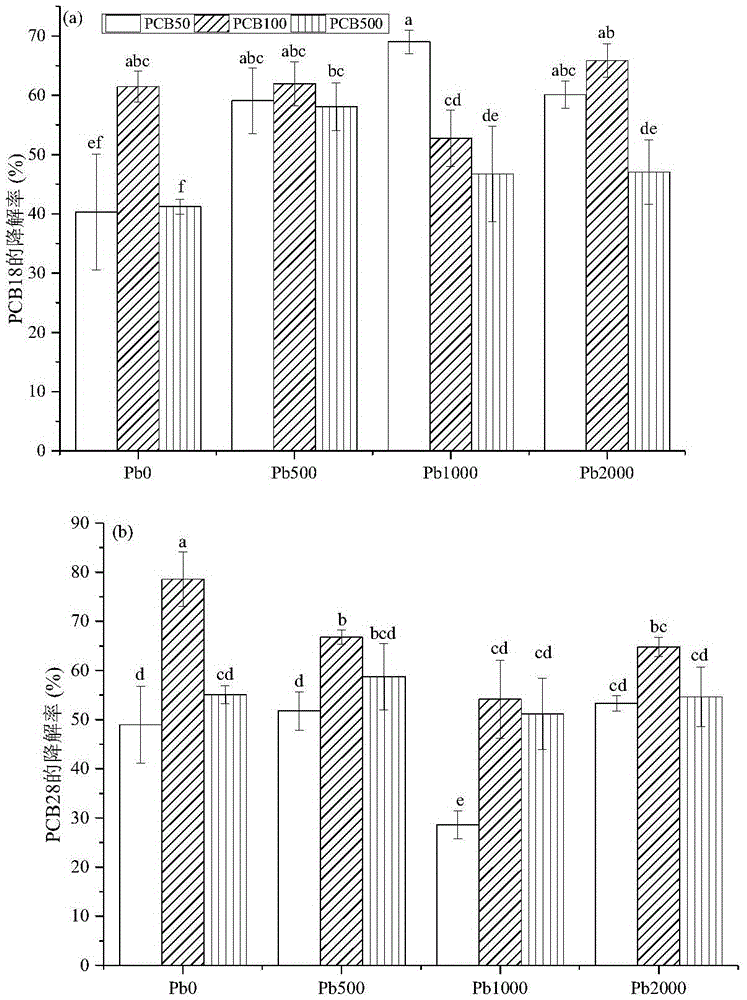
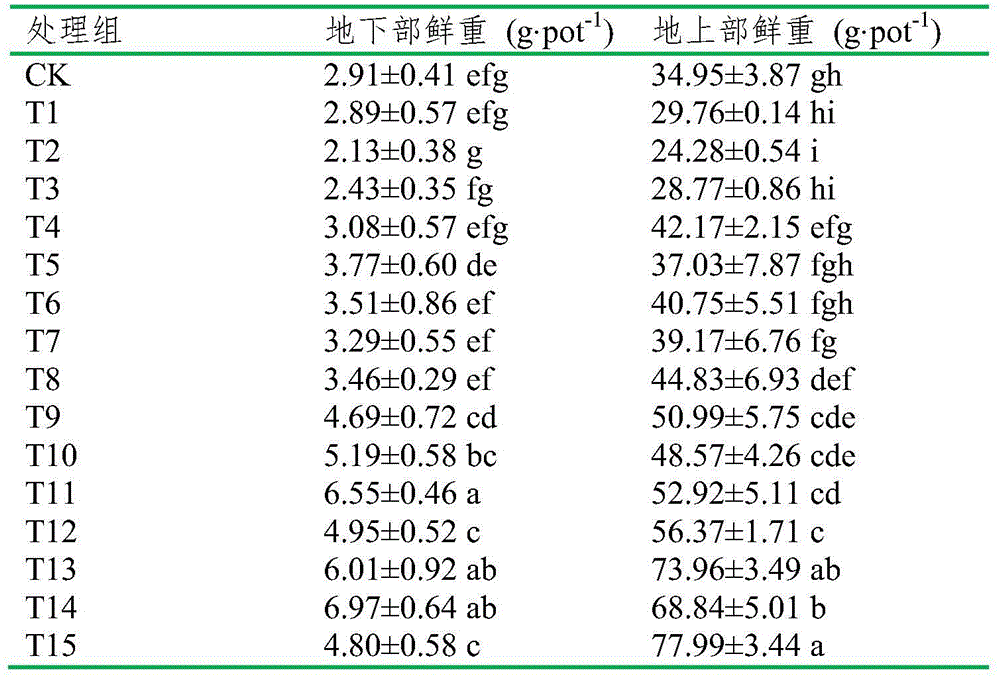
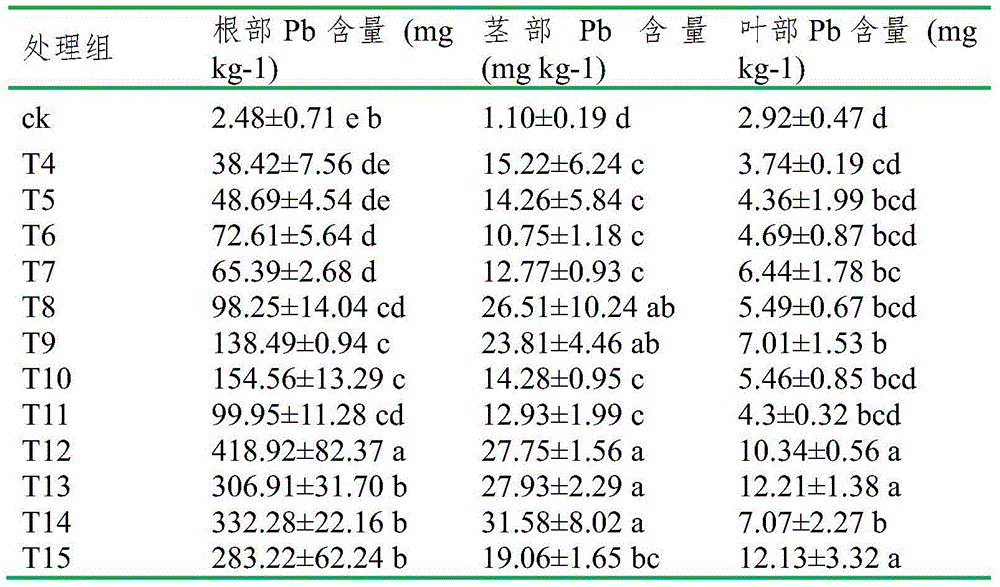
[0018] Example 1: Kochia remediation lead-polychlorinated biphenyl compound polluted soil experiment
[0019] The experimental site is in the greenhouse of Nankai University TEDA College, and the pollution sources around the experimental site. The experimental soil is the top soil (0-20cm) of the forest park in Tanggu District, Tianjin, and the soil type is coastal saline soil. In this experiment, 16 treatment groups were set up, each treatment was repeated 3 times, and the concentration of Pb-PCBs was 0-0 (CK), 0-50 (T1), 0-100 (T2), 0-500 (T3) , 500-0(T4), 500-50(T5), 500-100(T6), 500-500(T7), 1000-0(T8), 1000-50(T9), 1000-100(T10), 1000-100(T11), 2000-0(T12), 2000-50(T13), 2000-100(T14), 2000-500(T15), concentration of pollutants added in each treatment group ρPb-ρPCBs, Pb concentration unit mgkg -1 , PCBs concentration unit is μg kg -1 , where Pb is analytically pure Pb (NO 3 ) 2 , PCBs were added in the form of standard PCB18 and PCB28 with a concentration ratio of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com