Low-melting-point alloy and preparation method thereof
A low melting point, alloy technology, applied in the field of alloys, can solve the problems of high electrical conductivity and low melting point, achieve the effects of excellent electrical conductivity, increase the viscosity of the alloy, and reduce the melting point of the alloy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] This embodiment discloses a Ga-In-Sn-Cd-Zn plasticine low-melting alloy whose general formula is GaInSnCd 1.5 Zn.
[0031] GaInSnCd 1.5 The preparation method of Zn alloy is as follows: take Ga, In, Sn, Cd and Zn raw material according to the molar ratio of design, wherein Ga, In, Sn, Cd, Zn all select the industrial grade pure raw material that purity is more than 99wt% for use, then use Vacuum high frequency induction furnace for vacuum melting. When smelting alloys, the volatile raw materials Cd and Zn with lower boiling points are placed at the bottom, and Ga, In and Sn materials with higher boiling points are placed at the top to reduce volatilization during smelting. When the high-frequency induction furnace is evacuated to a vacuum degree of 5×10 -3 At Pa, backflush argon until the vacuum gauge reads -0.05 to -0.03Pa and then start melting; the melting temperature is about 425 degrees Celsius, and the melting time is about 1 minute. After melting, a homogeneo...
Embodiment 2
[0034] This embodiment discloses a Ga-In-Sn-Cd-Zn plasticine low-melting alloy whose general formula is GaInSnCdZn 1.5 .
[0035] The preparation method of the low-melting point alloy is as follows: Ga, In, Sn, Cd and Zn raw materials are weighed according to the designed molar ratio, wherein Ga, In, Sn, Cd, Zn are all selected as industrial-grade pure raw materials with a purity of more than 99 wt%, and then It adopts vacuum high-frequency induction furnace for vacuum melting. When smelting alloys, the volatile Cd and Zn raw materials are placed at the bottom, and the raw materials Ga, In and Sn are placed at the top to reduce volatilization. The high-frequency induction furnace is evacuated to a vacuum degree of 5×10 -3 At Pa, backflush argon until the reading of the vacuum gauge is -0.05Pa and then start melting; the melting temperature is about 425 degrees Celsius, and the melting time is about 1 minute. GaInSnCdZn can be freely deformed at room temperature 1.5 Alloys w...
Embodiment 3
[0038] This embodiment discloses a Ga-In-Sn-Cd-Zn plasticine low-melting alloy whose general formula is GaInSnCdZn 2.2 .
[0039] The preparation method of the low-melting point alloy of this embodiment is the same as that of Examples 1 and 2.
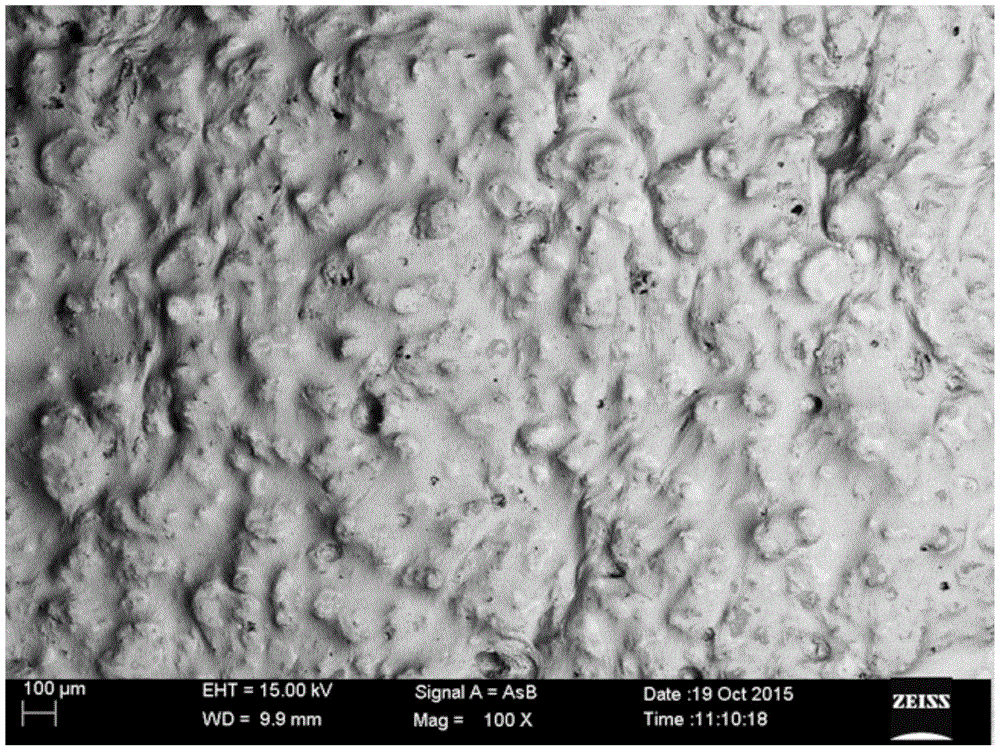
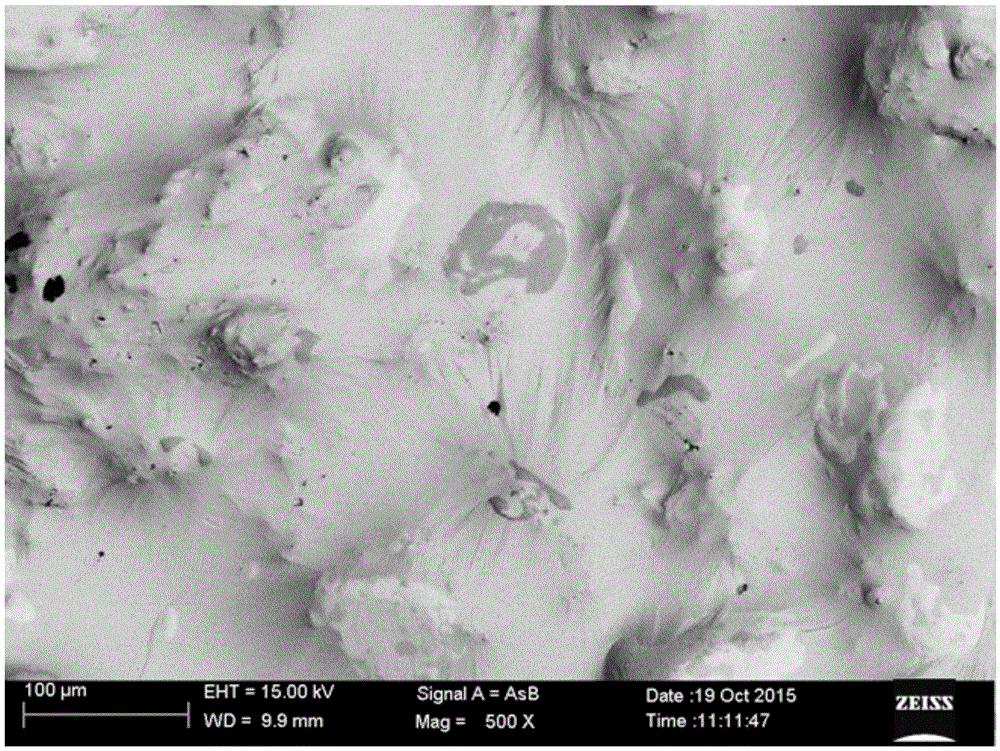
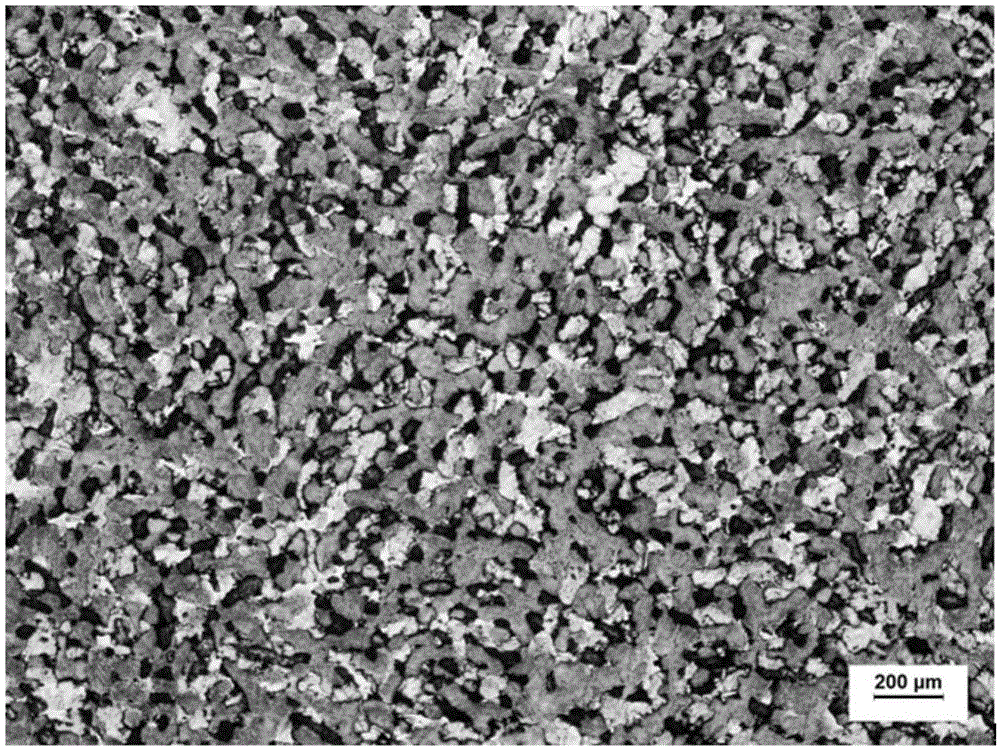
[0040] GaInSnCdZn that can be deformed arbitrarily at room temperature in this example 2.2 The 1000X scanning electron microscope structure picture of the low melting point alloy is as follows Figure 8 visible, Figure 8 It can be seen in GaInSnCdZn 2.2 The alloy is a mixture of multiphases with different colors, and it can be seen that the deformed alloy still has a pattern similar to river flow, which also shows that the deformation of the alloy is also a viscous flow deformation. Figure 9 GaInSnCdZn 2.2 From the DSC curve of the low melting point alloy, it can be seen from the curve that the alloy has a large phase transition peak at about 152.8°C, but it is not completely melted, and the melting point of the alloy should be ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com