Method for selectively and efficiently extracting zinc and removing iron from zinc-containing electric furnace dust
A selective, electric furnace technology, applied to the improvement of process efficiency, etc., can solve the problems of complex leachate purification process, inability to extract zinc ferrite, and trouble metallurgists, etc., to simplify purification and separation complex treatment process, easy to centrifuge Separate, increase the effect of production pathways
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
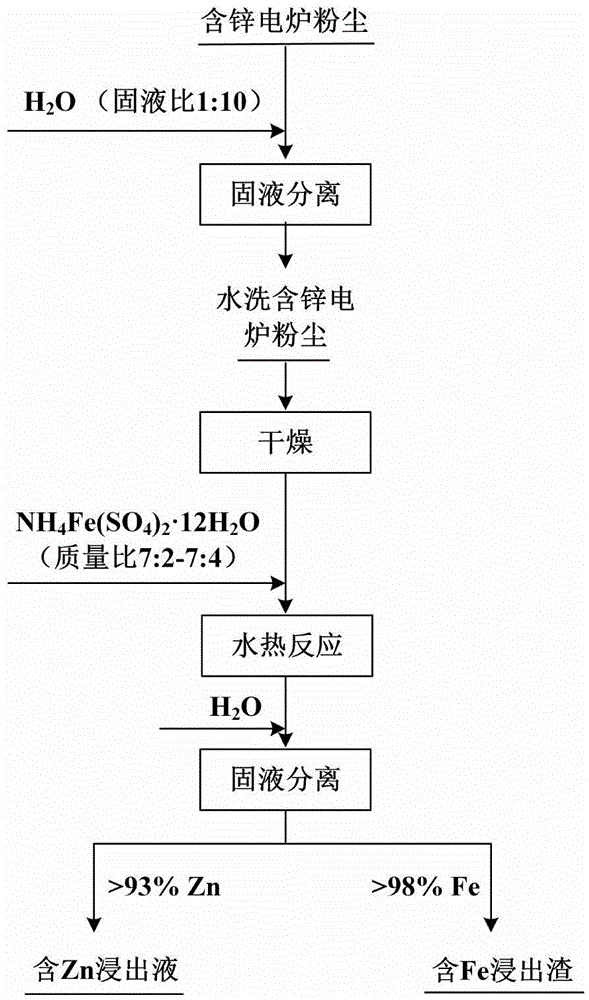
[0023] (1) Mix zinc-containing electric furnace dust and water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g·mL -1 ) were mixed, stirred at room temperature for 12 hours, and then solid-liquid separation was carried out to obtain water-washed zinc-containing electric furnace dust. The zinc-containing electric furnace dust washed with water was dried in an oven at 100° C. for 20 hours.
[0024] (2) The zinc-containing electric furnace dust after washing and drying in the step (1) with ammonium ferric sulfate dodecahydrate is according to mass ratio 7:3 (g·g -1 ) were uniformly mixed, put into a reaction kettle, and reacted hydrothermally at 220° C. for 10 h. After cooling to room temperature, add 80mL of water for solid-liquid separation to obtain zinc-containing leaching solution and iron-containing leaching slag.
Embodiment 2
[0026] (1) Mix zinc-containing electric furnace dust and water according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:10 (g·mL -1 ) were mixed, stirred at room temperature for 10 h, and then separated into solid and liquid. The zinc-containing electric furnace dust washed with water was obtained, and then the zinc-containing electric furnace dust was dried in an oven at 105° C. for 20 hours.
[0027] (2) Washing zinc-containing electric furnace dust after drying in step (1) with ammonium ferric sulfate dodecahydrate according to the mass ratio of 7:3 (g·g -1 ) were uniformly mixed, put into a reaction kettle, and reacted hydrothermally at 220° C. for 12 hours. After cooling to room temperature, add 80mL of water for solid-liquid separation to obtain zinc-containing leaching solution and iron-containing leaching slag.
Embodiment 3
[0029] (1) Mix zinc-containing electric furnace dust and water according to the liquid-solid ratio of 1:10 (g·mL -1 ) were mixed, stirred at room temperature for 11 h, and then solid-liquid separation was carried out. To obtain water-washed zinc-containing electric furnace dust. The zinc-containing electric furnace dust washed with water was dried in an oven at 100°C for 24 hours.
[0030] (2) The zinc-containing electric furnace dust after washing and drying in the step (1) with ammonium ferric sulfate dodecahydrate is according to mass ratio 7:4 (g·g -1 ) were uniformly mixed, put into a reaction kettle, and reacted hydrothermally at 220° C. for 12 hours. After cooling to room temperature, add 100mL of water for solid-liquid separation to obtain zinc-containing leaching solution and iron-containing leaching residue.
[0031] Specific experimental results
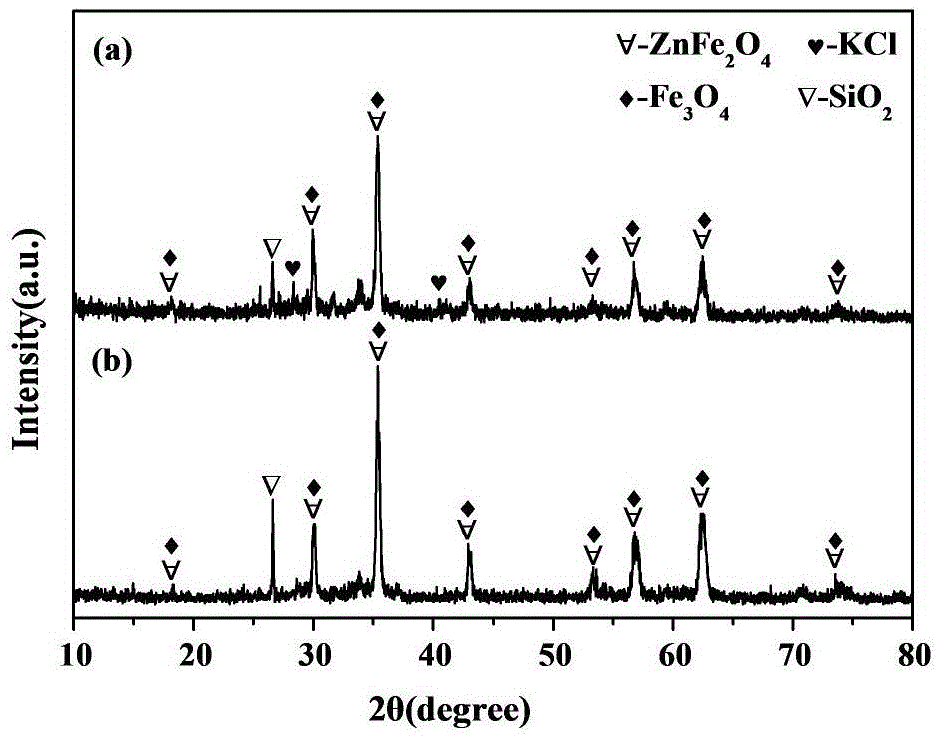
[0032] Under the above experimental conditions, the leaching rate of zinc is high (>93%), while the leaching rate of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com