Cooperative control method of four-wheel independent-drive electric car
A four-wheel independent drive and collaborative control technology, applied in electric vehicles, control drives, vehicle components, etc., can solve the problems of lack of real-time performance and poor self-adaptive ability, improve vehicle handling stability and safety, meet the Strong real-time, fast response effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
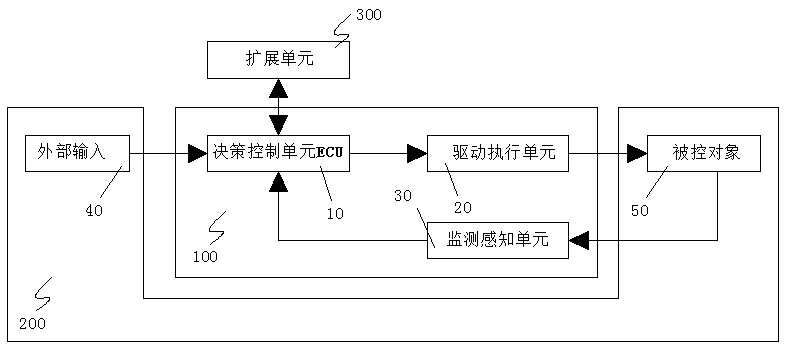
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
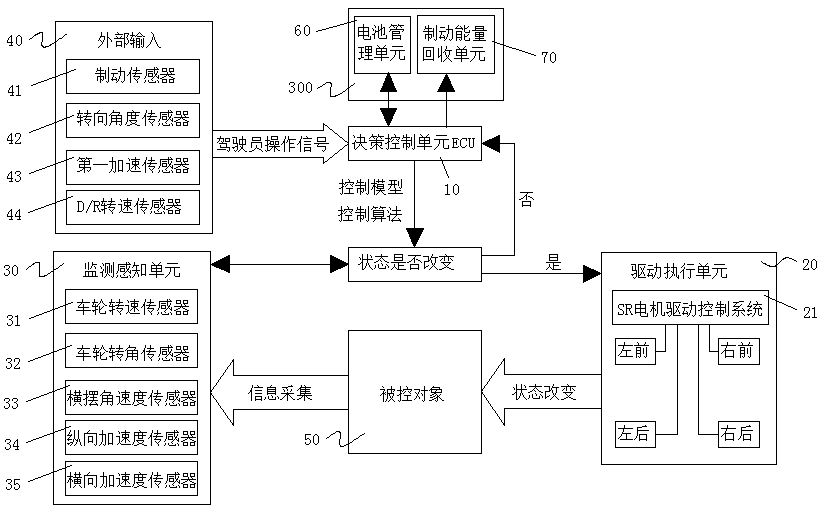
[0057] Embodiment 1, driving in a straight line, including starting acceleration, constant speed, and deceleration;
[0058] Step 1, the steering angle sensor 42 input is 0, the front wheel angle δ f =0, vehicle speed V 0 = 0;
[0059] Step 2, the first acceleration sensor 43 receives the acceleration signal and sends it to the decision-making control unit ECU10;
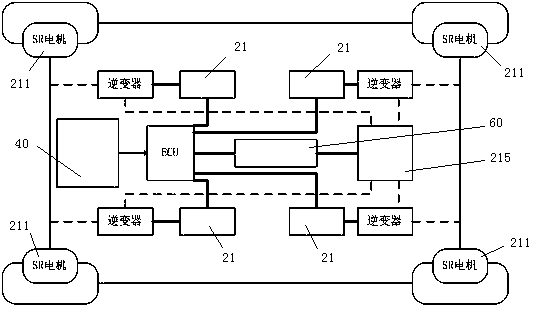
[0060] Step 3: After receiving the acceleration signal, the decision-making control unit ECU10 calls the battery management unit 60 to supply power to the drive execution unit 40, and outputs the desired torque T to the four SR motors 211 according to the set torque distribution strategy 0i , i=1,2,3,4;
[0061] Step 4, each SR motor drive system 21 controls the SR motor 211 to output torque after receiving the instruction;
[0062] Step 5, the monitoring perception unit 30 collects the vehicle speed V 1 (km / h), four wheel speed n i (r / s), i=1, 2, 3, 4, and feed back to the decision-making control unit ECU10, ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment two, turn to, particularly relate to front-wheel steering;
[0069] Step 1, the steering angle sensor inputs δ>0, the vehicle turns left (δ<0, turns right), and the initial velocity of the vehicle is V;
[0070] Step 2, the monitoring and sensing unit 30 collects the vehicle speed V, the yaw rate γ 0 , longitudinal acceleration lateral acceleration Front wheel angle δ 0 , center of mass slip angle β 0 , and sent to the decision-making control unit ECU10;
[0071] Step 3, the decision-making control unit ECU10 calculates the expected yaw rate γ and the expected center-of-mass sideslip angle β according to the formula, for Δγ=γ 0 -γ, △β=β 0 -β for sliding mode variable structure control;
[0072] Step 4, control the vehicle steering according to the driving force distribution strategy: define the sampling interval △t, the yaw acceleration increment
[0073] The driving torque distribution strategy includes the following four points:
[0074] (1), F...
Embodiment 3
[0085] Embodiment 3, reversing; the D / R conversion signal is input externally, and the D gear is switched to the R gear. The D / R conversion sensor 44 receives the shift signal and sends it to the decision-making control unit ECU10. The decision-making control unit ECU10 controls the four SR motors The drive system 21 issues instructions to change the energization sequence of each phase circuit of the SR motor 211 to realize the output of reverse torque and rotational speed, and realize the reverse.
[0086] From the perspective of CPS, the present invention realizes the real-time interaction between the external environment and the internal information environment of the four-wheel independently driven electric vehicle. The decision-making control unit ECU10 completes the calculation and decision-making of real-time information, and the drive execution unit 20 completes the motor torque and For speed control, the SR motor drive control system 21 adopts a control strategy optimize...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com