Rock breaking tool capable of achieving cutting in alternate trajectory
A trajectory and rock-breaking technology, applied in drilling equipment, drilling equipment and methods, earthwork drilling, etc., can solve the problem of high personalized design requirements of PDC bit structure, reduced formation penetration ability of the bit, and poor formation adaptability, etc. problems, to achieve the effect of flexible hydraulic structure of cones, not easy to crack or damage failure, and improve drilling safety.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
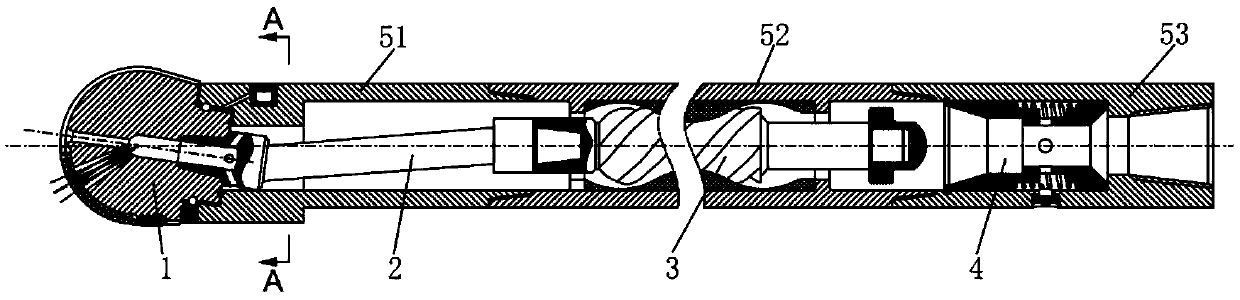
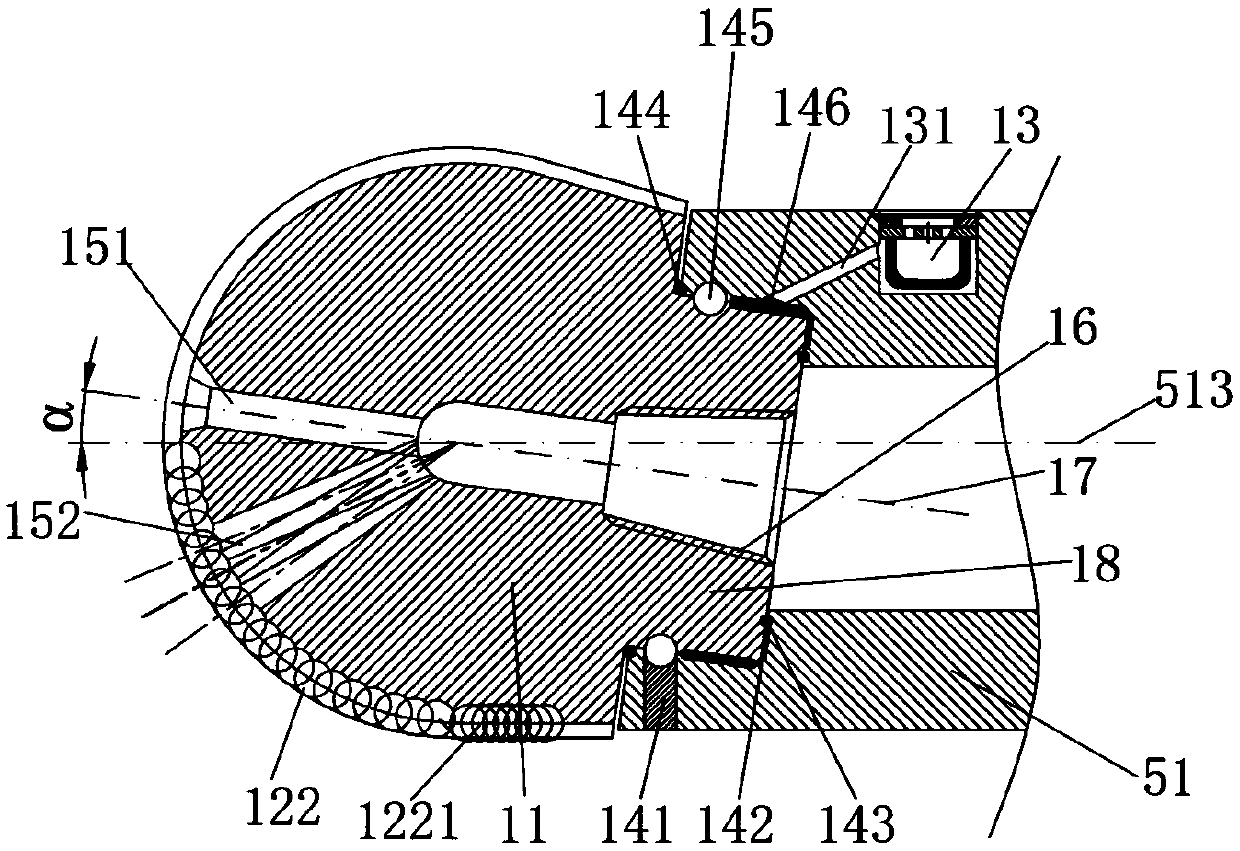
[0057] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 8 , Figure 13 to Figure 20 As shown, a rock-breaking tool with alternating trajectory cutting of the present invention is composed of a drill bit assembly 1, a cardan shaft assembly 2, a screw motor assembly 3, a bypass valve assembly 4, a lower casing 51, a middle casing Body 52 and upper case 53. The drill bit assembly includes a drill bit body 11, a bearing system, a sealing system, and a lubrication system. A plurality of blades 121 are arranged on the bit body 11, and main cutting teeth 122 and gauge teeth 1221 are fixed on the blades 121 as the cutting structure of the present invention. A central nozzle 151 and several side nozzles 152 are also arranged on the drill body 11 , and the flow channels between the blades together constitute the hydraulic structure of the drill body 11 .
[0058] Wherein: the bearing system of the drill bit assembly 1 includes a radial bearing 146, which mainly bears the radial force of the drill bit bod...
Embodiment 2
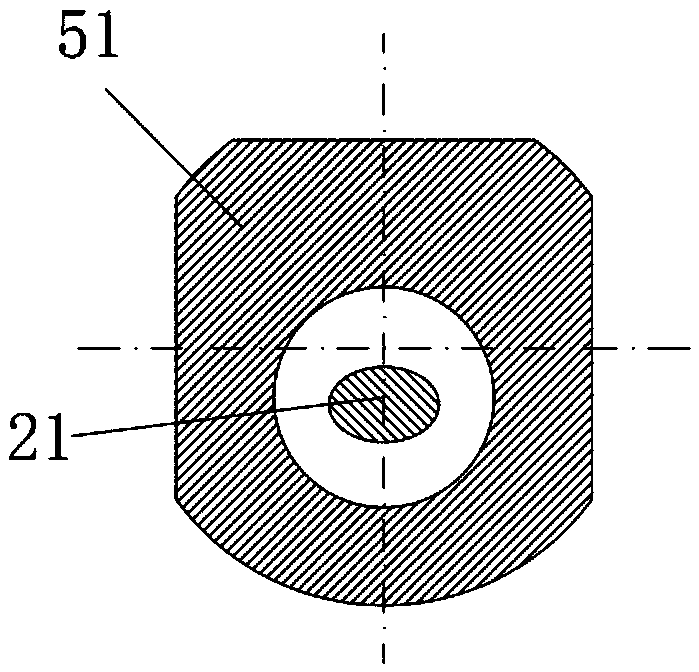
[0073] Such as Figure 9 As shown, this embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the difference is that active gauge teeth 5121 or passive gauge teeth 5122 are provided on the outer peripheral surface of the lower housing 51, or the active gauge teeth 5121 The gauge cloth tooth structure combined with the passive gauge tooth 5122. The active gauge teeth 5121 and the passive gauge teeth 5122 are preferentially made of polycrystalline diamond composite teeth, and may also be carbide cutting teeth, diamond-impregnated cutting teeth, composite teeth with a diamond layer, or other petroleum, natural gas, geological and mining tools. Cutting teeth for rock-breaking drill bits used in drilling engineering.
[0074] The structural scheme proposed in the second embodiment can further enrich the diameter-gauge cutting structure of the present invention, so that it has stronger diameter-gauge ability and drilling stability, thereby further improving the comprehensive workin...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Such as Figure 10 As shown, the present embodiment is basically the same as the second embodiment, the difference being that the drill bit body 11 is composed of two parts of different materials, which are the powder metallurgy material part 11a with the blade structure feature in the lower part, and the shaft part in the upper part. The metallic material portion 11b of the neck structural feature.
[0077] Powder metallurgy material (such as "WC-Co" cemented carbide, etc.) is an alloy material made of hard compound of refractory metal and bonding metal through powder metallurgy process. In the manufacture of PDC drill bits, powder metallurgy materials are commonly used to make the body structure of the drill bit, which has the advantages of high hardness, good wear resistance, and strong erosion resistance. PDC drill bits with the characteristics of this material are often used in high-hardness, high-abrasive dense formations. In this embodiment, the part 11a with t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com