Method for controlling iron scale structures of hot-rolled steel bars by stepped cooling
A technology of iron oxide scale and cooling control, which is applied in rolling mill control devices, metal rolling, temperature control, etc., and can solve the problems of steel bar corrosion speed and serious corrosion degree
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] 1) The internal control chemical composition of test steel bar 1: C0.22%, Si0.41%, Mn1.18%, P0.033%, S0.018%, Cr0.011%, Ni0.006%, V0.002%, Fe balance.
[0035] 2) Hot rolling is carried out after conventional heating of the billet, the rolling specification is Φ20mm, the billet heating temperature is 1150°C, the furnace temperature is 1100°C, the rolling start temperature is 1070°C, and the final rolling temperature is 1050°C;
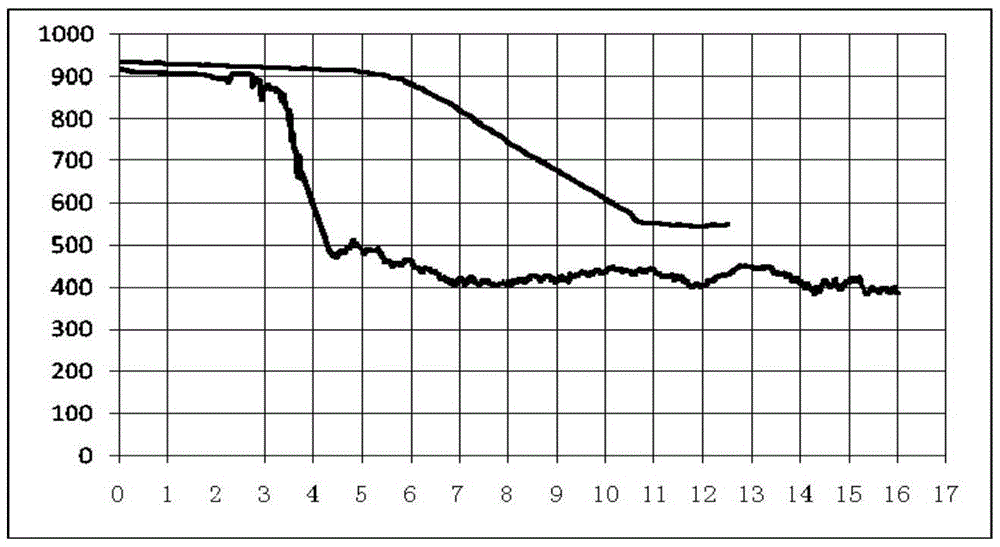
[0036] 3) After the final rolling, the steel bar runs at a speed of 14.0m / s, and the surface of the steel bar is subjected to rapid cooling treatment for 2s, and the average cooling rate V cooling ≥100°C / s; using the step-by-step controlled cooling method of fast cooling-return temperature-quick cooling-return temperature cycle, the return temperature of the upper cooling bed is controlled at 600-680°C;
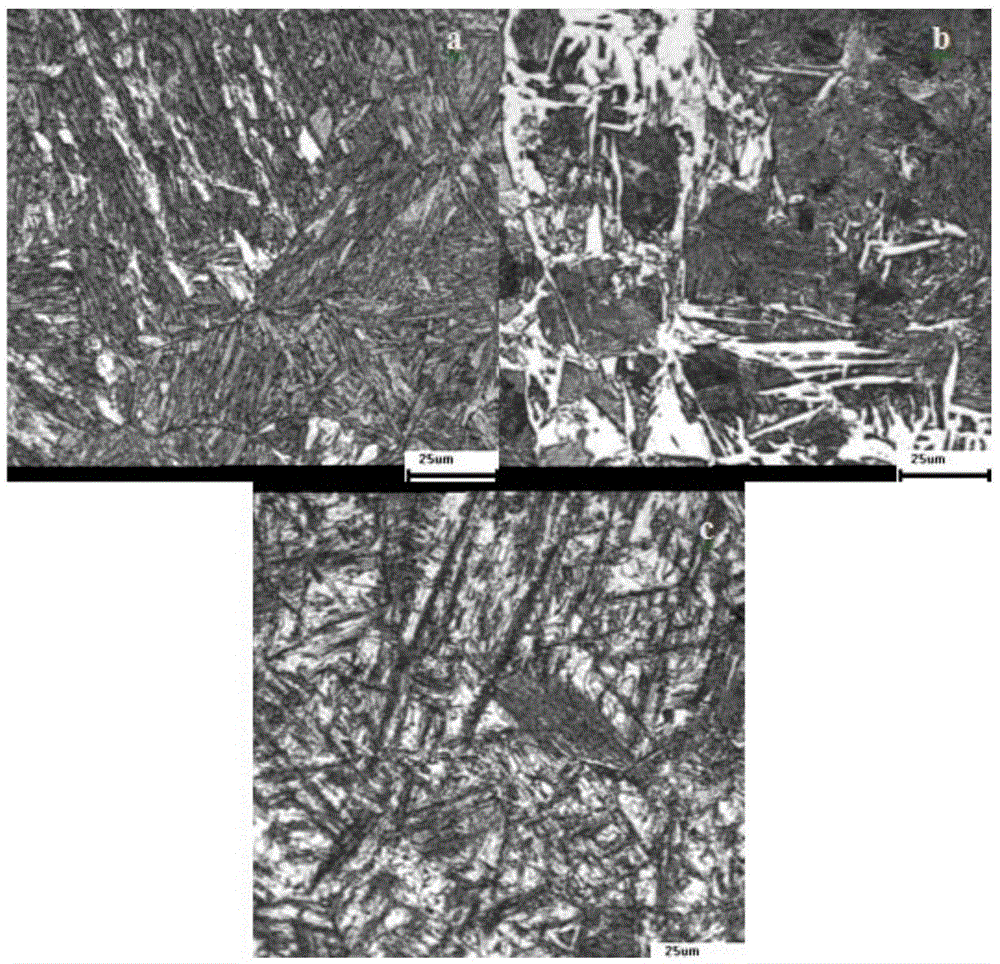
[0037] 4) For all the hot-rolled high-strength steel bars that adopt the staged cooling process, there is no red Fe on the surface after the co...
Embodiment 2
[0040] 1) The chemical composition of industrial test steel bars: C0.23%, Si0.44%, Mn1.39%, P0.035%, S0.030%, V0.032%, Fe balance.
[0041] 2) Hot rolling is performed on the slab after conventional heating, the rolling specification is Φ25mm, and the final rolling temperature is controlled at 1050°C;
[0042] 3) After the final rolling, the steel bar runs at a speed of 11.5m / s, and the surface of the steel bar is subjected to rapid cooling treatment for 2s, and the average cooling rate V cooling ≥100°C / s; using the staged controlled cooling method of fast cooling-return temperature-fast cooling-return temperature cycle, the return temperature of the upper cooling bed is controlled to be 770-980°C;
[0043] 4) There is no surface red Fe after the cooling bed 2 o 3 rust layer.
Embodiment 3
[0045] 1) Chemical composition of test steel bar 1: C0.25%, Si0.34%, Mn1.44%, P0.031%, S0.031%, Cr0.037%, Fe balance.
[0046] 2) Hot rolling is performed on the slab after conventional heating, the rolling specification is Φ20mm, and the final rolling temperature is controlled at: 1050°C;
[0047] 3) After the final rolling, the steel bar runs at a speed of 11.5m / s, and the surface of the steel bar is subjected to rapid cooling treatment for 2s, and the average cooling rate V cooling ≥100°C / s; using the step-by-step controlled cooling method of fast cooling-return temperature-quick cooling-return temperature cycle, the return temperature of the upper cooling bed is controlled at 680-770°C;
[0048] 4) For all the hot-rolled high-strength steel bars that adopt the staged cooling process, there is no red Fe on the surface after the cooling bed 2 o 3 rust layer.
[0049] 5) Placed in the open air for 1 month, the corrosion area is equivalent to 50% of the corrosion area of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com