Conductive treatment and oxide treatment method for continuous non-metal strip
A non-metallic, conductive technology, used in metal material coating process, fiber processing, electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of decreased conductivity and aesthetics, easy oxidation and discoloration of the surface, poor decoration, etc., to achieve beautiful decorative effects, Good wear and corrosion resistance, high hardness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
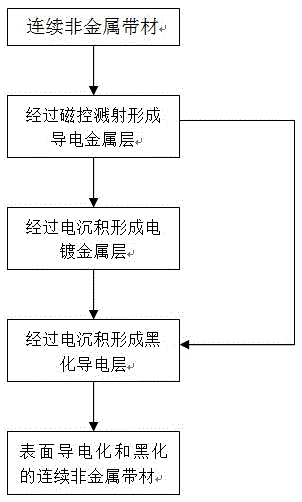
[0026] A continuous polyester polyurethane foam sponge is used as the substrate. The average pore diameter of the selected sponge is 200 μm and the thickness is 0.5 mm. First, a layer of Ni is deposited on the substrate as a conductive metal layer using vacuum magnetron sputtering technology. The average thickness of the layer is 500nm, and the process parameters used in the magnetron sputtering process are: the strip speed is 0.1 m / min, the target power density applied per decimeter target width is 0.6 kilowatts, and then the magnetron sputtering A Ni-Sn blackened conductive layer is formed on the obtained conductive metal layer through an electrodeposition process, and the average thickness of the blackened conductive layer is 5nm, thereby obtaining a continuous non-metallic strip with a conductive and blackened surface.
Embodiment 2
[0028] A continuous polyether polyurethane foam sponge is used as the substrate. The average pore diameter of the selected sponge is 1000 μm and the thickness is 7.0 mm. First, a layer of Ni-Cu alloy is deposited on the substrate by vacuum magnetron sputtering technology as a conductive metal layer. , the average thickness of the conductive metal layer is 300nm, the process parameters used in the magnetron sputtering process are: the strip travel speed is 10 m / min, the target power density applied per decimeter target width is 0.8 kilowatts, and then in the magnetic On the conductive metal layer obtained by controlled sputtering, a composite blackened conductive layer consisting of two types of blackened conductive layers, Ni-Zn and Ni-Sn-S, is formed by two electrodeposition processes. The average thickness of the composite blackened conductive layer is 500nm. Thus, a continuous non-metallic strip whose surface is conductive and blackened is obtained.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Use continuous non-woven fabric as the substrate, the thickness of the selected non-woven fabric is 0.02mm, first use vacuum magnetron sputtering technology to deposit a layer of Cu on the substrate as a conductive metal layer, the average thickness of the conductive metal layer is 50nm, the magnetic The process parameters used in the controlled sputtering process are: the strip travel speed is 20 m / min, the target power density applied per decimeter target width is 1 kW, and then the conductive metal layer obtained by magnetron sputtering is passed through two The secondary electrodeposition process forms a composite blackened conductive layer consisting of two types of blackened conductive layers, Ni-Cu-Sn and Ni-Zn-S. The average thickness of the composite blackened conductive layer is 300nm, thereby obtaining a surface conductive and blackened Chemicalized continuous non-metallic strip.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com