An In Vitro Method for the Label-Free Determination of the Cell Type of Cells
A cell-type technology, applied in the direction of individual particle analysis, using optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as limited reproducibility, low sample throughput, and continuous efforts to immobilize cells
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
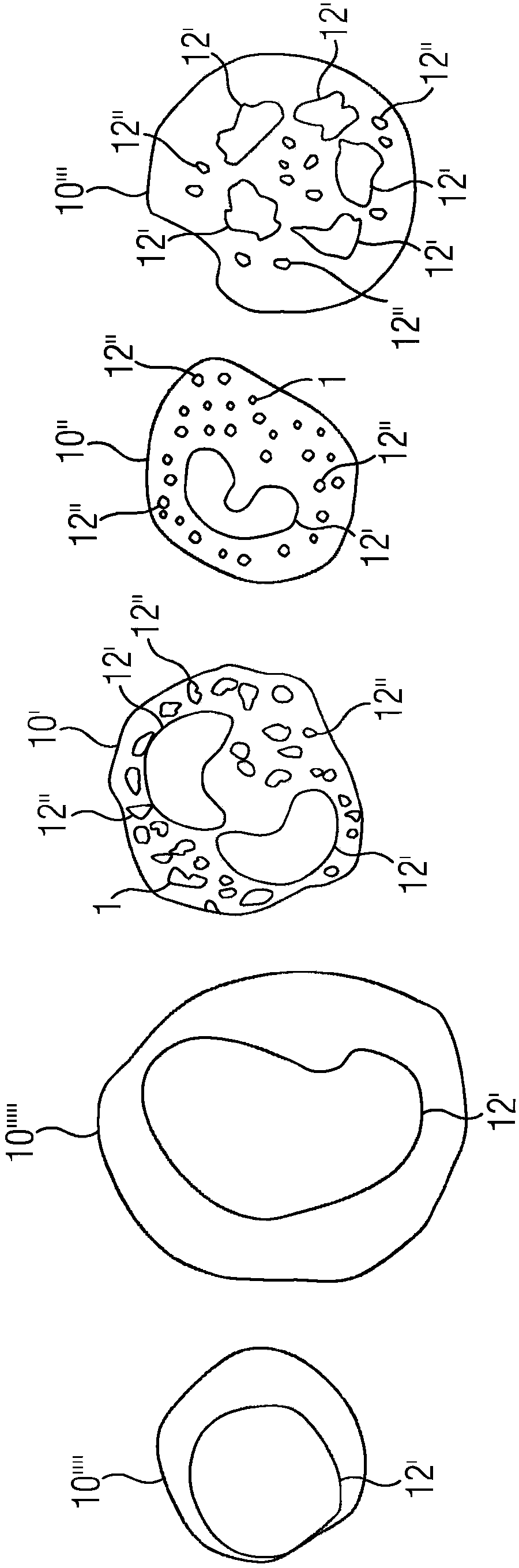
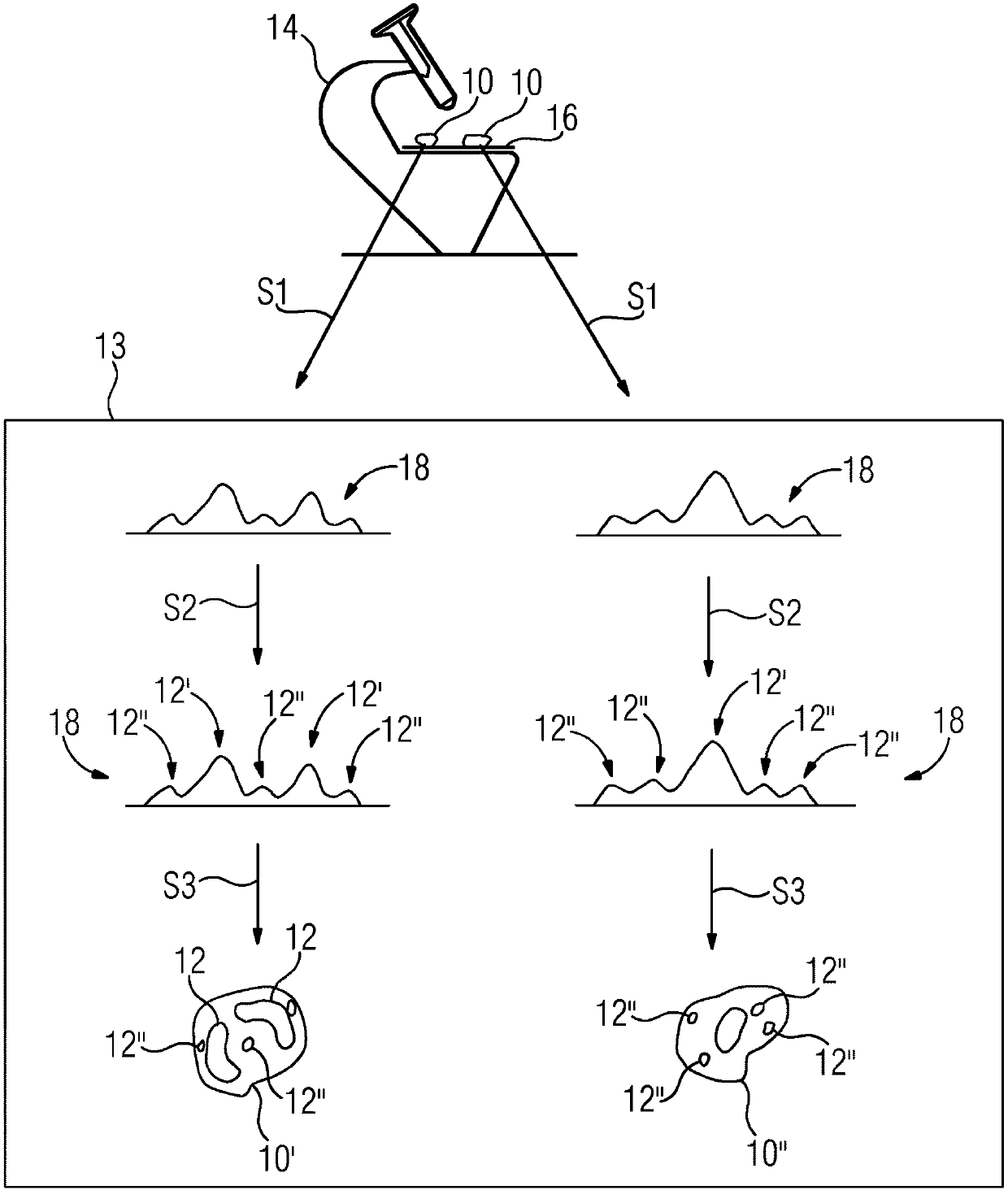
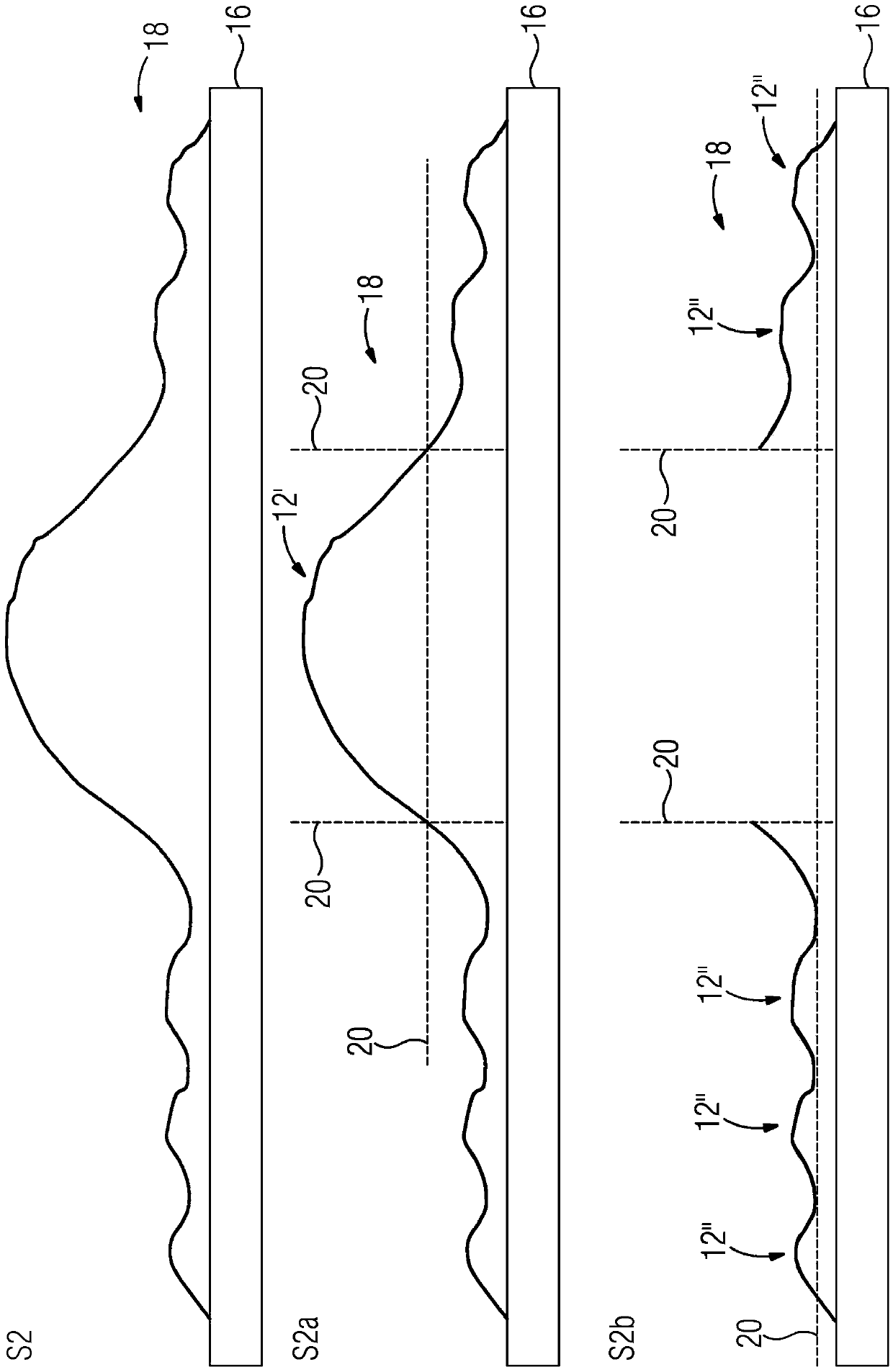
[0036] With the help of the inventive in vitro method, the cell type of cells in a biological sample can be determined in a marker-free manner. Label-free here means that the cells do not have to be labeled with eg fluorescent dyes or radioactive particles. A biological sample may eg comprise a sample of animal or plant cells, bacterial cells and / or protozoa. It is preferably a whole blood sample, comprising eg blood cells 10, eg leukocytes, eosinophils or basophils. For clarity, different exemplary cell types are in figure 1 with figure 2 , image 3 , Figures 4a and 4b are identified by the following reference numerals: eosinophil 10', basophil 10", neutrophil 10"', lymphocyte 10"" and monocyte"" '. However, for the sake of legibility, reference numeral 10 is used for each cell type in the following description of the exemplary embodiment.
[0037] exist figure 1 In the example of , for example, the five basic white blood cells that are distinguished in the case of a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com