Method for increasing yield of 2-keto-D-gluconic acid produced by fermentation process
A gluconic acid and fermentation technology, applied in the field of fermentation engineering, can solve problems such as complex components, bacteriophage contamination, unfavorable extraction, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
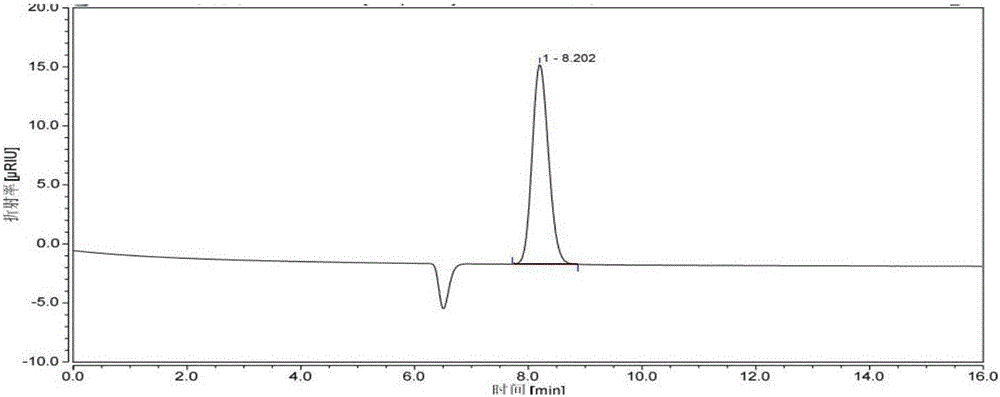
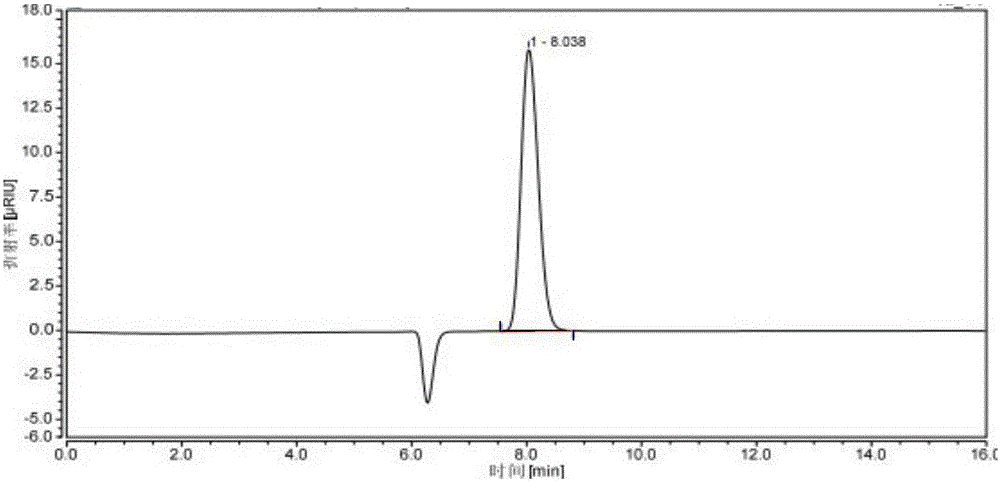
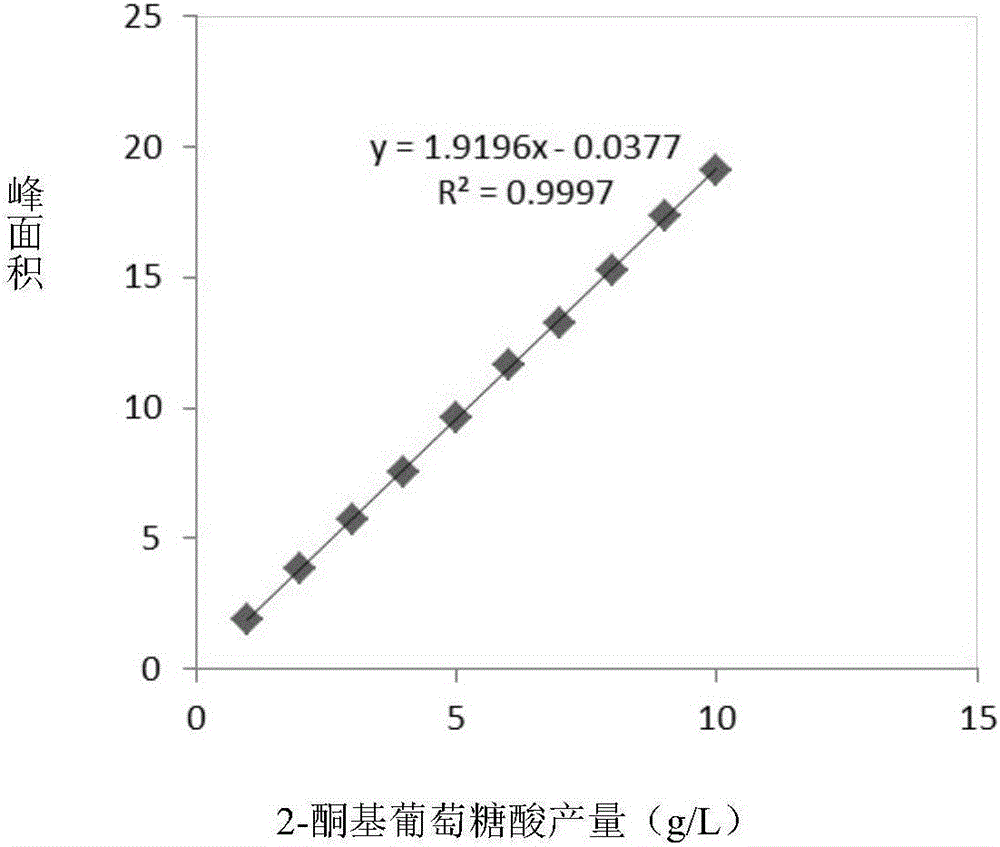
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Influence of glucose content on fermentation result in embodiment 1 fermentation medium
[0022] The activated preserved strains were inoculated on the slant medium, and cultivated in a 30°C incubator for 20h. Pick 3-4 loops of bacteria from the fresh slant with an inoculation needle, and then insert them into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 50mL of seed medium. Cultivate at 30°C and 200r / min for 12-14h. Insert 13% of the inoculum into a 30L fermenter with 16L fermentation medium for fermentation and cultivation. The fermentation temperature is 30°C, the initial stirring speed is 500r / min, the ventilation rate is 24.0L / min, and the dissolved oxygen setting during tank calibration It is 100%, and 8mol / L NaOH is automatically added to control the pH value at 6.0.
[0023] When the initial concentration of glucose in the fermentation medium was 100g / L, different times and times of supplementing glucose had an effect on the fermentation production of 2-KGA. Fed-batch...
Embodiment 2
[0031] The impact of embodiment 2 ammonium sulfate feeding on fermentation result
[0032] Under the same conditions of optimal glucose feeding method, maintenance of seeds and fermentation conditions, and feeding solution, when the initial ammonium sulfate concentration of the basic fermentation medium was 5g / L, the following three feeding methods were used for fed-batch fermentation.
[0033] Mode 1: Quantitative feeding at one time: after 16 hours of fermentation, a feeding solution containing 240 g of ammonium sulfate was added at one time.
[0034] Method 2: Intermittent quantitative feeding: add 64g of ammonium sulfate feeding solution at 16h of fermentation, add 80g of ammonium sulfate feeding solution at 22h, and add 96g of ammonium sulfate feeding solution at 28h.
[0035] Method 3: Feed at a constant rate intermittently: after 16 hours of fermentation, feed liquid at a rate of 1.25 g / L until the feed liquid containing 240 g of ammonium sulfate is completely replenis...
Embodiment 3
[0039] The influence of embodiment 3 dissolved oxygen control on fermentation result
[0040] Under the optimal feeding strategy of Examples 1 and 2, the influence of different DO concentrations on the synthesis of 2-KGA was investigated.
[0041] Table 3 Effects of different dissolved oxygen levels on 2-KGA fermentation
[0042] Feeding method
Bacterial dry weight (g / L)
2-KGA(g / L)
Sugar acid conversion rate (g / g)
Production intensity (g / L / h)
control
7.48
2401
0.96
5.20
20
7.54
248.7
0.99
5.23
30
7.75
250.4
1.00
5.32
40
8.37
265.8
1.03
6.13
50
8.56
261.4
1.01
5.98
[0043]It can be seen from Table 3 that with the increase of DO, the bacterial mass gradually increased, reaching the maximum when DO was 40%; when DO increased to 50%, the bacterial biomass decreased instead. When DO was controlled at 40%, the yield, yield and yield of 2-K...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com