Light emitting diode and manufacturing method therefor
A technology of light-emitting diodes and manufacturing methods, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of uneven light extraction efficiency, poor antistatic ability of LEDs, and low light extraction efficiency, so as to reduce the carrier aggregation effect and improve The effect of LED reliability and enhanced light extraction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
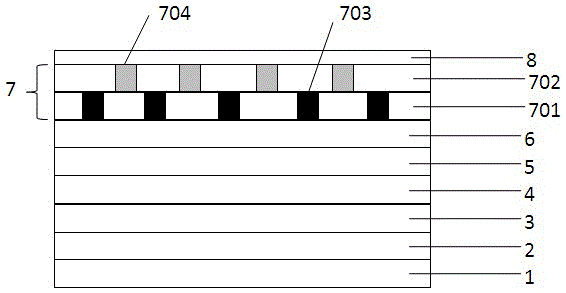
[0017] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of a light-emitting diode epitaxial wafer implemented according to the present invention. In this embodiment, the epitaxial layer includes from bottom to top: (1) sapphire substrate 1; (2) low-temperature buffer layer 2, which can be gallium nitride, nitrogen Aluminum oxide, or aluminum-gallium-nitride combination, with a film thickness between 10 and 100 μm; (3) non-doped gallium nitride layer 3, with a film thickness between 300 and 7000 μm, preferably 3500 μm; (4) N-type gallium nitride layer 4. The thickness is greater than 1 μm; (5) The quantum well light-emitting layer 5 is composed of InGaN as the well layer and GaN or AlGaN or a combination of the two as the barrier layer, wherein the thickness of the barrier layer is between 50 and 150 nm, and the thickness of the well layer is 1 ~20nm; (6) P-type layer 6, thickness between 0.05-1μm; (7) insertion layer 7; (8) contact layer 8, thickness between 0.1nm~20nm.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com