A method of manufacturing and manipulating a flexible micro-actuator for manipulating micro-nano particles
A technology of micro-nano particles and micro-actuators, applied in the direction of nanostructure manufacturing, nanotechnology, nanotechnology, etc., can solve the problems of difficult miniaturization and integration of optical paths, high cost, and long time, and achieve easy magnetic field drive and manufacturing process Simple, highly reliable results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2
[0042] A method for manufacturing and manipulating a flexible micro-actuator for manipulating micro-nano particles, comprising the following steps:
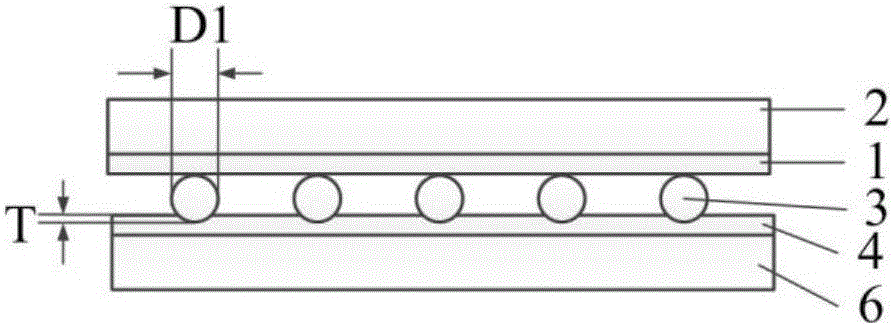
[0043] 1) First coat the hydrosol adhesive layer 1 on the surface of the substrate 2, then obtain a micro-nano patterned photoresist on the hydrosol adhesive layer 1 through a photolithography process; Micro-nanoparticles 3 are patterned, and then the photoresist is removed to obtain a patterned template of magnetic micro-nanoparticles 3, and the magnetic micro-nanoparticles 3 are iron powder with a particle size of D1=20 μm;
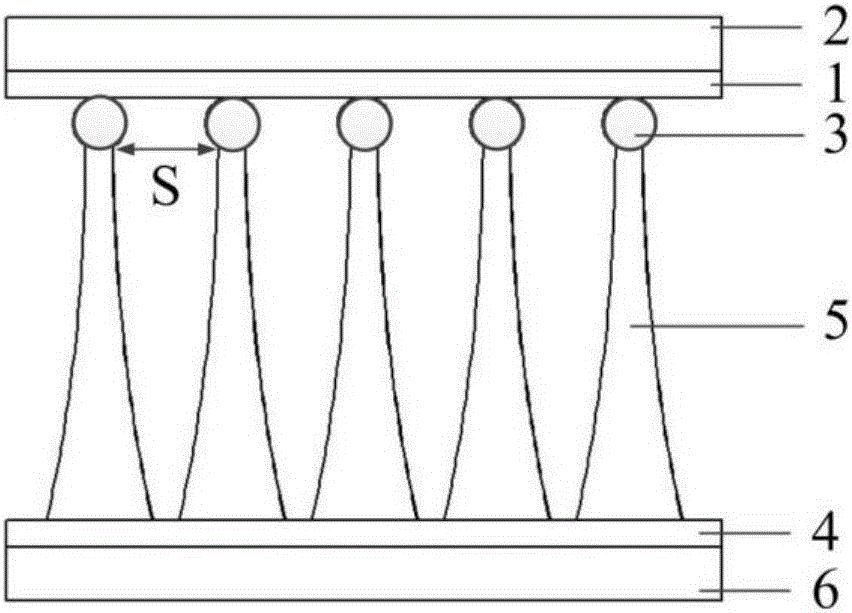
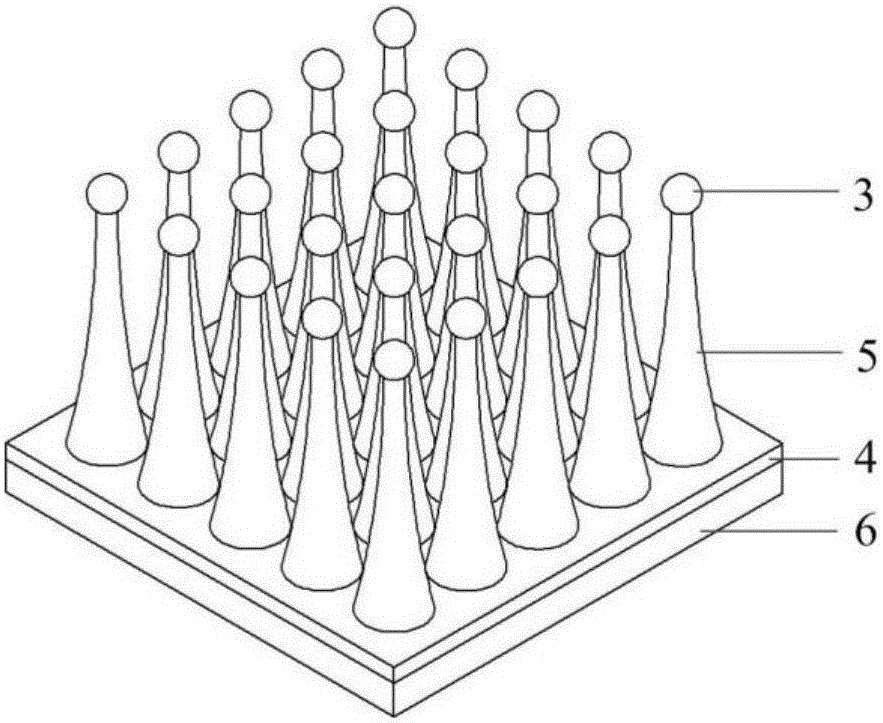
[0044] 2) Refer to figure 1 , coating the polymer 4 on the surface of the non-magnetic substrate 6, and then pre-heating the non-magnetic substrate 6, the pre-heating parameters: the temperature is 75°C, and the time is 6 minutes; then the magnetic micro-nano on the surface of the patterned template The particle 3 contacts and embeds the polymer 4, the embedding depth is T=10 μm, where T<D1, the polymer 4...
Embodiment 3
[0054] A method for manufacturing and manipulating a flexible micro-actuator for manipulating micro-nano particles, comprising the following steps:
[0055] 1) First coat the hydrosol adhesive layer 1 on the surface of the substrate 2, then obtain a micro-nano patterned photoresist on the hydrosol adhesive layer 1 through a photolithography process; The micro-nanoparticles 3 are patterned, and then the photoresist is removed to obtain a patterned template of the magnetic micro-nanoparticles 3. The magnetic micro-nanoparticles 3 are cobalt powders with a particle size of D1=150 μm;
[0056] 2) Refer to figure 1 , coating the polymer 4 on the surface of the non-magnetic substrate 6, and then preheating the non-magnetic substrate 6, the pre-heating parameters: the temperature is 90°C, and the time is 2 minutes; then the magnetic micro-nanoparticles on the surface of the patterned template 3 contacting and embedding the polymer 4, the embedding depth is T=50 μm, where T<D1, the p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com