Glyphosate-resistant selective marker gene and application thereof in maize transgenic technology
A technology for screening marker genes and glyphosate resistance, which can be used in applications, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., and can solve the problem of high false positive rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
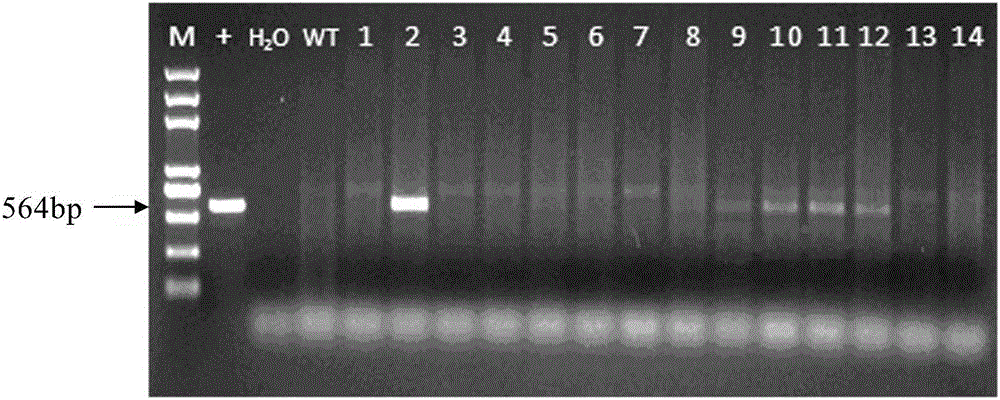
[0026] Example 1 Obtaining of glyphosate-resistant screening marker gene G23V-EPSPS
[0027]The fusion sequence of the chloroplast leader peptide sequence derived from the maize rbcS gene (ie, the 491-631 base sequence in Genbank: Y00322.1, a total of 141bp) and the EPSPS gene (1245bp) of GenBank: GM718572.1 is highly expressed according to the maize genome The codon of the gene was optimized, and a BamHI site was added at the 5' end of the gene coding sequence, and KpnI and SacI sites were added at the 3' end of the coding sequence. The G23V-EPSPS gene with added restriction sites was synthesized by Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd. The synthesized EPSPS gene is named G23V-EPSPS, and its base sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, wherein the 1st-6th base sequence from the 5' end is the BamHI site, and the 13th-15th base sequence The sequence ATG is the translation initiation codon, the 154th-156th base sequence ATG is the EPSP translation initiation codon, the 1393-1395th...
Embodiment 2
[0029] The glyphosate resistance of the G23V-EPSPS gene synthesized in embodiment 2 in escherichia coli (E.Coli)
[0030] The plasmid pGH-G23V containing the target gene G23V-EPSPS and the plasmid pGH-CP4 containing the CP4 type EPSPS gene (prepared by Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd.) were respectively transferred into different Escherichia coli DH5α, and the G23V-EPSPS gene was combined with The CP4-type EPSPS gene was compared to detect the glyphosate resistance of the G23V-EPSPS gene and the CP4-type EPSPS gene in Escherichia coli. The specific experimental steps are as follows:
[0031] 1) The plasmids pGH-G23V and pGH-CP4 were transformed into different Escherichia coli DH5α by heat shock method, and cultured overnight at 37° C. on solid LB medium containing 50 mg / L ampicillin.
[0032] 2) Pick a single colony and culture it overnight at 37°C in liquid LB medium containing 50 mg / L ampicillin, then extract the plasmid for enzyme digestion verification, and then p...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3 Construction of recombinant expression vector pBAC9200
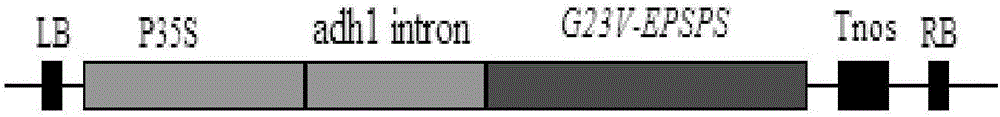
[0040] The pGH-G23V plasmid synthesized by Shanghai Jierui Bioengineering Co., Ltd. was digested with BamHI / KpnI to recover the 1.4kbp target gene, and then inserted the target gene into the pBAC823 vector (see the construction method of the invention patent ZL201110294326.6). Between the BamHI / KpnI sites, the expression vector pBAC9200 (base number 5895bp) driven by the CaMV 35S promoter and maize Adh1intron1 to drive the target gene G23V-EPSP is obtained. For the map of its T-DNA region, see figure 1 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com